Abstract
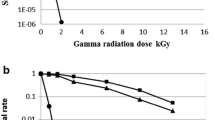
The ionizing radiation toxicity becomes a major concern for the modern world, recent years, several special interest has been given to the research for the radiation resistant and the mechanisms of which the radiation resistant bacteria survive after the irradiation. In the current study, we have isolated strain DG31D was isolated from gamma ray-irradiated soil sample and showed resistant to gamma and UV radiation. The aim of this study is to understanding the radiation resistant mechanisms and their genomic features of the strain DG31D, which can be potentially used for the biotechnological application to degrade harmful soil contamination near the nuclear power stations and other radiation-affected areas. Strain DG31D showed resistant to UV and gamma radiation with D10 value of 10 kGy. The genome comprised of 4,820,793 bp with the G+C content of 51.4%. It contains the genomic features of enzymes involved in the nucleotide excision repair (NER) pathway that protect the damaged DNA.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Abaydulla, G. et al. Rufibacter tibetensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel member of the family Cytophagaceae isolated from soil. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 101:725–731 (2012).
Srinivasan, S. et al. Hymenobacter terrae sp. nov., a bacterium isolated from soil. Curr Microbiol 70:643–650 (2015).
Collins, M. D., Hutson, R. A., Grant, I. R. & Patterson, M. F. Phylogenetic characterization of a novel radiation-resistant bacterium from irradiated pork: description of Hymenobacter actinosclerus sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 50:731–734 (2000).
Zhang, Q. et al. Hymenobacter xinjiangensis sp. nov., a radiation-resistant bacterium isolated from the desert of Xinjiang, China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:1752–1756 (2007).
Dai, J. et al. Hymenobacter tibetensis sp. nov., a UV-resistant bacterium isolated from Qinghai-Tibet plateau. Syst Appl Microbiol 32:543–548 (2009).
Chung, A. P., Lopes, A., Nobre, M. F. & Morais, P. V. Hymenobacter perfusus sp. nov., Hymenobacter flocculans sp. nov. and Hymenobacter metalli sp. nov. three new species isolated from an uranium mine waste water treatment system. Syst Appl Microbiol 33:436–43 (2010).
Lee, J. J. et al. Hymenobacter swuensis sp. nov., a gamma-radiation-resistant bacteria isolated from mountain soil. Curr Microbiol 68:305–310 (2014).
Jung, J. H. et al. Complete genome sequence of Hy-menobacter swuensis, an ionizing-radiation resistant bacterium isolated from mountain soil. J Biotechnol 178:65–66 (2014).
Srinivasan, S., Joo, E. S., Lee, J. J. & Kim, M. K. Hymenobacter humi sp. nov., a bacterium isolated from soil. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 107:1411–1419 (2015).
Zhang, Z. D. et al. Rufibacter roseus sp. nov., isolated from radiation-polluted soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 65:1572–1577 (2015).
Polkade, A. V., Ramana, V. V., Joshi, A., Pardesi, L. & Shouche, Y. S. Rufibacter immobilis sp. nov., isolated from a high-altitude saline lake. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 65:1592–1597 (2015).
Ortiz de Orue Lucana, D., Wedderhoff, I. & Groves, M. R. ROS-mediated signalling in bacteria: Zinc-containing Cys-X-X-Cys redox centres and iron-based oxidative stress. J Signal Transduct 2012:605905 (2012).
Waldeck, W. et al. RO S-mediated killing efficiency with visible light of bacteria carrying different red fluorochrome proteins. J Photochem Photobiol B 109:28–33 (2012).
Benson, D. A. et al. GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res 43: D30–35 (2015).
Tatusov, R. L. et al. The COG database: an updated version includes eukaryotes. BMC Bioinformatics 4:41 (2003).
Kawanishi, M. et al. Molecular evidence of the involvement of the nucleotide excision repair (NER) system in the repair of the mono (ADP-ribosyl)ated DNA adduct produced by pierisin-1, an apoptosis-inducing protein from the cabbage butterfly. Chem Res Toxicol 20:694–700 (2007).
Earl, A. M., Mohundro, M. M., Mian, I. S. & Battista, J. R. The IrrE protein of Deinococcus radiodurans R1 is a novel regulator of recA expression. J Bacteriol 184:6216–6224 (2002).
Cai, Y., Geacintov, N. E. & Broyde, S. Ribonucleotides as nucleotide excision repair substrates. DNA Repair (Amst) 13:55–60 (2014).
Ferrezuelo, F., Prieto-Alamo, M. J., Jurado, J. & Pueyo, C. Role of DNA repair by (A)BC excinuclease and Ogt alkyltransferase in the final distribution of LacI-d mutations induced by N-butyl-N-nitrosourea in Escherichia coli. Mutagenesis 13:507–514 (1998).
Lee, J. J. et al. Deinococcus swuensis sp. nov., a gamma-radiation-resistant bacterium isolated from soil. J Microbiol 51:305–311 (2013).
Daly, M. J. A new perspective on radiation resistance based on Deinococcus radiodurans. Nat Rev Microbiol 7:237–245 (2009).
Kim, O. S. et al. Introducing EzTaxon-e: a prokaryotic 16S rRNA gene sequence database with phylotypes that represent uncultured species. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:716–721 (2012).
Srinivasan, S. et al. Deinococcus radioresistens sp. nov., a UV and gamma radiation-resistant bacterium isolated from mountain soil. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 107:539–545 (2015).
Cha, S., Srinivasan, S., Seo, T. & Kim, M. K. Deinococcus soli sp. nov., a gamma-radiation-resistant bacterium isolated from rice field soil. Curr Microbiol 68: 777–783 (2014).
Srinivasan, S., Lee, J. J., Lim, S., Joe, M. & Kim, M. K. Deinococcus humi sp. nov., isolated from soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:2844–2850 (2012).
Srinivasan, S., Kim, M. K., Lim, S., Joe, M. & Lee, M. Deinococcus daejeonensis sp. nov., isolated from sludge in a sewage disposal plant. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:1265–1270 (2012).
Im, S. et al. Comparative survival analysis of 12 histidine kinase mutants of Deinococcus radiodurans after exposure to DNA-damaging agents. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 36:781–789 (2013).
Selvam, K., Duncan, J. R., Tanaka, M. & Battista, J. R. DdrA, DdrD, and PprA: components of UV and mitomycin C resistance in Deinococcus radiodurans R1. PLoS One 8:e69007 (2013).
Hall, T. A. In Nucleic acids symposium series 95–98 (1999).
Thompson, J. D., Gibson, T. J., Plewniak, F., Jeanmougin, F. & Higgins, D. G. The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882 (1997).
Kimura, M. The neutral theory of molecular evolution. Sci Am 241:98–100, 102, 108 passim (1979).
Saitou, N. & Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425 (1987).
Tamura, K. et al. MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739 (2011).
Felsenstein, J. Confidence Limits on Phylogenies: An approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791 (1985).
Fitch, W. M. Toward defining the course of evolution: Minimum change for a specific tree topology. Syst Zool 20:406–416 (1971).
Field, D. et al. The minimum information about a genome sequence (MIGS) specification. Nat Biotechnol 26:541–547 (2008).
Markowitz, V. M. et al. IMG ER: a system for microbial genome annotation expert review and curation. Bioinformatics 25:2271–2278 (2009).
Lowe, T. M. & Eddy, S. R. tRNAscan-SE: a program for improved detection of transfer RNA genes in genomic sequence. Nucleic Acids Res 25:955–964 (1997).
Lagesen, K. et al. RNAmmer: consistent and rapid annotation of ribosomal RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res 35:3100–3108 (2007).
Nawrocki, E. P., Kolbe, D. L. & Eddy, S. R. Infernal 1.0: inference of RNA alignments. Bioinformatics 25:1335–1337 (2009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Srinivasan, S., Kim, M.K., Joo, E.S. et al. Complete genome sequence of Rufibacter sp. DG31D, a bacterium resistant to gamma and UV radiation toxicity. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 11, 415–421 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-015-0044-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-015-0044-0