Abstract
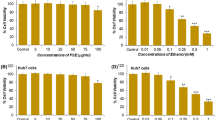
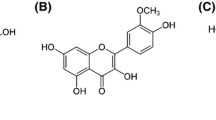
Ellagic acid (EA) is a phenolic compound found in fruits and nuts, including raspberries, strawberries, grapes and walnuts. In the present study, we examined the hepatoprotective effects of ellagic acid from the Korean raspberry (Rubus coreanus Miq.) compared to alcohol-induced toxicity in vitro. Ethanolinduced HepG2 cells were treated with EA at three concentrations (1, 10 and 100 μM), and then the protective effects of EA were evaluated through the regulation of NO, TGF-β1 and SR-B1 production. In response to the exposure of ethanol, the productions of NO, TGF-β1 and SR-B1 were increased and EA pretreatment significantly recovered NO release and TGF-β1 expression at the baseline level except for SR-B1 protein. EA at 100 μM more increased SR-B1 expression in ethanol treated cells whereas there is no changed without ethanol. Elevated SR-B1 expression seems to be positive effects on the regulation of cholesterol efflux and atherosclerosis. These findings suggest that EA from R. coreanus could be beneficial for the alleviation of alcohol-induced hepatotoxicity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Daniel, E. M. et al. Extraction, stability and quantitation of ellagic acid in various fruits and nuts. J Food Compos Anal 2:338–349 (1989).
Han, D. H., Lee, M. J. & Kim, J. H. Antioxidant and apoptosis-inducing activities of ellagic acid. Anticancer Research 26:3601–3606 (2006).
Larrosa, M., Tomás-Barberán, F. A. & EspÍn, J. C. The dietary hydrolysable tannin punicalagin releases ellagic acid that induces apoptosis in human colon adenocarcinoma Caco-2 cells by using the mitochondrial pathway. J Nutr Biochem 17:611–625 (2005).
Edderkaoui, M. et al. Ellagic acid induces apoptosis through inhibition of nuclear factor kappa B in pancreatic cancer cells. World J Gastroenterol 14:3672–3680 (2008).
Narayanan, B. A., Geoffroy, O., Willingham, M. C., Re, G. G. & Nixon, D. W. p53/p21(WAF1/CIP1) expression and its possible role in G1 arrest and apoptosis in ellagic acid treated cancer cells. Cancer Lett 136:215–221 (1999).
Päivärinta, E., Pajari, A. M., Törrönen, R. & Mutanen, M. Ellagic acid and natural sources of ellagitannins as possible chemopreventive agents against intestinal tumorigenesis in the Min mouse. Nutr Cancer 54:79–83 (2006).
Skupień, K., Oszmiański, J., Kostrzewa-Nowak, D. & Tarasiuk, J. In vitro antileukemic activity of extracts from berry plant leaves against sensitive and multidrug resistant HL60 cells. Cancer Lett 236:282–291 (2006).
Hwang, J. M., Cho, J. S., Kim, T. H. & Lee, Y. I. Ellagic acid protects hepatocytes from damage by inhibiting mitochondrial production of reactive oxygen species. Biomed Pharmacother 64:264–270 (2010).
Buniatian, G. H. Stages of activation of hepatic stellate cells: Effects of ellagic acid, an inhibitor of liver fibrosis, on their differentiation in culture. Cell Prolif 36:307–319 (2003).
Fleming, M. F., Manwell, L. B., Barry, K. L. & Johnson, K. At-risk drinking in an HMO primary care sample: prevalence and health policy implications. Am J Public Health 88:90–93 (1998).
Timberlake, W. E. & Marshall, M. A. Genetic engineering of filamentous fungi. Science 244:1313–1317 (1989).
Mandal, P., Pritchard, M. T. & Nagy, L. E. Anti-inflammatory pathways and alcoholic liver disease: role of an adiponectin/interleukin-10/heme oxygenase-1 pathway. World J Gastroenterol 16:1330–1336 (2010).
Albano, E. Alcohol, oxidative stress and free radical damage. Proc Nutr Soc 65:278–290 (2006).
Koch, O. R. et al. Oxidative stress and antioxidant defenses in ethanol-induced cell injury. Mol Aspects Med 25:191–198 (2004).
Xu, B. J., Zheng, Y. N. & Sung, C. K. Natural medicines for alcoholism treatment: a review. Drug Alcohol Rev 24:525–536 (2005).
Maxfield, F. R. & Tabas, I. Role of cholesterol and lipid organization in disease. Nature 438:612–621 (2005).
Naveau, S. et al. Body fat distribution and risk factors for fibrosis in patients with alcoholic liver disease. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 37:332–338 (2012).
Arai, T., Wang, N., Bezouevski, M., Welch, C. & Tall, A. R. Decreased atherosclerosis in heterozygous low density lipoprotein receptor-deficient mice expressing the scavenger receptor BI transgene. J Biol Chem 274:2366–2371 (1999).
Kozarsky, K. F. et al. Overexpression of the HDL receptor SR-BI alters plasma HDL and bile cholesterol levels. Nature 387:414–417 (1997).
Li, X. C., Elsohly, H. N., Hufford, C. D. & Clark, A. M. MNR assignments of ellagic acid derivatives. Magn Reson Chem 37:858 (1999).
Valacchi, G., Sticozzi, C., Lim, Y. & Pecorelli, A. Scavenger receptor class B type I: a multifunctional receptor. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1229:E1–7 (2011).
Reaven, E., Leers-Sucheta, S., Nomoto, A. & Azhar, S. Expression of scavenger receptor class B type 1 (SR-BI) promotes microvillar channel formation and selective cholesteryl ester transport in a heterologous reconstituted system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:1613–1618 (2001).
Muriel, P. Nitric oxide protection of rat liver from lipid peroxidation, collagen accumulation, and liver damage induced by carbon tetrachloride. Biochem Pharmacol 56:773–779 (1998).
Zima, T. et al. Oxidative stress, metabolism of ethanol and alcohol-related diseases. J Biomed Sci 8:59–70 (2001).
Goldstein, R. S. & Schnellmann, R. G. Casarett and Doull’S Toxicology-The Basic Science of Poisons. Toxic Responses of the Kidney. (In: Klaassen CD, Amdur MO, Doull J, editors) 417–442 (New York: McGraw-Hill Companies Inc. 1998).
Polikandriotis, J. A., Rupnow, H. L. & Hart, C. M. Chronic ethanol exposure stimulates endothelial cell nitric oxide production through PI-3 kinase-and hsp90-dependent mechanisms. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 29:1932–1938 (2005).
Matsuo, S. et al. Effect of red wine and ethanol on production of nitric oxide in healthy subjects. Am J Cardiol 87:1029–1031 (2001).
Song, Z. et al. Silymarin protects against acute ethanolinduced hepatotoxicity in mice. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 30:407–413 (2006).
Majano, P. L. et al. N-Acetyl-cysteine modulates inducible nitric oxide synthase gene expression in human hepatocytes. J Hepatol 40:632–627 (2004).
Bissell, D. M., Roulot, D. & George, J. Transforming growth factor beta and the liver. Hepatology 34:859–867 (2001).
Michalopoulos, G. K. Liver regeneration. J Cell Physiol 213:286–300 (2007).
Dooley, S., Weng, H. & Mertens, P. R. Hypotheses on the role of transforming growth factor-beta in the onset and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig Dis 27:93–101 (2009).
Cahill, P. A. & Redmond, E. M. Alcohol and cardiovascular disease-modulation of vascular cell function. Nutrients 4:297–318 (2012).
Li, G. et al. Farnesoid X receptor induces murine scavenger receptor Class B type I via intron binding. PLoS One 7:e35895 (2012).
Nicholson, A. C., Han, J., Febbraio, M., Silversterin, R. L. & Hajjar, D. P. Role of CD36, the macrophage class B scavenger receptor, in atherosclerosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci 947:224–228 (2001).
Van Eck, M. et al. Differential effects of scavenger receptor BI deficiency on lipid metabolism in cells of the arterial wall and in the liver. J Biol Chem 278:23699–23705 (2003).
Kozarsky, K. F., Donahee, M. H., Glick, J. M., Krieger, M. & Rader, D. J. Gene transfer and hepatic overexpression of the HDL receptor SR-BI reduces atherosclerosis in the cholesterol-fed LDL receptor-deficient mouse. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 20:721–727 (2000).
Emeson, E. E., Manaves, V., Emeson, B. S., Chen, L. & Jovanovic, I. Alcohol inhibits the progression as well as the initiation of atherosclerotic lesions in C57Bl/6 hyperlipidemic mice. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 24:1456–1466 (2000).
Ronksley, P. E., Brien, S. E., Turner, B. J., Mukamal, K. J. & Ghali, W. A. Association of alcohol consumption with selected cardiovascular disease outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 342:d671 (2011).
Mukamal, K. J. et al. Roles of drinking pattern and type of alcohol consumed in coronary heart disease in men. N Engl J Med 348:109–118 (2003).
Mudráková, E. & Kovár, J. Ethanol consumption affects lipoprotein lipase gene expression in C57BL/6 mice. Physiol Res 56:497–501 (2007).
Insel, P. A. & Patel, H. H. Membrane rafts and caveolae in cardiovascular signaling. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 18:50–56 (2009).
Namkoong, S., Kim, Y. J., Kim, T. & Sohn, E. H. Study on the immunomodulatory effects of ellagic acid and their mechanisms related to toll-like receptor 4 in macrophages. Korean J Plant Res 25:561–567 (2012).
Ding, A. H. & Nathan, C. F. The measurement of cytochrome b559 in polymorphonuclear leukocytes and macrophages in the presence of hemoglobin or mitochondrial cytochromes. Anal Biochem 175:22–29 (1988).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sohn, EH., Koo, H.J., Hang, D.T.T. et al. Protective effects of ellagic acid on ethanol-induced toxicity in hepatic HepG2 cells. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 9, 249–256 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-013-0032-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-013-0032-1