Abstract
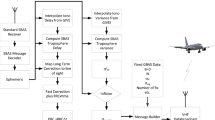
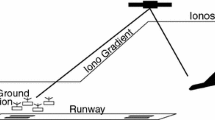
As the international air traffic becomes more and more complex there is a growing demand for new operational procedures. Especially quiet and fuel efficient approaches are desired. As a Ground Based Augmentation System (GBAS) provides more flexibility than current precision landing systems, it is identified as a potential main technology for providing different approach procedures tailored for the demands at a special location. Especially steep precision approaches have a high potential for noise reduction as the aircraft stays at a higher altitude for a longer time. A GBAS uses GPS reference receivers to calculate corrections for the observed ranges of the satellite signals. Together with a VHF Data Broadcast that transmits the corrections as well as one or multiple desired approach paths the GBAS becomes a precision approach system (GLS). The possibility of broadcasting multiple approaches for a single runway end offers approaching aircraft to choose the most efficient and quiet approach that can be operationally achieved with the respective type of aircraft. As steep approaches with a single glide path angle introduce some operational limitations, the flexibility of a GLS offers the design and the execution of segmented steep precision approaches which are a compromise between the possible efficiency and the introduced operational limitations.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boniface, L.: The ILS equivalency methodology and GBAS flight test results (2002)
Hecker, P., Schachtebeck, P., Feuerle, T., Bestmann, U., Butzmuehlen, C.: Preparation for GBAS at Braunschweig research airport first flight test results, ION NTM (2006)
Holtmann, J.: K-ATM Abschlussprsentation GBAS Bremen (2007)
UK AIP, Instrument Approach Chart LONDON City ILS (5.5 Deg GP)/DME/NDB(L) RWY 27 - ICAO, NATS Aeronautical Information Service, http://www.nats-uk.ead-it.com, (2011)
Boehm-Davis, D.A., Casali, J.G., Kleiner, B.M., Lancaster, J.A., Saleem, J.J., Wochinger, K.: Pilot performance, strategy, and workload while executing approaches at steep angles and with lower landing minima, Hum. Factors. 49, 759–772 (2007)
Morioka, H., Higami, K., Funabiki, K.: Curved approach and GLS application trial—FFS trial report (2010)
Rollet, P., Authesserre, M., Sandri, F.: Flight testing of rotorcraft IFR steep approaches using SBAS and GBAS guidance (2008)
Haverdings, H., van der Vorst, J., Gille, M.: Design and execution of piloted simulation tests of steep segmented and curved rotorcraft IFR procedures at NLR. National Aerospace Laboratory NLR (2007)
Radio Technical Commission for Aeronautics, Inc., DO-246D—GNSS-based Precision Approach Local Area Augmentation System (LAAS) Signal-in-Space Interface Control Document (ICD) (2008)
The European Organisation for Civil Aviation Equipment, ED-114—Minimum Operational Performance Specification for Global Navigation Satellite Ground Based Augmentation System Ground Equipment to Support Category I Operations (2003)
International Civil Aviation Organisation, Annex 10 to the Convention on International Civil Aviation, Aeronautical Telecommunications, Radio Navigation Aids, Vol I (2006)
Radio Technical Commission for Aeronautics, Inc., DO-245A—Minimum Aviation System Performance Standards for the Local Area Augmentation System (LAAS) (2004)
International Civil Aviation Organisation, Doc 8168—Procedures for Air Navigation Services, Aircraft Operations, Construction of Visual and Instrument Flight Procedures, Vol II (2006)
Federal Aviation Administration, Order 8260.19D—Flight procedures and airspace (2007)
Geister R.: Validierung neuer, satellitengestuetzter Anflugverfahren im Cockpitsimulator, Deutscher Luft- und Raumfahrtkongress (2010)
Geister R., Schuettpelz A., Kaelberer U.: GBAS ground station implementation and improved test and validation methods, ENC GNSS (2010)
Geister R. (2010) Flight testing of Steep precision approaches Based on GBAS, ICAS
Radio Technical Commission for Aeronautics, Inc., DO-253C—Minimum Operational Performance Standards for GPS Local Area Augmentation System Airborne Equipment (2008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This paper is based on a presentation at the German Aerospace Congress, September 27–29, 2011, Bremen, Germany.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Geister, R. Segmented steep precision approaches based on GLS. CEAS Aeronaut J 2, 139–146 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13272-011-0016-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13272-011-0016-6