Abstract
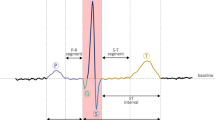
Electrocardiogram (ECG) signal gives a lot of information on the physiology of heart. In reality, noise from various sources interfere with the ECG signal. To get the correct information on physiology of the heart, noise cancellation of the ECG signal is required. In this paper, the effectiveness of extended Kalman smoother (EKS) with the differential evolution (DE) technique for noise cancellation of the ECG signal is investigated. DE is used as an automatic parameter selection method for the selection of ten optimized components of the ECG signal, and those are used to create the ECG signal according to the real ECG signal. These parameters are used by the EKS for the development of the state equation and also for initialization of the parameters of EKS. EKS framework is used for denoising the ECG signal from the single channel. The effectiveness of proposed noise cancellation technique has been evaluated by adding white, colored Gaussian noise and real muscle artifact noise at different SNR to some visually clean ECG signals from the MIT-BIH arrhythmia database. The proposed noise cancellation technique of ECG signal shows better signal to noise ratio (SNR) improvement, lesser mean square error (MSE) and percent of distortion (PRD) compared to other well-known methods.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Panigrahy D, Rakshit M, Sahu PK (2016) FPGA implementation of heart rate monitoring system. J Med Syst 40:1–12. doi:10.1007/s10916-015-0410-4
Matsuyama A, Jonkman M (2006) The application of wavelet and feature vectors to ECG signals. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med 29:13–17
Lee S, Kim IY, Park YC (2007) Approximated affine projection algorithm for feedback cancellation in hearing aids. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 87:254–261. doi:10.1016/j.cmpb.2007.05.014
Joshi SL, Vatti RA, Tornekar RV (2013) A survey on ECG signal denoising techniques. In: 2013 Int Conf Commun Syst Netw Technol, pp 60–64. doi: 10.1109/CSNT.2013.22
Chang KM (2010) Ensemble empirical mode decomposition for high frequency ECG noise reduction. Biomed Tech 55:193–201. doi:10.1515/BMT.2010.030
Lu G, Brittain J-S, Holland P et al (2009) Removing ECG noise from surface EMG signals using adaptive filtering. Neurosci Lett 462:14–19. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2009.06.063
Marque C, Bisch C, Dantas R et al (2005) Adaptive filtering for ECG rejection from surface EMG recordings. J Electromyogr Kinesiol 15:310–315. doi:10.1016/j.jelekin.2004.10.001
Izzetoglu M, Devaraj A, Bunce S, Onaral B (2005) Motion artifact cancellation in NIR spectroscopy using Wiener filtering. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 52:934–938. doi:10.1109/TBME.2005.845243
Singh BN, Tiwari AK (2006) Optimal selection of wavelet basis function applied to ECG signal denoising. Digit Signal Process A Rev J 16:275–287. doi:10.1016/j.dsp.2005.12.003
Kabir MA, Shahnaz C (2012) Denoising of ECG signals based on noise reduction algorithms in EMD and wavelet domains. Biomed Signal Process Control 7:481–489. doi:10.1016/j.bspc.2011.11.003
Blanco-Velasco M, Weng B, Barner KE (2008) ECG signal denoising and baseline wander correction based on the empirical mode decomposition. Comput Biol Med 38:1–13. doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2007.06.003
Gokgoz E, Subasi A (2014) Effect of multiscale PCA de-noising on EMG signal classification for diagnosis of neuromuscular disorders. J Med Syst. doi:10.1007/s10916-014-0031-3
Güler I, Übeyli ED (2005) ECG beat classifier designed by combined neural network model. Pattern Recognit 38:199–208. doi:10.1016/j.patcog.2004.06.009
He T, Clifford G, Tarassenko L (2006) Application of independent component analysis in removing artefacts from the electrocardiogram. Neural Comput Appl 15:105–116. doi:10.1007/s00521-005-0013-y
Tracey BH, Miller EL (2012) Nonlocal means denoising of ECG signals. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 59:2383–2386. doi:10.1109/TBME.2012.2208964
Sameni R, Shamsollahi MB, Jutten C, Clifford GD (2007) A nonlinear Bayesian filtering framework for ECG denoising. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 54:2172–2185. doi:10.1109/TBME.2007.897817
Naik G, Selvan S, Nguyen H (2015) Single-channel EMG classification with ensemble-empirical-mode-decomposition-based ICA for diagnosing neuromuscular disorders. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 99:1. doi:10.1109/TNSRE.2015.2454503
Poornachandra S (2008) Wavelet-based denoising using subband dependent threshold for ECG signals. Digit Signal Process A Rev J 18:49–55. doi:10.1016/j.dsp.2007.09.006
Manikandan MS, Soman KP (2012) A novel method for detecting R-peaks in electrocardiogram (ECG) signal. Biomed Signal Process Control 7:118–128. doi:10.1016/j.bspc.2011.03.004
Rakshit M, Panigrahy D, Sahu PK (2015) EKF with PSO technique for delineation of P and T wave in electrocardiogram(ECG) signal. In: 2015 2nd Int Conf Signal Process Integr Networks, IEEE, New York, pp 696–701
McSharry PE, Clifford GD, Tarassenko L, Smith LA (2003) A dynamical model for generating synthetic electrocardiogram signals. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 50:289–294. doi:10.1109/TBME.2003.808805
Storn R, Price KV (1997) Differential evolution—a simple and efficient heuristic for global optimization over continuous spaces. J Glob Optim 11:341–359
Qin AK, Huang VL, Suganthan PN (2009) Differential evolution algorithm with strategy adaptation for global numerical optimization. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 13:398–417. doi:10.1109/TEVC.2008.927706
Omran MGH, Engelbrecht AP, Salman A (2009) Bare bones differential evolution. Eur J Oper Res 196:128–139. doi:10.1016/j.ejor.2008.02.035
Welch G, Bishop G (2006) An introduction to the Kalman filter. In Pract. pp 1–16
Goldberger AL, Amaral LAN, Glass L et al (2000) Physiobank, physiotoolkit, and physionet: components of a new research resource for complex physiologic signals. Circulation 101:215–220. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.101.23.e215
Gao Z, Wu J, Zhou J et al (2012) Design of ECG signal acquisition and processing system. In: 2012 Int Conf Biomed Eng Biotechnol, pp 762–764
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Panigrahy, D., Sahu, P.K. Extended Kalman smoother with differential evolution technique for denoising of ECG signal. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med 39, 783–795 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13246-016-0468-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13246-016-0468-4