Abstract
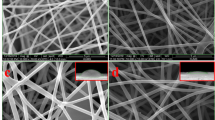
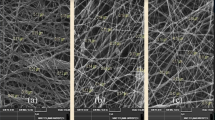
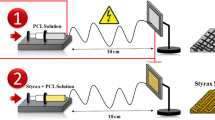
Our investigation for the first time explores the possibility of fabrication of a Capsaicin/polyurethane-based bioactive wound dressing. A micro/nanofibrous bandage was synthesized by electrospinning polyurethane supplemented with natural anti-inflammatory agent, Capsaicin. Herein, the best concentration (3%) of Capsaicin in polyurethane to get a consistent solution was standardized in order to acquire the composite micro/nanofibrous dressing. The as-spun bandage has been investigated by scanning electron microscopy and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and biocompatibility of muscle cells on the bioactive bandage was also examined. Free radical scavenging activity of the fabricated micro/nanofiber bandage was estimated using 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl assay. Inclusion of Capsaicin in polyurethane transformed the morphology as well as dimension of the fibers. Anti-oxidant wound bandage with diameters around 150–500 nm was fabricated by physical unification of polyurethane with natural Capsaicin. Here, polyurethane was used as a foundation polymer, which was blended with Capsaicin to attain desirable characteristics such as better anti-oxidant activity, hydrophilicity and excellent cell attachment. The polyurethane wound bandage possesses enlarged surface, proscribed evaporation, and fluid drainage ability. These results suggest the beneficial influence of antioxidant Capsaicin on wound repairing process. Therefore, a biologically active, natural compounds such as Capsaicin is material of choice for fabrication of future wound dressings.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.-P. Chen and Y. Chiang, J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol., 10, 7560 (2010).
A. R. Unnithan, G. Gnanasekaran, Y. Sathishkumar, Y. S. Lee, and C. S. Kim, Carbohyd. Polym., 102, 884 (2014).
S. J. Lee, D. N. Heo, J.-H. Moon, H. N. Park, W.-K. Ko, M. S. Bae, J. B. Lee, S. W. Park, E.-C. Kim, C. H. Lee, B.-Y. Jung, and I. K. Kwon, J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol., 14, 7488 (2014).
M. S. Khil, D. I. Cha, H. Y. Kim, I. S. Kim, and N. Bhattarai, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B, 67B, 675 (2003).
B. M. Illigens and C. H. Gibbons, PloS One, 8, e54760 (2013).
S. O. Udegbunam, R. I. Udegbunam, T. O. Nnaji, M. U. Anyanwu, R. O. Kene, and S. M. Anika, J. Intercult. Ethnopharmacol., 4, 239 (2015).
K. S. Chen, P. N. Chen, Y. S. Hsieh, C. Y. Lin, Y. H. Lee, and S. C. Chu, Chem.-Biol. Interact., 228, 35 (2015).
M. Materska, M. Konopacka, J. Rogolinski, and K. Slosarek, Food Chem., 168, 546 (2015).
T. Amna, M. S. Hassan, F. A. Sheikh, H. K. Lee, K. S. Seo, D. Yoon, and I. H. Hwang, Appl. Microbiol. Biot., 97, 1725 (2013).
S. T. Russell and M. J. Tisdale, Mol. Cell. Biochem., 330, 171 (2009).
T. Amna, M. S. Hassan, W. S. Shin, H. Van Ba, H. K. Lee, M. S. Khil, and I. H. Hwang, Colloid. Surf. B, 101, 424 (2013).
W. Brand-Williams, M. E. Cuvelier, and C. Berset, LWT-Food Sci. Technol., 28, 25 (1995).
E. J. Garcia, T. L. C. Oldoni, S. M. D. Alencar, A. Reis, A. D. Loguercio, and R. H. M. Grande, Braz. Dent. J., 23, 22 (2012).
H. W. Yang, K. J. Hwang, H. C. Kwon, H. S. Kim, K. W. Choi, and K. S. Oh, Hum. Reprod., 13, 998 (1998).
T. K. Giri, P. Mukherjee, T. K. Barman, and S. Maity, Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 88, 236 (2016).
R. Qi, R. Guo, M. Shen, X. Cao, L. Zhang, J. Xu, J. Yu, and X. Shi, J. Mater. Chem., 20, 10622 (2010).
T. Amna, M. S. Hassan, J. Yang, M.-S. Khil, K.-D. Song, J.-D. Oh, and I. Hwang, Int. J. Nanomedicine, 9, 891 (2014).
L. D. Tijing, M. T. G. Ruelo, A. Amarjargal, H. R. Pant, C.-H. Park, D. W. Kim, and C. S. Kim, Chem. Eng. J., 197, 41 (2012).
R. L. Teku, C. K. Mylangam, and V. Kolapalli, Wor. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci., 5, 1017 (2015).
P. Vashisth, N. Kumar, M. Sharma, and V. Pruthi, Biotechnol. Rep., 8, 36 (2015).
A. Saklani and S. K. Kutty, Drug Discov. Today, 13, 161 (2008).
R. Geethalakshmi, C. Sakravarthi, T. Kritika, M. Arul Kirubakaran, and D. Sarada, Biomed. Res. Int., 2013, 607109 (2013).
C. W. Pyun, J. H. Kim, K. H. Han, G. E. Hong, and C. H. Lee, Biofactors, 40, 494 (2014).
D. Yaffe and O. Saxel, Nature, 270, 725 (1977).
F. Horio, H. Sakurai, Y. Ohsawa, S. Nakano, M. Matsukura, and I. Fujii, eNeurologicalSci, 6, 9 (2017).
S. F. Albaayit, Y. Abba, A. Rasedee, and N. Abdullah, Drug. Des. Dev. Ther., 9, 3507 (2015).
D. Altiok, E. Altiok, and F. Tihminlioglu, J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. M., 21, 2227 (2010).
C. M. Srivastava and R. Purwar, Macromol. Res., 26, 872 (2018).
M. Suryamathi, C. Ruba, P. Viswanathamurthi, V. Balasubramanian, and P. Perumal, Macromol. Res., 27, 55 (2019).
R. Rosic, P. Kocbek, J. Pelipenko, J. Kristl, and S. Baumgartner, Acta Pharmaceut, 63, 295 (2013).
A. Rusak and Z. Rybak, Polim. Med., 43, 199 (2013).
X. Chen, G. Zhang, Q. Zhang, X. Zhan, and F. Chen, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 54, 3813 (2015).
M.-N. Zhang, X.-H. Piao, Z. Li, Y.-T. Zhang, J.-H. Zhao, and N.-P. Feng, Chinese J. Exper. Traditional Medical Formulae, 17, 006 (2016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Acknowledgments: This work was supported in part by a grant from the Next Generation Bio-green 21 (PJ013169), Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea. The authors also extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at Albaha University for research grant (Proposal No. 54-1436) to help in research work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amna, T., Gharsan, F.N., Shang, K. et al. Electrospun Twin Fibers Encumbered with Intrinsic Antioxidant Activity as Prospective Bandage. Macromol. Res. 27, 663–669 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13233-019-7088-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13233-019-7088-2