Abstract
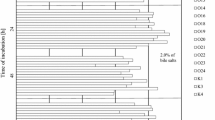
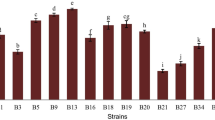
Twenty-seven Lactobacillus strains isolated from traditional Chinese cheese were evaluated for their probiotic potential by in vitro and in vivo tests. Seven strains were selected as they showed high resistance to low pH and simulated gastrointestinal juice. Further study indicated that five strains exhibited good adhesion to Caco-2 cells. Bile salt hydrolase (BSH) and high β-galactosidase activities were shown by the five strains. They also showed various antimicrobial activity against pathogens. Among the five strains, an atypical resistance to chloramphenicol was detected in strain BJFU 10241. After a series of tests, the cat gene was observed in plasmids but not in genomic DNA. In vivo experiments showed that strains BJFU 10256, BJFU 10041, BJFU 10205, and BJFU 10025 could regulate intestinal flora. Significant increases in Lactobacillus spp. were observed. Moreover, the numbers of Enterobacter and Clostridium perfringens decreased significantly. The ability of the four strains to lower serum total and low density lipoprotein cholesterol in mice was observed, and this property was enhanced by ingestion of cell suspension compared to fermented milk. These four strains showed the best probiotic potential and could be used in fermented food in the future.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adebawo OO, Banjoko Y, Osilesi T (2008) Evaluation of the hypocholesterolemic effect of Lactobacillus acidophilus fermented maize meal (ogi) in rats. FASEB J 22:1092–1097
Angelakis E, Bastelica D, Amara AB, Filali AE, Dutour A, Mege JL, Alessi MC, Raoult D (2012) An evaluation of the effects of Lactobacillus ingluviei on body weight, the intestinal microbiome and metabolism in mice. Microb Pathog 52:61–68
Cebeci A, Gurakan C (2003) Properties of potential probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum strains. Food Microbiol 20:511–518
Collado MC, Gueimonde M, Hernandez M, Sanz Y, Salminen S (2005) Adhesion of selected Bifidobacterium strains to human intestinal mucus and its role in enteropathogen exclusion. J Food Protect 68:2672–2678
Conway PL, Gorbach SL, Goldin BR (1987) Survival of lactic acid bacteria in the human stomach and adhesion to intestinal cells. J Dairy Sci 70:1–12
Danielsen M, Wind A (2003) Susceptibility of Lactobacillus spp. to Antimicrobial Agents. Food Microbiol 82:5–11
FAO/WHO (2001) Evaluation of health and nutritional properties of probiotics in food including powder milk with live lactic acid bacteria. Expert consultation report: Cordoba, Argentina
Fernandez MF, Boris S, Barbes C (2003) Probiotic properties of human lactobacilli strains to be used in the gastrointestinal tract. J Appl Microbiol 94:449–455
Fogh J, Fogh JM, Orfeo T (1977) One hundred and twenty-seven cultured human tumor cell lines producing tumors in nude mice. J Natl Cancer Inst 59:221–226
Hyronimus B, Marrec LC, Hadj SA, Deschamps A (2000) Acid and bile tolerance of spore-forming lactic acid bacteria. Int J Food Microbiol 61:193–197
Lou K, Ban R, Zhao X (2002) Curing of the Bacillus subtilis plasmid using sodium dodecyl sulfate. Trans Tianjin Univ China 8:148–151
Mishra V, Prasad DN (2005) Application of in vitro methods for selection of Lactobacillus casei strains as potential probiotics. Int J Food Microbiol 103:109–115
Pan D, Zeng X, Yan Y (2011) Characterisation of Lactobacillus fermentum SM-7 isolated from koumiss, a potential probiotic bacterium with cholesterol-lowering effects. J Sci Food Agric 91:512–518
Park YS, Lee JY, Kim YS, Shin DH (2002) Isolation and characterization of lactic acid bacteria from feces of newborn baby and from dongchimi. J Agric Food Chem 50:2531–2536
Pennacchia C, Ercolini D, Blaiotta G, Pepe O, Mauriello G, Villani F (2004) Selection of Lactobacillus strains from fermented sausages for their potential use as probiotics. Meat Sci 67:309–317
Pinto MGV, Franz CMAP, Schillinger U, Holzapfel WH (2006) Lactobacillus spp. with in vitro probiotic properties from human faeces and traditional fermented products. Int J Food Microbiol 109:205–214
Pitino I, Randazzo CL, Mandalari G, Lo Curto A, Faulks RM, Le Marc Y, Bisignano C, Caggia C, Wickham MSJ (2010) Survival of Lactobacillus rhamnosus strains in the upper gastrointestinal tract: static and dynamic digestion systems. Food Microbiol 27:1121–1127
Reis JA, Paula AT, Casarotti SN, Penna ALB (2012) Lactic acid bacteria antimicrobial compounds: characteristics and applications. Food Eng Rev 4:124–140
Seppo L, Jauhiainen T, Poussa T, Korpela R (2003) A fermented milk high in bioactive peptides has a blood pressure-lowering effect in hypertensive subjects. Am J Clin Nutr 77:326–330
Sreekumar O, Hosono A (2000) Immediate effect of Lactobacillus acidophilus on the intestinal flora and fecal enzymes of rats and the in vitro inhibition of Escherichia coli in coculture. J Dairy Sci 83:931–939
Steffen EK, Berg RD (1983) Relationship between caecal population levels of indigenous bacteria and translocation to mesenteric lymphnodes. Infect Immun 39:1215–1259
Vinderola G, Matar C, Perdigon G (2007) Milk fermented by Lactobacillus helveticus R389 and its non-bacterial fraction confer enhanced protection against Salmonella enteritidis serovar Typhimurium infection in mice. Immunobiology 212:107–118
Zago M, Fornasari ME, Carminati D, Burns P, Suàrez V, Vinderola G, Reinheimer J, Giraffa G (2011) Characterization and probiotic potential of Lactobacillus plantarum strains isolated from cheeses. Food Microbiol 28:1033–1040
Zhao SJ, Luo HX, Yang HY, Jiang JL, Ren FZ (2008) Effect of Bifidobacterium BBMN01 on mouse intestinal flora. China J Food Sci 29:394–397
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by “the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (NO.BLX2014-21)” and National High Technology Research and Development Program and National Science-technology Support Program for the 12th Five-year Plan, The Ministry of Science and Technology of The People’s Republic of China (No. 2011AA100902, and 2 012AA022108).
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, Z., Hongfei, Z., Junyu, Z. et al. Evaluation of probiotic properties of Lactobacillus strains isolated from traditional Chinese cheese. Ann Microbiol 65, 1419–1426 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-014-0980-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-014-0980-2