Abstract
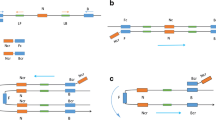
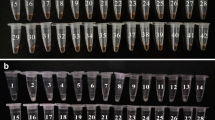
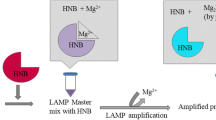
Vibrio parahaemolyticus is an important human pathogen responsible for foodborne gastroenteritis worldwide. In this paper, a loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) method was developed for detection of V. parahaemolyticus in seafood. A set of four primers, two outer and two inner, was designed specifically to recognize the thermolabile hemolysin gene (tlh) of V. parahaemolyticus. The LAMP assay was capable of detecting a minimum of 900 fg test tube−1 for V. parahaemolyticus genomic DNA and 2.4 × 102 CFU mL−1 for pure cultures. The detection limit for the seeded seafood samples was 8.9 × 102 CFU g−1. In addition, 42 shares of natural seafood samples were tested and 8 samples were recorded positive for V. parahaemolyticus, while 6 were positive by conventional culture methods. In conclusion, the LAMP assay is an effective and low-cost method with high specificity and sensitivity for rapid detection and identification of V. parahaemolyticus both in culture isolates and seafood samples.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bej AK, Patterson DP, Brasher CW, Vickery MCL, Jones DD, Kaysner CA (1999) Detection of total and hemolysin-producing Vibrio parahaemolyticus in shellfish using multiplex PCR amplification of tl, tdh and trh. J Microbiol Methods 36:215–225
Blanco-Abad V, Bermejo J, Rodriguez-Castro A, Matinez-Urtaza J (2008) Evaluation of different procedures for the optimized detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in mussels and environmental samples. Int J Food Micriobiol 129:229–236
Cañigral I, Moreno Y, Alonso JL, González A, Ferrús MA (2010) Detection of Vibrio vulnificus in seafood, seawater and wastewater samples from a Mediterranean coastal area. Microbiol Res 165:657–664
Dileep V, Kumar HS, Kumar Y, Nishibuchi M, Karunasagar I, Karunasagar I (2003) Application of polymerase chain reaction for detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus associated with tropical seafoods and coastal environment. Lett Appl Microbiol 36:423–427
Drake SL, DePaola A, Jaykus LA (2007) An Overview of Vibrio vulnificus and Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Compre Rev Food Sci F 6:120–144
Fall J, Chakraborty G, Kono T, Naeda M, Itami T, Sakai M (2008) Establishment of loop-mediated isothermal amplification method (LAMP) for the detection of Vibrio nigripulchritudo in shrimp. FEMS Microbiol Lett 288:171–177
Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (2004) Bacteriological analytical manual on line http://www.fda.gov/Food/ScienceResearch/LaboratoryMethods/BacteriologicalAnalyticalManualBAM/UCM070830
Han FF, Ge BL (2008) Evaluation of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for detecting Vibrio vulnificus in raw oysters. Foodborne Pathog Dis 5:311–320
Hara-Kudo Y, Yoshino M, Kojima T, Ikedo M (2005) Loop-mediated isothermal amplification for the rapid detection of Salmonella. FEMS Microbiol Lett 253:155–161
Hara-Kudo Y, Nemoto J, Ohtsuka K, Segawa Y, Takatori K, Kojima T, Ikedo M (2007) Sensitive and rapid detection of Vero toxin-producing Escherichia coli using loop-mediated isothermal amplification. J Med Microbiol 56:398–406
Horisaka T, Taniguchi T, Honda E, Yokomizo Y, Hayashidani H (2004) Sensitive and specific detection of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis by loop-mediated isothermal amplification. J Clin Microbiol 42:5349–5352
Kamachi K, Toyoizumi-Ajisaka H, Toda K, Soeung SC, Sarath S, Nareth Y, Horiuchi Y, Kojima K, Takahashi M, Arakawa Y (2006) Development and evaluation of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification method for rapid diagnosis of Bordetella pertussis infection. J Clin Microbiol 44:1899–1902
Kaneko H, Kawana T, Fukushima E, Suzutani T (2007) Tolerance of loop-mediated isothermal amplification to a culture medium and biological substances. J Biochem Biophys Methods 70:499–501
Kaufman GE, Blackstone GM, Vickery MC, Bej AK, Bowers J, Bowen MD, Meyer RF, DePaola A (2004) Real-time PCR quantification of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in oysters using an alternative matrix. J Food Prot 67:2424–2429
Li XF, Zhang S, Zhang HW, Tao H, Yu Jia, Zheng WJ, Liu CH, LÜ D, Xiang R, Liu Y (2009) A loop-mediated isothermal amplification method targets the phoP gene for the detection of Salmonella in food samples. Int J Food Micriobiol 133:252–258
Liu XM (2004) Studies on the techniques for the monitoring and controlling foodborne illness. Chin J Food Hyg 16:3–9
McCarthy SA, DePaola A, Cook DW, Kaysner CA, Hill WE (1999) Evaluation of alkaline phosphatase- and digoxigenin-labeled probes for detection of the thermolabile hemolysin (tlh) gene of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Lett Appl Microbiol 28:66–70
Nemoto J, Sugawara C, Akahane K, Hashimoto K, Kojima T, Ikedo M, Konuma H, Hara-kudo Y (2009) Rapid and specific detection of the thermostable direct hemolysin gene in Vibrio parahaemolyticus by loop-mediated isothermal amplification. J Food Prot 72:748–754
Notomi T, Okayama H, Masubuchi H, Yonekawa J, Watanabe K, Amino N, Hase T (2000) Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 28:e63
Ohtsuka K, Yanagawa K, Takatori K, Hara-Kudo Y (2005) Detecton of Salmonella enterica in naturally contaminated liquid eggs by loop-mediated isothermal amplification, and characterization of Salmonella isolates. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:6730–6735
Raghunath P, Acharya S, Bhanumathi A, Karunasagar I, Karunasagar I (2008) Detection and molecular characterization of Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolated from seafood harvested along the southwest coast of India. Food Microbiol 25:824–830
Ren CH, Hu CQ, Luo P, Wang QB (2009) Sensitive and rapid identification of Vibrio vulnificus by loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Microbiol Res 5:514–521
Song T, Toma C, Nakasone N, Iwanaga M (2005) Sensitive and rapid detection of Shigella and enteroinvasive Escherichia coli by a loop-mediated isothermal amplification method. FEMS Microbiol Lett 243:259–263
Su YC, Liu CC (2007) Vibrio parahaemolyticus: a concern of seafood safety. Food Microbiol 24:549–558
Taniguchi H, Ohta H, Ogawa M, Mizuguchi Y (1985) Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of Vibrio parahaemolyticus thermostable direct hemolysin and thermolabile hemolysin genes. J Bacteriol 162:510–515
Taniguchi H, Hirano H, Kubomura S, Higashi K, Mizuguchi Y (1986) Comparison of the nucleotide sequences of the genes for the thermo-stable direct hemolysin and the thermolabile hemolysin from Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Microb Pathog 1:425–432
Wang L, Shi L, Alam MJ, Cheng YH, Li L (2008) Specific and rapid detection of foodborne Samonella by loop-mediated isothermal amplification method. Food Res Int 41:69–74
Ward LN, Bej AK (2006) Detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in shellfish by use of multiplexed real-time PCR with TaqMan fluorescent probes. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:2031–2042
Wong HC, Liu SH, Wang TK, Lee CL, Chiou CS, Liu DP, Nishibuchi M, Lee BK (2000) Characteristics of Vibrio parahaemolyticus O3:K6 from Asia. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:3981–3986
Yano A, Ishimaru R, Hujikata R (2007) Rapid and sensitive detection of heat-liable I and heat-stable I enterotoxin genes of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli by loop-mediated isothermal amplification. J Microbiol Methods 68:414–420
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by Fok Ying Dong Education Foundation of China 114035 and Leading Academic Discipline Project of Shanghai Municipal Education Commission J50704.This work was also supported by the Maine Agricultural and Forest Experiment Station at the University of Maine with external publication number 3187.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, X., Xu, Q., Pan, Y. et al. A loop-mediated isothermal amplification method for rapid detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in seafood. Ann Microbiol 62, 263–271 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-011-0255-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-011-0255-0