Abstract
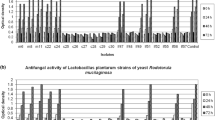
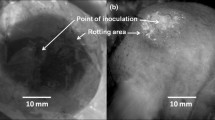
Thirty-five of the 77 colonies of lactic acid bacteria isolated from koumiss showed antifungal activity against Botrytis cinerea, when tested by the Poison Food Technique. Of these, the most promising isolate having a broad spectrum of antifungal activity, including against Botrytis cinerea, Alternaria solani, Phytophthora drechsleri Tucker, Fusarium oxysporum and Glomerella cingulata, was identified as Lactobacillus plantarum IMAU10014. The effect of pH, temperature and protease on the antifungal activity of L. plantarum IMAU10014 was determined. The activity substance was heat stable. The maximum antifungal activity was observed at pH 4.0. When the supernatant was adjusted to pH 8.0, the activity was lost irreversibly. However, after enzymatic treatment of supernatant with trypsin, neutral protease and proteinase K, loss of part of the antifungal activity was observed which indicated there are other substances in addition to the proteinaceous substance with the antifungal activity.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bevan P, Ryder H (1995) Identifying small-molecule lead compounds: the screening approach to drug discovery. Trends Biotechnol 113:115–121
Broberg A, Jacobsson K, Strom K, Schnurer J (2007) Metabolite profiles of lactic acid bacteria in grass silage. Appl Environ Microb 73:5547–5552
Cabo ML, Braber AF, Koenraad P (2002) Apparent antifungal activity of several lactic acid bacteria against Penicillium discolor is due to acetic acid in the medium. J Food Protect 65:1309–1316
Fabio C, Simone C, Emanuele A, Cristiana C, Luigi G, Carlo Z (2007) Antifungal activityof lactobacilli isolated from salami. Fed Eur Microbiol Soc 271:245–250
Hassan YI, Bullerman L (2008) Antifungal Activity of Lactobacillus paracasei subsp. tolerans against Fusarium proliferatum and Fusarium graminearum in a Liquid Culture Setting. J Food Prot 71:2213–2216
Hudacek J, Zalan Z, Chumchalova J, Halasz A (2007) Antifungal effect of Lactobacilli on Fusarium and Aspergillus molds. Chem Listy 101:730–737
Jaroszewski DE, Halabi WJ, Blair JE, Coakley BJ, Wong RK, Parish JM, Vaszar LT, Kusne S, Vikram HR, DeValeria PA, Lanza LA, Arabia FA (2009) Surgery for Pulmonary Coccidioidomycosis: A 10-Year Experience. Ann Thorac Surg 88:1765–1772
Laitila A, Alakomi HL, Raaska L, Mattila-Sandholm T, Haikara A (2002) Antifungal activities of two Lactobacillus plantarum strains against Fusarium moulds in vitro and in malting of barley. J Appl Microbiol 93:566–576
Lavermicocca P, Valerio F, Evidente A, Lazzaroni S, Corsetti A, Gobbetti M (2000) Purification and characterization of novel antifungal compounds from the sourdough Lactobacillus plantarum strain 21B. Appl Environ Microb 66: 4084-4090
Magnusson J, Strom K, Roos S, Sjogren J, Schnurer J (2003) Broad and complex antifungal activity among environmental isolates of lactic acid bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett 219:129–135
Niku-Paavola ML, Laitila A, Mattila-Sandholm T, Haikara A (1999) New types of antimicrobial compounds produced by Lactobacillus plantarum. J Appl Microbiol 86:29–35
Prema P, Smila D, Palavesam A, Immanuel G (2010) Production and characterization of an antifungal compound (3-phenyllactic acid) produced by lactobacillus plantarum strain. Food Bioprocess Technol 3:379–386
Park SC, Kim JY, Lee JK, Hwang I, Cheong H, Nah JW, Hahm KS, Park Y (2009) Antifungal mechanism of a novel antifungal protein from pumpkin rinds against various fungal pathogens. J Agr Food Chem 57:9299–9304
Rouse S, Harnett D, Vaughan A, van Sinderen D (2008) Lactic acid bacteria with potential to eliminate fungal spoilage in foods. J Appl Microbiol 104:915–923
Roy U, Batish VK, Grover S, Neelakantan S (1996) Production of antifungal substance by Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis CHD-28.3. Int J Food Microbiol 32:27–34
Roy U, Jai KK, Sunita G, Virender KB (2009) Partial purification of an antifungal protein produced by Enterococcus faecalis CHD 28.3. Ann Microbiol 59:279–284
Schnurer J, Magnusson J (2005) Antifungal lactic acid bacteria as biopreservatives. Trends Food Sci Tech 16:70–78
Sjogren J, Magnusson J, Broberg A, Schnurer J, Kenne L (2003) Antifungal 3-hydroxy fatty acids from Lactobacillus plantarum MiLAB 14. Appl Environ Microb 69:7554–7557
Sridhar SR, Velusamy Rajagopal RV, Rajavel R, Masilamani S, Narasimhan S (2003) Antifungal Activity of Some Essential Oils. J Agr Food Chem 51:7596–7599
Strange RN, Scott PR (2005) Plant disease: A threat to global food security. Annu Rev Phytopathol 43:83–116
Strom K, Sjogren J, Broberg A, Schnurer J (2002) Lactobacillus plantarum MiLAB 393 produces the antifungal cyclic dipeptides cyclo(L-Phe-L-Pro) and cyclo(L-Phe-trans-4-OH-L-Pro) and 3-phenyllactic acid. Appl Environ Microb 68:4322–4327
Sun JH, Wang HK, Lu FP, Du LX, Wang GF (2008) The efficacy of nematicidal strain Syncephalastrum racemosum. Ann Microbiol 58:369–373
Sun TS, Zhao SP, Wang HK, Cai CK, Chen YF, Zhang HP (2009) ACE-inhibitory activity and gamma-aminobutyric acid content of fermented skim milk by Lactobacillus helveticus isolated from Xinjiang koumiss in China. Eur Food Res Technol 228:607–612
Todorov SD, Dicks LMT (2004) Partial characterization of bacteriocins produced by four lactic acid bacteria isolated from regional South African barley beer. Ann Microbiol 54:403–413
Tuma S, Vogensen FK, Plockova M, Chumchalova J (2007) Isolation of antifungally active lactobacilli from Edam cheese. Acta Aliment 36:405–414
Yang EJ, Chang HC (2010) Purification of a new antifungal compound produced by Lactobacillus plantarum AF1 isolated from kimchi. Int J Food Microbiol 139:56–63
Yang LP, Xie JT, Jiang DH, Fu YP, Li GQ, Lin FC (2008) Antifungal substances produced by Penicillium oxalicum strain PY-1—potential antibiotics against plant pathogenic fungi. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 24:909–915
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge the financial support provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 20876116 and No. 30900961) and Key Laboratory of Dairy Biotechnology and Engineering, Ministry of Education, Inner Mongolia Agricultural University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Yan, H., Shin, J. et al. Activity against plant pathogenic fungi of Lactobacillus plantarum IMAU10014 isolated from Xinjiang koumiss in China. Ann Microbiol 61, 879–885 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-011-0209-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-011-0209-6