Abstract
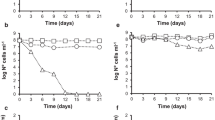
The survival of bacteria in natural environments is of practical importance. In this study, we investigated the effect of starvation on the survival and adhesion ability of Shigella in domestic treatment plant effluent microcosms after incubation at either room temperature or 4°C for 1 month. Our results showed that the number of cells decreased considerably after this period of stress. We also revealed some modifications to the biochemical and enzymatic profiles, and antibiotic susceptibility of stressed cells. Adherence assays to the human oral cavity epidermoid carcinoma (KB) cell line revealed an increase in the number of adherent cells from 0.7 to 1.85% after 1 month of incubation in domestic treatment plant effluent.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amy PS, Morita RY (1953) Starvation-survival patterns of sixteen freshly isolated open-ocean bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 45:1109–1115
Ben Abdallah F, Chaieb K, Snoussi M, Bakhrouf A, Gadour K (2007) Phenotypic variations and molecular identification of Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium cells under starvation in seawater. Curr Microbiol 55:485–491
Chatti A, Daghfous D, Landoulsi A (2007) Effect of seqA mutation on Salmonella typhimurium virulence. J Infect 54:241–245
Duguay AR, Silhavy TJ (2004) Quality control in the bacterial periplasm. Biochim Biophys Acta 1694:121–134
Ellafi A, Denden I, Ben AF, Souissi I, Bakhrouf A (2009) Survival and adhesion ability of Shigella spp. strains after their incubation in seawater microcosms. World. J Microbiol Biotechnol 25:1161–1168
Hartman AB, Venkatesan MM, Oaks EV, Buysse JM (1990) Sequence and molecular characterization of multicopy invasion plasmid antigen gene, ipaH, of Shigella flexneri. J Bacteriol 172(4):1905–1915
Hoben HJ, Somasegaran P (1982) Comparaison of the pour, spread, and drop plate methods for enumeration of Rhizobium spp. in inoculants made from presterilized peat. Appl Environ Microbiol 44:1246–1247
Huisman GW, Siegele DA, Zambrano MM, Kolter R (1996) Morphological and physiological changes during stationary phase. In: Neidhardt FC et al (eds) Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium: cellular and molecular biology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, pp 1672–1682
Hyams KC, Merrell BR, Bourgeois AL (1991) Diarrheal disease during operation desert shield. N Engl J Med 325(20):1423–1428
Islam MS, Hasan MK, Miah MA, Sur GC, Felsenstein M, Venkatesan M, Sack RB, Albert MJ (1993) Use of the polymerase chain reaction and fluorescent-antibody methods for detecting viable and nonculturable Shigella dysenteriae Type 1 in laboratory microcosms. Appl Environ Microbiol 59(2):536–540
Monier JM, Lindow SE (2003) Differential survival of solitary and aggregated, bacterial cells promotes aggregate formation on leaf surfaces. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:15977–15982
NCCLS (1999) Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing; Ninth Informational Supplement, vol. 19, No. 1. National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards document M100-S9. Villanova, PA
Oliveira K, Oliveira T, Teixeira P, Azeredo J, Oliveira R (2007) Adhesion of Salmonella enteritidis to stainless steel surfaces. Braz J Microbiol 38:318–323
Pergram GC, Rollins N, Esprey Q (1998) Estimating the costs of diarrhoea and epidemic dysentery in KwaZulu-Natal and South Africa. Water SA 24(1):11–20
Ravva S, Korn A (2007) Extractable organic components and nutrients in wastewater from dairy lagoons influence the growth and survival of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:2191–2198
Rosenberg ML, Hazlet KK, Schaefer J, Wells JG, Pruneda RC (1976) Shigellosis from swimming. J Am Med Assoc 236(16):1849–1852
Rowe B, Gross RJ (1984) Facultatively anaerobic Gram negative rods. Genus II. Shigella. In: Krieg NR, Holt JG (eds) Bergey's manual of systematic bacteriology. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 423–427
Russell NJ (1984) Mechanisms of thermal adaptation in bacteria: blueprints for survival. Trends Biochem Sci 9(3):108–112
Siu LK (2002) Antibiotics: action and resistance in Gram negative bacteria. J Microbiol Immunol Infect 35:1–11
Teyssou R, Gerome P, Buisson Y (1994) Triple shigellose chez un même malade contractée pendant l'opération "Turquoise" au Ruande. Bull Soc Pathol Exot 87:228–230
Theron J, Morar D, Preez MDU, Brozel VS, Venter SN (2001) A sensitive seminested pcr method for the detection of Shigella in spiked environmental water samples. Water Res 35(4):869–874
Van GH, Kuen JG (1984) Strategies for growth and evolution of microorganisms in oligotrophic habitats. In: Hobbie JE, Williams PJB (eds) Heterotrophic activity in the sea. Nato Conference series IV. Plenum, New York, pp 25–54
Zhang JP, Normark S (1996) Induction of gene expression in Escherichia coli after pilus-mediated adherence. Science 273:1234–1236
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ellafi, A., Abdallah, F.B. & Bakhrouf, A. Effect of starvation on survival and adhesion ability of Shigella spp. in domestic treatment plant effluent microcosms. Ann Microbiol 60, 383–389 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-010-0053-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-010-0053-0