Abstract
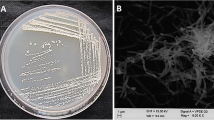
A new deep-sea-derived actinomycete 12A22 was isolated from the sediment of the South China Sea which showed potential cytotoxic and antimicrobial activities. The actinomycete was identified as Actinoalloteichus cyanogriseus by investigating morphological characteristics and phylogenetic analyses based on its 16S rRNA gene sequence. Two compounds, cyclo-(L-Pro-D-Pro-L-Tyr-L-Tyr) (1) and 2-hydroxyethyl-3-methyl-1,4-naphthoquinone (2), were isolated and characterized from the fermentation broth of the strain 12A22. Compound 2 exhibited significant inhibitory activities against a variety of phytopathogenic fungi (Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cucumerinum, Setosphaeria turcica, and Botrytis cinerea) and Gram-positive bacterium (Bacillus subtilis). In particular, this compound showed better antifungal activity against Botrytis cinerea than positive control amphotericin B. Besides, compound 2 showed moderate cytotoxic activity against human breast cancer MDA-MB-435 cells with IC50 10.59 µM, weaker than the positive control diaminedichloroplatinum with 5.91 μM. Our results suggested that this naphthoquinone could be used as a potential antimicrobial and antitumor agent.



Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information.
References
Barra-Bucarei L, France Iglesias A, Gerding Gonzalez M, Silva Aguayo G, Carrasco-Fernandez J, Castro JF, Ortiz Campos J (2020) Antifungal activity of Beauveria bassiana endophyte against Botrytis cinerea in two Solanaceae crops. Microorganisms 8:65. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8010065
Berdy J (2012) Thoughts and facts about antibiotics: where we are now and where we are heading. J Antibiot 65:385–395. https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2012.54
Boudjelal F, Zitouni A, Mathieu F, Lebrihi A, Sabaou N (2011) Taxonomic study and partial characterization of antimicrobial compounds from a moderately halophilic strain of the genus Actinoalloteichus. Braz J Microbiol 42:835–845. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1517-83822011000300002
Boudjelal F, Zitouni A, Bouras N, Schumann P, Sproer C, Sabaou N, Klenk HP (2015) Actinoalloteichus hoggarensis sp. nov., an actinomycete isolated from Saharan soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 65:2006–2010. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.000216
Chen L, Wang N, Wang X, Hu J, Wang S (2010) Characterization of two anti-fungal lipopeptides produced by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SH-B10. Bioresour Technol 101:8822–8827. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.06.054
Choi BK, Lee HS, Kang JS, Shin HJ (2019) Dokdolipids A-C, hydroxylated rhamnolipids from the marine-derived actinomycete Actinoalloteichus hymeniacidonis. Mar Drugs 17:237. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17040237
Duncan KR, Haltli B, Gill KA, Correa H, Berrue F, Kerr RG (2015) Exploring the diversity and metabolic potential of actinomycetes from temperate marine sediments from Newfoundland, Canada. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 42:57–72. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-014-1529-x
Fu P, Wang S, Hong K, Li X, Liu P, Wang Y, Zhu W (2011) Cytotoxic bipyridines from the marine-derived actinomycete Actinoalloteichus cyanogriseus WH1-2216-6. J Nat Prod 74:1751–1756. https://doi.org/10.1021/np200258h
Fu P, Kong F, Li X, Wang Y, Zhu W (2014) Cyanogramide with a new spiro indolinone-pyrroloimidazole skeleton from Actinoalloteichus cyanogriseus. Org Lett 16:3708–3711. https://doi.org/10.1021/ol501523d
Fujita K, Sugiyama R, Nishimura S, Ishikawa N, Arai MA, Ishibashi M, Kakeya H (2016) Stereochemical assignment and biological evaluation of BE-14106 unveils the importance of one acetate unit for the antifungal activity of polyene macrolactams. J Nat Prod 79:1877–1880. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.6b00250
Fukami A, Nakamura T, Kawaguchi K, Rho MC, Matsumoto A, Takahashi Y, Shiomi K, Hayashi M, Komiyama K, Omura S (2000) A new antimicrobial antibiotic from Actinoplanes capillaceus sp. K95–5561T. J Antibiot 53:1212–1214. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.53.1212
Huang H, Song Y, Li X, Wang X, Ling C, Qin X, Zhou Z, Li Q, Wei X, Ju J (2018) Abyssomicin monomers and dimers from the marine-derived Streptomyces koyangensis SCSIO 5802. J Nat Prod 81:1892–1898. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.8b00448
Igarashi M, Sawa R, Umekita M, Hatano M, Arisaka R, Hayashi C, Ishizaki Y, Suzuki M, Kato C (2021) Sealutomicins, new enediyne antibiotics from the deep-sea actinomycete Nonomuraea sp. MM565M-173N2. J Antibiot 74:291–299. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41429-020-00402-1
Jansen R, Mohr KI, Bernecker S, Stadler M, Muller R (2014) Indothiazinone, an indolyl thiazolyl ketone from a novel myxobacterium belonging to the sorangiineae. J Nat Prod 77:1054–1060. https://doi.org/10.1021/np500144t
Jose PA, Jebakumar SR (2013) Phylogenetic appraisal of antagonistic, slow growing actinomycetes isolated from hypersaline inland solar salterns at Sambhar salt Lake, India. Front Microbiol 4:190. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2013.00190
Kamjam M, Sivalingam P, Deng Z, Hong K (2017) Deep sea actinomycetes and their secondary metabolites. Front Microbiol 8:760. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.00760
Karuppiah V, Li Y, Sun W, Feng G, Li Z (2015) Functional gene-based discovery of phenazines from the actinobacteria associated with marine sponges in the South China Sea. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:5939–5950. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6547-8
Kumar S, Solanki DS, Parihar K, Tak A, Gehlot P, Pathak R, Singh SK (2021) Actinomycetes isolates of arid zone of Indian Thar desert and efficacy of their bioactive compounds against human pathogenic bacteria. Biol Futur. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42977-021-00073-5
Li Y, Xu Y, Liu L, Han Z, Lai PY, Guo X, Zhang X, Lin W, Qian PY (2012) Five new amicoumacins isolated from a marine-derived bacterium Bacillus subtilis. Mar Drugs 10:319–328. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10020319
Liu S, Fu L, Tan H, Jiang J, Che Z, Tian Y, Chen G (2021) Resistance to boscalid in Botrytis cinerea from greenhouse-grown tomato. Plant Dis. https://doi.org/10.1094/pdis-06-20-1191-re
Lu S, Wang J, Sheng R, Fang Y, Guo R (2020) Novel bioactive polyketides isolated from marine actinomycetes: an update review from 2013 to 2019. Chem Biodivers 17:e2000562. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbdv.202000562
Ma Z, Liu B, He S, Gao Z (2020) Analysis of physiological races and genetic diversity of Setosphaeria turcica (Luttr.) KJ Leonard & Suggs from different regions of China. Can J Plant Pathol 42:396–407. https://doi.org/10.1080/07060661.2019.1679261
Manivasagan P, Sivakumar K, Gnanam S, Venkatesan J, Kim SK (2014) Production, biochemical characterization and detergents application of Keratinase from the marine actinobacterium Actinoalloteichus sp MA-32. J Surfact Deterg 17:669–682. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11743-013-1519-4
Mei X, Lan M, Cui G, Zhang H, Zhu W (2019) Caerulomycins from Actinoalloteichus cyanogriseus WH1-2216-6: isolation, identification and cytotoxicity. Org Chem Front 6:3566–3574. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9qo00685k
Mitousis L, Thoma Y, Musiol-Kroll EM (2020) An update on molecular tools for genetic engineering of actinomycetes-the source of important antibiotics and other valuable compounds. Antibiotics 9:494. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9080494
Mitova M, Tommonaro G, De Rosa S (2003) A novel cyclopeptide from a bacterium associated with the marine sponge Ircinia muscarum. Z Naturforsch C J Biosci 58:740–745. https://doi.org/10.1515/znc-2003-9-1026
Nouioui I, Rueckert C, Willemse J, van Wezel GP, Klenk HP, Busche T, Kalinowski J, Bredholt H, Zotchev SB (2017) Actinoalloteichus fjordicus sp nov isolated from marine sponges: phenotypic, chemotaxonomic and genomic characterisation. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 110:1705–1717. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-017-0920-9
Pan HQ, Zhang SY, Wang N, Li ZL, Hua HM, Hu JC, Wang SJ (2013) New spirotetronate antibiotics, lobophorins H and I, from a South China Sea-derived Streptomyces sp. 12A35. Mar Drugs 11:3891–3901. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11103891
Pan HQ, Cheng J, Zhang DF, Yu SY, Khieu TN, Son CK, Jiang Z, Hu JC, Li WJ (2015a) Streptomyces bohaiensis sp. nov., a novel actinomycete isolated from Scomberomorus niphonius in the Bohai Sea. J Antibiot 68:246–252. https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2014.137
Pan HQ, Yu SY, Song CF, Wang N, Hua HM, Hu JC, Wang SJ (2015b) Identification and characterization of the antifungal substances of a novel Streptomyces cavourensis NA4. J Microbiol Biotechnol 25:353–357. https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.1407.07025
Petrasch S, Knapp SJ, Van Kan JAL, Blanco-Ulate B (2019) Grey mould of strawberry, a devastating disease caused by the ubiquitous necrotrophic fungal pathogen Botrytis cinerea. Mol Plant Pathol 20:877–892. https://doi.org/10.1111/mpp.12794
Pilkington LI (2019) A chemometric analysis of deep-sea natural products. Molecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24213942
Prudence SMM, Addington E, Castano-Espriu L, Mark DR, Pintor-Escobar L, Russell AH, McLean TC (2020) Advances in actinomycete research: an actinobase review of 2019. Microbiology 166:683–694. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.000944
Qin L, Yi W, Lian XY, Zhang Z (2020) Bioactive alkaloids from the actinomycete Actinoalloteichus sp. ZZ1866. J Nat Prod 83:2686–2695. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.0c00588
Sato S, Iwata F, Yamada S, Katayama M (2012) Neomaclafungins A-I: oligomycin-class macrolides from a marine-derived actinomycete. J Nat Prod 75:1974–1982. https://doi.org/10.1021/np300719g
Scarlett K, Tesoriero L, Daniel R, Maffi D, Faoro F, Guest DI (2015) Airborne inoculum of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cucumerinum. Eur J Plant Pathol 141:779–787. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-014-0578-3
Sharma S, Fulke AB, Chaubey A (2019) Bioprospection of marine actinomycetes: recent advances, challenges and future perspectives. Acta Oceanol Sin 38:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-018-1340-z
Singla AK, Mayilraj S, Kudo T, Krishnamurthi S, Prasad GS, Vohra RM (2005) Actinoalloteichus spitiensis sp nov., a novel actinobacterium isolated from a cold desert of the Indian Himalayas. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:2561–2564. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.63720-0
Tamura T, Zhiheng L, Yamei Z, Hatano K (2000) Actinoalloteichus cyanogriseus gen. nov., sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 50:1435–1440. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-50-4-1435
Toma F, Bouhet JC, Pham Van Chuong P, Fromageot P (1975) Carbon-13 NMR spectroscopy of the biological pigments luteoskyrin and rugulosin and some polyhydroxyanthraquinone analogues. Org Magn Reson 7:496–503. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrc.1270071008
Tong L, Liu Z, Cui J, Hu J, Zhang RY (2017) First report of leaf blight caused by Setosphaeria turcica on sweet sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) in China. Plant Dis. https://doi.org/10.1094/pdis-03-17-0412-pdn
Wang XJ, Zhang J, Qian PT, Wang JD, Liu CX, Xiang WS (2014) Three new cyclopentenone derivatives from Actinoalloteichus nanshanensis NEAU 119. J Asian Nat Prod Res 16:587–592. https://doi.org/10.1080/10286020.2014.921909
Wang P, Wang D, Zhang R, Wang Y, Kong F, Fu P, Zhu W (2021) Novel macrolactams from a deep-sea-derived Streptomyces species. Mar Drugs 19:13. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19010013
Xiang W, Liu C, Wang X, Du J, Xi L, Huang Y (2011) Actinoalloteichus nanshanensis sp nov., isolated from the rhizosphere of a fig tree (Ficus religiosa). Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:1165–1169. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.023283-0
Yi W, Qin L, Lian XY, Zhang Z (2020) New antifungal metabolites from the mariana trench sediment-associated actinomycete Streptomyces sp. SY1965. Mar Drugs. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18080385
Zhang H, Zheng W, Huang J, Luo H, Jin Y, Zhang W, Liu Z, Huang Y (2006) Actinoalloteichus hymeniacidonis sp. nov., an actinomycete isolated from the marine sponge Hymeniacidon perleve. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:2309–2312. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.64217-0
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31872036, 41776178, and 41576136), the LiaoNing Revitalization Talents Program (XLYC1807268), the Science and Technology Innovation Program for the Youth Talents of Shenyang (RC170266), and the Youth Innovation Promotion Association CAS (2018229).
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31872036, 41776178 and 41576136), the LiaoNing Revitalization Talents Program (XLYC1807268), the Science and Technology Innovation Program for the Youth Talents of Shenyang (RC170266), and the Youth Innovation Promotion Association CAS (2018229).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HP designed and conducted the experiments, and analyzed the data. XZ and CS participated in the bioactivity assays and data analysis. XZ and HP wrote the manuscript. YB and JH revised the manuscript. All authors reviewed and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Song, C., Bai, Y. et al. Cytotoxic and antimicrobial activities of secondary metabolites isolated from the deep-sea-derived Actinoalloteichus cyanogriseus 12A22. 3 Biotech 11, 283 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-021-02846-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-021-02846-0