Abstract
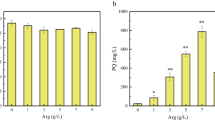
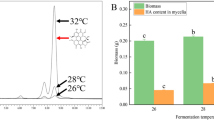
Perylenequinones (PQ), a class of naturally occurring polypeptides, are widely used as a clinical drug for treating skin diseases and as a photodynamic therapy against cancers and viruses. In this study, the effects of different carbon sources on PQ biosynthesis by Shiraia sp. Slf14 were compared, and the underlying molecular mechanism of fructose as the sole carbon to enhance PQ production was investigated by transcriptome analysis. The results indicated that fructose enhanced PQ yield to 1753.64 mg/L, which was 1.73-fold higher than that obtained with glucose. Comparative transcriptome analysis demonstrated that most of the upregulated genes were related to transport systems, energy and central carbon metabolism in Shiraia sp. Slf14 cultured in fructose. The genes involved in glycolysis and pentose phosphate pathways, and encoding citrate synthase, ATP-citrate lyase, and acetyl-CoA carboxylase were substantially upregulated, resulting in increased overall acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA production. However, genes involved in gluconeogenesis, glyoxylate cycle pathway, and fatty acid synthesis were significantly downregulated, resulting in higher acetyl-CoA influx for PQ formation. In particular, the putative PQ biosynthetic cluster was upregulated in Shiraia sp. Slf14 cultured in fructose, leading to a significant increase in PQ production. The results of real-time qRT-PCR and related enzyme activities were also consistent with those of transcriptome analysis. These findings provide a remarkable insight into the underlying mechanism of PQ biosynthesis and pave the way for improvements in PQ production by Shiraia sp. Slf14.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bellou S, Triantaphyllidou IE, Mizerakis P, Aggelis G (2016) High lipid accumulation in Yarrowia lipolytica cultivated under double limitation of nitrogen and magnesium. J Biotechnol 234:116–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2016.08.001
Bok JW, Keller NP (2004) LaeA, a regulator of secondary metabolism in Aspergillus spp. Eukaryot Cell 3(2):527–535. https://doi.org/10.1128/ec.3.2.527-535.2004
Cai Y, Liao X, Liang X, Ding Y, Sun J, Zhang D (2011) Induction of hypocrellin production by Triton X-100 under submerged fermentation with Shiraia sp. SUPER-H168. N Biotechnol 28(6):588–592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbt.2011.02.001
Chen HQ, Lee MH, Chung KR (2007a) Functional characterization of three genes encoding putative oxidoreductases required for cercosporin toxin biosynthesis in the fungus Cercospora nicotianae. Microbiol 153:2781–2790. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.2007/007294-0
Chen HQ, Lee MH, Daub ME, Chung KR (2007b) Molecular analysis of the cercosporin biosynthetic gene cluster in Cercospora nicotianae. Mol Microbiol 64(3):755–770. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2007.05689.x
Chettri P, Bradshaw RE (2016) LaeA negatively regulates dothistromin production in the pine needle pathogen Dothistroma septosporum. Fungal Genet Biol 97:24–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fgb.2016.11.001
Deng H, Chen J, Gao R, Liao X, Cai Y (2016a) Adaptive responses to oxidative stress in the filamentous fungal Shiraia bambusicola. Molecules 21(9):1118. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21091118
Deng H, Gao R, Liao X, Cai Y (2016b) Reference genes selection and relative expression analysis from Shiraia sp. SUPER-H168 productive of hypocrellin. Gene 580:67–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2016.01.019
Diwu Z, Lown JW (1990) Hypocrellins and their use in photosensitization. Photochem Photobiol 52:609–616. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1751-1097.1990.tb01807.x
Du W, Liang ZQ, Zou X, Han YF, Liang JD, Yu JP, Chen WH, Wang YR, Sun CL (2013) Effects of microbial elicitor on production of hypocrellin by Shiraia bambusicola. Folia Microbiol 58:283–289. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-012-0203-9
Du W, Liang J, Han Y, Yu J, Liang Z (2015) Nitric oxide mediates hypocrellin accumulation induced by fungal elicitor in submerged cultures of Shiraia bambusicola. Biotechnol Lett 37(1):153–159. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-014-1665-4
Gangwar M, Sood A, Bansal A, Chauhan RS (2018) Comparative transcriptomics reveals a reduction in carbon capture and flux between source and sink in cytokinin-treated inflorescences of Jatropha curcas L. 3 Biotech 8(1):64. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-018-1089-2
Geer BW, Krochko D, Oliver MJ, Walker VK, Williamson JH (1980) A comparative study of the NADP-malic enzymes from Drosophila and chick liver. Comp Biochem Physiol 65(1):25–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/0305-0491(80)90109-1
Hu M, Cai Y, Liao X, Hu Y, Li Z, Zhang D (2010) Optimization submerged fermentation of hypocrellin. Food Mach 26(5):141–143. https://doi.org/10.3696/j.issn.1003-5788.2010.05.041
Jin WB, Balajee SA, Marr KA, Andes D, Nielsen KF, Frisvad JC, Keller NP (2005) LaeA, a regulator of morphogenetic fungal virulence factors. Eukaryot Cell 4(9):1574–1582. https://doi.org/10.1128/EC.4.9.1574-1582.2005
Kayali HA, Tarhan L, Sazak A, Sahin N (2011) Carbohydrate metabolite pathways and antibiotic production variations of a novel Streptomyces sp. M3004 depending on the concentrations of carbon sources. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 165(1):369–381. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-1445-6
Kishi T, Tahara S, Taniguchi N, Tsuda M, Tanaka C, Takahashi S (1991) New perylenequinones from Shiraia bambusicola. Planta Med 57(4):376–379. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2006-960121
Kornberg A (1955) Isocitric dehydrogenase of yeast (TPN). Methods Enzymol 1:705–709. https://doi.org/10.1016/0076-6879(55)01123-3
Lei XY, Zhang MY, Ma YJ, Wang WJ (2017) Transcriptomic responses involved in enhanced production of hypocrellin A by addition of Triton X-100 in submerged cultures of Shiraia bambusicola. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 44(10):1415–1429. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-017-1965-5
Li T, Fan Y, Nambou K, Hu F, Imanaka T, Wei L, Hua Q (2015) Improvement of ansamitocin p-3 production by Actinosynnema mirum with fructose as the sole carbon source. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 175(6):2845–2856. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-1445-6
Li T, Hou C, Shen X (2019) Efficient agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Shiraia bambusicola and activation of a specific transcription factor for hypocrellin production. Biotechnol Biotec Eq 33(1):1365–1371. https://doi.org/10.1080/13102818.2019.1667874
Liang XH, Cai YJ, Liao XR, Wu K, Wang L, Zhang DB, Meng Q (2009) Isolation and identification of a new hypocrellin a-producing strain Shiraia sp. SUPER-H168. Microbiol Res 164:9–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2008.08.004
Liang SL, Wang B, Pan L, Ye YR, He MH, Han SY, Zheng SP, Wang XN, Lin Y (2012) Comprehensive structural annotation of Pichia pastoris transcriptome and the response to various carbon sources using deep paired-end RNA sequencing. BMC Genom 13:738. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-13-738
Lin Z, An J, Wang J, Niu J, Ma C, Wang L, Yuan G, Shi L, Liu L, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Qi J, Lin S (2017) Integrated analysis of 454 and Illumina transcriptomic sequencing characterizes carbon fux and energy source for fatty acid synthesis in developing Lindera glauca fruits for woody biodiesel. Biotechnol Biofuels 10:134–154. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-017-0820-2
Liu XY, Shen XY, Fan L, Gao J, Hou CL (2016) High-efficiency biosynthesis of hypocrellin a in Shiraia sp. using gamma-ray mutagenesis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 10(11):4875–4883. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-7222-9
Liu B, Bao J, Zhang Z, Yan R, Wang Y, Yang H, Zhu D (2018) Enhanced production of perylenequinonesin the endophytic fungus Shiraia sp. Slf14 by calcium/calmodulin signal transduction. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102(1):153–163. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8602-0
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 25(4):402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Martin JF (2000) Molecular control of expression of penicillin biosynthesis genes in fungi regulatory proteins interact with a bidirectional promoter region. J Bacteriol 182(9):2355–2362. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.182.9.2355-2362.2000
Mulrooey CA, Obrien EM, Morgan BJ, Kozlowski MC (2012) Perylenequinones: isolation, synthesis, and biological activity. Eur J Org Chem 21:3887–3904. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejoc.201200184
Newman AG, Townsend CA (2016) Molecular characterization of the cercosporin biosynthetic pathway in the fungal plant pathogen Cercospora nicotianae. J Am Chem Soc 138(12):4219–4228. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.6b00633
Pan WS, Ji YY, Yang ZY, Wang JW (2012) Screening of high-yield hypocrellin A producing mutants from Shiraia sp. S8 by protoplast mutagenesis and ultraviolet irradiation. Chin J Bioprocess Eng 10(6):18–23. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1672-3678.2012.06.004
Peng SL, Yang HL, Li EH, Wang XL, Zhu D (2015) The prokaryotic expression, purification and bioinformatics of type III polyketide synthase from Shiraia sp Slf14, which is an endophytic fungus of Huperzia serrata. J Jiangxi Norm Univ 39: 430–434. https://www.org/CNKI:SUN:CAPE0.2015-04-019
Price MS, Yu J, Nierman WC, Kim HS, Pritchard B, Jacobus CA, Bhatnagar D, Cleveland TE, Payne GA (2006) The aflatoxin pathway regulator AflR induces gene transcription inside and outside of the aflatoxin biosynthetic cluster. FEMS Microbiol Lett 255(2):275–279. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2005.00084.x
Sauer U, Canonaco F, Heri S, Perrenoud A, Fisher E (2004) The soluble and membrane-bound transhydrogenases UdhA and PntAB have divergent functions in NADPH metabolism of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 279:6613–6619. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M311657200
Shen XY, Zheng DQ, Gao J, Hou CL (2012) Isolation and evaluation of endophytic fungi with antimicrobial ability from Phyllostachys edulis. Bangl J Pharmacol 7(4):249–257. https://doi.org/10.3329/bjp.v7i4.12068
Silva CAA, Oka ML, Fonseca GG (2019) Physiology of yeast strains isolated from Brazilian biomes in a minimal medium using fructose as the sole carbon source reveals potential biotechnological applications. 3 Biotech 9:191. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-019-1721-9
Srere PA (1959) The citrate cleavage enzyme. I. Distribution and purification. J Biol Chem 234(10):2544–2547
Stoops JK, Awad ES, Arslanian MJ, Gunsberg S, Wakil SJ, Oliver RM (1978) Studies on the yeast fatty acid synthetase subunit composition and structural organization of a large multifunctional enzyme complex. J Biol Chem 253(12):4464–4475
Su Y, Si S, Qiao L, Cai Y, Xu Z, Yang Y (2011) The effect of a hypocrellin A enriched diet on egg yolk quality and hypocrellin A distributions in the meat of laying hens. Eur Food Res Technol 232:935–940. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-011-1461-5
Sun CX, Ma YJ, Wang JW (2017) Enhanced production of hypocrellin A by ultrasound stimulation in submerged cultures of Shiraia bambusicola. Ultrason Sonochem 38:214–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2017.03.020
Tamayo EN, Villanueva A, Hasper AA, De Graaff LH, Ramon D, Orejas M (2008) CreA mediates repression of the regulatory gene xlnr which controls the production of xylanolytic enzymes in Aspergillus nidulans. Fungal Genet Biol 45(6):984–993. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fgb.2008.03.002
Tilburn J, Sarkar S, Widdick DA, Espeso EA, Orejas M, Mungroo J, Pefnalva MA, Arst HN (1995) The Aspergillus pacc zinc finger transcription factor mediates regulation of both acid- and alkaline-expressed genes by ambient pH. EMBO J 14(4):779–790. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07056.x
Tong ZW, Mao LW, Liang HL, Zhang ZB, Wang Y, Yan RM, Zhu D (2017) Simultaneous determination of six perylenequinones in Shiraia sp. Slf14 by HPLC. J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol 40(10):536–540. https://doi.org/10.1080/10826076.2017.1331172
Wu H, Lao XF, Wang QW, Lu RR, Shen C, Zhang F, Liu M, Jia L (1989) The shiraia chromes: novel fungal perylenequinone pigments from Shiraia bambusicola. J Nat Prod 52:948–951. https://doi.org/10.1021/np50065a006
Xiang XY, Zheng AF, Xie L (2011) Effect of different metal ions for submerged culture of Shiraia bambusicola. Chin Tradit Herbal Drugs 42:164–166. https://doi.org/10.1088/1009-0630/13/1/25
Xiang XY, Zhang ZX, Xie L, Zheng AF (2012) Study on fermentation hypocrellin by Shiraia bambusicolain submerged cultures. Guihaia 32(2):264–268. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-3142.2012.02.024
Xu YN, Zhong JJ (2012) Impacts of calcium signal transduction on the fermentation production of antitumor ganoderic acids by medicinal mushroom Ganoderma lucidum. Biotechnol Adv 30:1301–1308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2011.10.001
Yan R, Li X, Wang Y, Yu J, Zhang Z, Zhu D (2014) Chemical constituents of endophytic fungi Shiraia sp. Slf14 from Huperzia serrata and their antibacterial activity. Nat Prod Res Dev 26:1393–1397. https://doi.org/10.16333/j.1001-6880.2014.09.013
Yang H, Xiao C, Ma W, He G (2009) The production of hypocrellin colorants by submerged cultivation of the medicinal fungus Shiraia bambusicola. Dyes Pigments 82(2):142–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2008.12.012
Yang HL, Wang Y, Zhang ZB, Yan RM, Zhu D (2014) Whole-genome shotgun assembly and analysis of the genome of Shiraia sp. strain Slf14, a novel endophytic fungus producing huperzine A and hypocrellin A. Genome Announc 2:343–349. https://doi.org/10.1128/genomeA.00011-14
Zhao N, Lin X, Qi SS, Luo ZM, Chen SL, Yan SZ (2016) De Novo transcriptome assembly in Shiraia bambusicola to investigate putative genes involved in the biosynthesis of hypocrellin A. Int J Mol Sci 17(3):311. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17030311
Zhu D, Wang J, Zeng Q, Zhang Z, Yan R (2010) A novel endophytic Huperzine A-producing fungus, Shiraia sp. Slf14, isolated from Huperzia serrata. J Appl Microbiol 109(4):1469–1478. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2010.04777.x
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31460021) and Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province of China (Grant Nos. 20151BAB204002; 20151BAB204003; 20181BAB215044).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Z., Bao, J., Yang, H. et al. Transcriptome analysis on fructose as the sole carbon source enhancing perylenequinones production of endophytic fungus Shiraia sp. Slf14. 3 Biotech 10, 190 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-02181-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-02181-w