Abstract
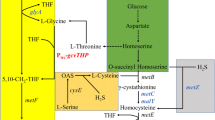
Microbial fermentation for L-methionine (L-Met) production based on natural renewable resources is attractive and challenging. In this work, the effects of medium composition and fermentation conditions were investigated to improve L-Met production by genetically engineered Escherichia coli MET-3. Statistical optimization techniques including Plackett–Burman (PB) design and Box–Behnken design (BBD) were adopted first to optimize the culture medium. Results of PB-designed experiments indicated that the culture medium components including glucose, yeast extract, KH2PO4, and MgSO4.7H2O had significant effects on L-Met biosynthesis. With their best-predicted concentration established by BBD (glucose 37.43 g/L, yeast extract 0.95 g/L, KH2PO4 1.82 g/L, and MgSO4.7H2O 4.51 g/L), L-Met titer was increased to 3.04 g/L from less than 2.0 g/L. For further enhancement of L-Met biosynthesis, the fermentation conditions of batch cultivation carried out in a 5-L fermentor were optimized, and the optimum results were obtained at an agitation rate of 300 rpm, medium pH of 7.0, and induction temperature of 28 °C. Based on the optimization parameters, fed-batch fermentation with the modified medium was conducted. As a result, great improvement of L-Met titer (12.80 g/L) and yield (0.13 mol/mol) were achieved, with an increase of 38.53% and 30.0% compared with those of the basal medium, respectively. Furthermore, higher L-Met productivity of 0.261 g/L/h was obtained, representing 2.13-fold higher in comparison to the original medium. The results may provide a helpful reference for further study on strain improvement and fermentation control.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asadi N, Zilouei H (2017) Optimization of organosolv pretreatment of rice straw for enhanced biohydrogen production using Enterobacter aerogenes. Bioresour Technol 227:335–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.12.073
Bicas JL, Barros FFC, Wagner R, Godoy HT, Pastore GM (2008) Optimization of R-(+)-α-terpineol production by the biotransformation of R-(+)-limonene. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 35:1061–1070. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-008-0383-0
Chen Y, Li D, Dai Z, Piao X, Wu Z, Wang B, Zhu Y, Zeng Z (2014) L-Methionine supplementation maintains the integrity and barrier function of the small-intestinal mucosa in post-weaning piglets. Amino Acids 46:1131–1142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-014-1675-5
Dayana Priyadharshini S, Bakthavatsalam AK (2016) Optimization of phenol degradation by the microalga Chlorella pyrenoidosa using Plackett–Burman design and response surface methodology. Bioresour Technol 207:150–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.01.138
Dischert W, Vasseur P, Figge R (2016) Microorganism for methionine production with improved methionine synthase activity and methionine efflux. United States Patent (US20160177352A1)
Duan X, Hu S, Qi X, Gu Z, Wu J (2017) Optimal extracellular production of recombinant Bacillus circulans β-galactosidase in Escherichia coli BL21(DE3). Process Biochem 53:17–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2016.11.008
Figge R, Soucaille P, Barbier G, Bestel-Corre G, Boisart C, Chateau M (2016) Increasing methionine yield. European Patent (EP2573189:B1)
Giancristofaro RA, Salmaso L (2007) Model performance analysis and model validation in logistic regression. Statistica 63:375–396. https://doi.org/10.6092/issn.1973-2201/358
Gomes J, Kumar D (2005) Production of L-methionine by submerged fermentation: a review. Enzyme Microb Technol 37:3–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2005.02.008
Hou FN, Mu TH, Ma MM, Blecker C (2019) Optimization of processing technology using response surface methodology and physicochemical properties of roasted sweet potato. Food Chem 278:136–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.11.034
Huang JF, Liu ZQ, Jin LQ, Tang XL, Shen ZY, Yin HH, Zheng YG (2017) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for microbial production of L-methionine. Biotechnol Bioeng 114:843–851. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.26198
Huang JF, Shen ZY, Mao QL, Zhang XM, Zhang B, Wu JS, Liu ZQ, Zheng YG (2018a) Systematic analysis of bottlenecks in a multibranched and multilevel regulated pathway: the molecular fundamentals of L-methionine biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. ACS Syn Biol 7:2577–2589. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.8b00249
Huang JF, Zhang B, Shen ZY, Liu ZQ, Zheng YG (2018b) Metabolic engineering of E. coli for the production of O-succinyl-L-homoserine with high yield. 3 Biotech 8:310. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-018-1332-x
Jankowski J, Kubińska M, Zduńczyk Z (2014) Nutritional and immunomodulatory function of methionine in poultry diets-a review. Ann Anim Sci 14:17–31. https://doi.org/10.2478/aoas-2013-0081
Kase H, Nakayama K (1975) L-Methionine production by methionine analog-resistant mutants of Corynebacterium glutamicum. Agr Biol Chem 39:153–160. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb1961.39.153
Kim YK, Kang DG, Choi SS, Kim JH, Chung JC, Cha HJ (2004) Co-expression of bacterial hemoglobin overrides high glucose-induced repression of foreign protein expression in Escherichia coli W3110. Biotechnol Lett 26:1173–1178. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BILE.0000035491.64912.84
Kumar D, Garg S, Bisaria VS, Sreekrishnan TR, Gomes J (2003) Production of methionine by a multi-analogue resistant mutant of Corynebacterium lilium. Process Biochem 38:1165–1171. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-9592(02)00287-X
Labbeiki G, Attar H, Heydarinasab A, Sorkhabadi S, Rashidi A (2014) Enhanced oxygen transfer rate and bioprocess yield by using magnetite nanoparticles in fermentation media of erythromycin. DARU J Pharm Sci 22:66. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40199-014-0066-5
Lee A, Choi KH, Yoon D, Kim S, Cha J (2017) Characterization of a thermostable glycoside hydrolase family 36 alpha-galactosidase from Caldicellulosiruptor bescii. J Biosci Bioeng 124:289–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2017.04.011
Li H, Wang BS, Li YR, Zhang L, Ding ZY, Gu ZH, Shi GY (2017) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli W3110 for the production of L-methionine. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 44:75–88. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-016-1870-3
Liu ZQ, Dong SC, Yin HH, Xue YP, Tang XL, Zhang XJ, He JY, Zheng YG (2017a) Enzymatic synthesis of an ezetimibe intermediate using carbonyl reductase coupled with glucose dehydrogenase in an aqueous-organic solvent system. Bioresour Technol 229:26–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.12.098
Liu ZQ, Wu L, Zhang XJ, Xue YP, Zheng YG (2017b) Directed evolution of carbonyl reductase from Rhodosporidium toruloides and its application in stereoselective synthesis of tert-butyl (3R,5S)-6-chloro-3,5-dihydroxyhexanoate. J Agr Food Chem 65:3721–3729. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b00866
Liu ZQ, Lu MM, Zhang XH, Cheng F, Xu JM, Xue YP, Jin LQ, Wang YS, Zheng YG (2018a) Significant improvement of the nitrilase activity by semi-rational protein engineering and its application in the production of iminodiacetic acid. Int J Biol Macromol 116:563–571. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.05.045
Liu ZQ, Wu L, Zheng L, Wang WZ, Zhang XJ, Jin LQ, Zheng YG (2018b) Biosynthesis of tert-butyl (3R,5S)-6-chloro-3,5-dihydroxyhexanoate by carbonyl reductase from Rhodosporidium toruloides in mono and biphasic media. Bioresour Technol 249:161–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.09.204
Ma L, Wang L, Tang J, Yang Z (2016) Optimization of arsenic extraction in rice samples by Plackett–Burman design and response surface methodology. Food Chem 204:283–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.02.126
Mampel J, Schröder H, Haefner S, Sauer U (2005) Single-gene knockout of a novel regulatory element confers ethionine resistance and elevates methionine production in Corynebacterium glutamicum. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 68:228–236. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-005-1893-6
Maresi E, Janson G, Fruncillo S, Paiardini A, Vallone R, Dominici P, Astegno A (2015) Functional characterization and structure-guided mutational analysis of the transsulfuration enzyme cystathionine-lyase from Toxoplasma gondii. Int J Mol Sci 19:1–19. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19072111
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31:426–428. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac60147a030
Mondal S, Das YB, Chatterjee SP (1996) Methionine production by microorganisms. Folia Microbiol 41:465–472. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02814659
Park SD, Lee JY, Sim SY, Kim Y, Lee HS (2007) Characteristics of methionine production by an engineered Corynebacterium glutamicum strain. Metab Eng 9:327–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2007.05.001
Plackett RL, Burman JP (1946) The design of optimum multifactorial experiments. Biometrika 33:305–325. https://doi.org/10.2307/2332195
Rahman Z, Zidan AS, Habib MJ, Khan MA (2010) Understanding the quality of protein loaded PLGA nanoparticles variability by Plackett–Burman design. Int J Pharm 389:186–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2009.12.040
Shahbazmohammad H, Omidinia E (2017) Medium optimization for improved production of dihydrolipohyl dehydrogenase from Bacillus sphaericus PAD-91 in Escherichia coli. Mol Biotechnol 59:260–270. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-017-0013-z
Sibanda W, Pretorius P (2012) Comparative study of the application Box Behnken design (BBD) and binary logistic regression (BLR) to study the effect of demographic characteristics on HIV risk in south Africa. JAMS 1:15–40. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13721-013-0032-z
Teleki A, Rahnert M, Bungart O, Gann B, Ochrombel I, Takors R (2017) Robust identification of metabolic control for microbial L-methionine production following an easy-to-use puristic approach. Metab Eng 41:159–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2017.03.008
Usuda Y, Kurahashi O (2005) Effects of deregulation of methionine biosynthesis on methionine excretion in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:3228–3234. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.71.6.3228-3234.2005
Wan M, Liu P, Xia J, Rosenberg JN, Oyler GA, Betenbaugh MJ, Nie Z, Qiu G (2011) The effect of mixotrophy on microalgal growth, lipid content, and expression levels of three pathway genes in Chlorella sorokiniana. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 91:835–844. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3399-8
Wang XX, Lin CP, Zhang XJ, Liu ZQ, Zheng YG (2018) Improvement of a newly cloned carbonyl reductase and its application to biosynthesize chiral intermediate of duloxetine. Process Biochem 70:124–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2018.04.010
Weissbach H, Brot N (1991) Regulation of methionine synthesis in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol 5:1593–1597. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01905.x
Willke T (2014) Methionine production-a critical review. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:9893–9914. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-6156-y
Ye Z, Wang W, Yuan Q, Ye H, Sun Y, Zhang H, Zeng X (2016) Box–Behnken design for extraction optimization, characterization and in vitro antioxidant activity of Cicer arietinum L. hull polysaccharides. Carbohydr Polym 147:354–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.03.092
Zhang X, Zhao T, Cheng T, Liu X, Zhang H (2012) Rapid resolution liquid chromatography (RRLC) analysis of amino acids using pre-column derivatization. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 906:91–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2012.08.030
Zheng YG, Yin HH, Yu DF, Chen X, Tang XL, Zhang XJ, Xue YP, Wang YJ, Liu ZQ (2017) Recent advances in biotechnological applications of alcohol dehydrogenases. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101:987–1001. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-8083-6
Zou SP, Zhong W, Xia CJ, Gu YN, Niu K, Zheng YG, Shen YC (2015) Mutagenesis breeding of high echinocandin B producing strain and further titer improvement with culture medium optimization. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 38:1845–1854. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-015-1425-4
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31500031), the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (No. LQ14B060004), and the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang University of Technology (No. 2012XY010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that they have no competing interests.
Ethical statement
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, HY., Wu, WJ., Niu, K. et al. Enhanced L-methionine production by genetically engineered Escherichia coli through fermentation optimization. 3 Biotech 9, 96 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-019-1609-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-019-1609-8