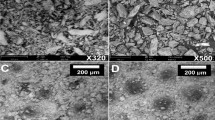
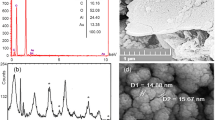
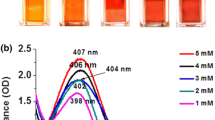
Abstract
Hydroxyapatite nanoparticles have been demonstrated as eminent nanomaterials because of their upgraded bioactivity, non-toxicity and biocompatibility properties. In this current examination, an upgraded wound healing activity of bioactive metabolites of medicinal polyherbal formulation Triphala fabricated hydroxyapatite nanocomposite was explored utilising in vivo excision wound Wistar rat model. Antibacterial activity of nanocomposite was studied against human pathogenic bacterial strains Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. Nanofabrication of the nanocomposite on wound dressing material and its antibacterial activity was additionally examined. Metabolites were extricated from Triphala utilising ethanol, and the extracted metabolites were fabricated with nano-hydroxyapatite utilising green science standards as profoundly stable hydroxyapatite nanocomposite. An ointment prepared from the synthesised nanocomposite was assessed for in vivo wound healing on excision wound created in a Wistar rat model. Nanocomposite treatment has shown complete wound-healing activity on the 21st day by recording all signs of the healing mechanism. Synthesised nanocomposite reveals growth inhibition of both the tested bacterial strains by showing zone of inhibition, biofilm inhibition. Antibacterial activity was also studied with nanocomposite, fabricated on dressing material which reveals the fabricated material inhibited the growth of the tested bacterial pathogenic strains. The current investigation proposes the possible use of phytonanotechnology standards as a successful course of wound mending and restraint of twisted disease without the help of manufactured antimicrobials.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afshar A, Ghorbani M, Ehsani N, Saeri MR, Sorrell CC (2003) Some important factors in the wet precipitation process of hydroxyapatite. Mater Des 24:197–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0261-3069(03)00003-7
Bjarnsholt T (2013) The role of bacterial biofilms in chronic infections. APMIS Suppl 121:1–51. https://doi.org/10.1111/apm.12099
Boudemagh D, Venturini P, Fleutot S, Cleymand F (2019) Elaboration of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles and chitosan/hydroxyapatite composites: a present status. Polym Bull 76:2621–2653. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-018-2483-y
Cefalu JE, Barrier KM, Davis AH (2017) Wound infections in critical care. Crit Care Nurs Clin North Am 29:81–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cnc.2016.09.009
Chakrabarti S, Chattopadhyay P, Islam J, Ray S, Raju PS, Mazumder B (2018) Aspects of Nanomaterials in Wound Healing. Curr Drug Deliv 16:26–41. https://doi.org/10.2174/1567201815666180918110134
Eming SA, Martin P, Tomic-Canic M (2014) Wound repair and regeneration: Mechanisms, signaling, and translation. Sci Transl Med. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3009337
Evelhoch SR (2020) Biofilm and Chronic Nonhealing Wound Infections. Surg Clin North Am 100:727–732. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.suc.2020.05.004
Geuli O, Metoki N, Zada T, Reches M, Eliaz N, Mandler D (2017) Synthesis, coating, and drug-release of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles loaded with antibiotics. J Mater Chem B 5:7819–7830. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7tb02105d
Hajialyani M, Tewari D, Sobarzo-Sánchez E, Nabavi SM, Farzaei MH, Abdollahi M (2018) Natural product-based nanomedicines for wound healing purposes: Therapeutic targets and drug delivery systems. Int J Nanomed 13:5023–5043. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S174072
Hamdan S, Pastar I, Drakulich S, Dikici E, Tomic-Canic M, Deo S, Daunert S (2017) Nanotechnology-driven therapeutic interventions in wound healing: potential uses and applications. ACS Cent Sci 3:163–175. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscentsci.6b00371
Kawai K, Larson BJ, Ishise H, Carre AL, Nishimoto S, Longaker M, Lorenz HP (2011) Calcium-based nanoparticles accelerate skin wound healing. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0027106
Koppikar SJ, Jagtap SD, Devarshi PP, Jangle NM, Awad VB, Wele AA, Harsulkar AM (2014) Triphala, an Ayurvedic formulation improves the antioxidant status on TNBS induced IBD in rats. Eur J Integr Med 6:646–656. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eujim.2014.08.005
Kumar MS, Kirubanandan S, Sripriya R, Sehgal PK (2008) Triphala Promotes Healing of Infected Full-Thickness Dermal Wound. J Surg Res 144:94–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2007.02.049
Lazić S, Zec S, Miljević N, Milonjić S (2001) The Effect of temperature on the properties of hydroxyapatite precipitated from calcium hydroxide and phosphoric acid. Thermochim Acta 374:13–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-6031(01)00453-1
Leaper D, Assadian O, Edmiston CE (2015) Approach to chronic wound infections. Br J Dermatol 173:351–358. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjd.13677
Ma XY, Tian LX, Liang HP (2016) Early prevention of trauma-related infection/sepsis. Mil Med Res 3:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40779-016-0104-3
Mahalunkar S, Yadav AS, Gorain M, Pawar V, Braathen R, Weiss S, Bogen B, Gosavi SW, Kundu GC (2019) Functional design of pH-responsive folate-targeted polymer-coated gold nanoparticles for drug delivery and in vivo therapy in breast cancer. Int J Nanomedicine 14:8285–8302. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S215142
Mondal S, Bardhan R, Mondal B, Dey A, Mukhopadhyay SS, Roy S, Guha R, Roy K (2012) Synthesis, characterisation and in vitro cytotoxicity assessment of hydroxyapatite from different bioresources for tissue engineering application. Bull Mater Sci 35:683–691
Panda NN, Pramanik K, Sukla LB (2014) Extraction and characterisation of biocompatible hydroxyapatite from fresh water fish scales for tissue engineering scaffold. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 37:433–440. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-013-1009-0
Patra JK, Das G, Fraceto LF, Campos EVR, Rodriguez-Torres MDP, Acosta-Torres LS, Diaz-Torres LA, Grillo R, Swamy MK, Sharma S, Habtemariam S, Shin HS (2018) Nano based drug delivery systems: Recent developments and future prospects. J Nanobiotechnology 16:71. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-018-0392-8
Pires DP, Melo LDR, Vilas Boas D, Sillankorva S, Azeredo J (2017) Phage therapy as an alternative or complementary strategy to prevent and control biofilm-related infections. Curr Opin Microbiol 39:48–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mib.2017.09.004
Shanmugasundaram T, Radhakrishnan M, Gopikrishnan V, Kadirvelu K, Balagurunathan R (2017) In vitro antimicrobial and in vivo wound healing effect of actinobacterially synthesised nanoparticles of silver, gold and their alloy. RSC Adv 7:51729–51743. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra08483h
Wang P, Li C, Gong H, Jiang X, Wang H, Li K (2010) Effects of synthesis conditions on the morphology of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles produced by wet chemical process. Powder Technol 203:315–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2010.05.023
Zeng R, Lin C, Lin Z, Chen H, Lu W, Lin C, Li H (2018) Approaches to cutaneous wound healing: basics and future directions. Cell Tissue Res 374:217–232. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-018-2830-1
Zhang W, Chai Y, Xu X, Wang Y, Cao N (2014) Rod-shaped hydroxyapatite with mesoporous structure as drug carriers for proteins. Appl Surf Sci 322:71–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.10.064
Zhou H, Yang M, Hou S, Deng L (2017) Mesoporous hydroxyapatite nanoparticles hydrothermally synthesised in aqueous solution with hexametaphosphate and tea polyphenols. Mater Sci Eng C 71:439–445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2016.10.040
Acknowledgements
Thanks to Dr Hari Hara Sivakumar, Professor, Department of Pharmacology, KMCH College of Pharmacy, Coimbatore, and Tamil Nadu, for assisting in animal model studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Animal model studies was followed by the rules of the Committee for Control and Supervision of Experiments on Rats (CPCSEA), and the convention was affirmed by the Institutional Animal Ethics Committee (IAEC No: KMCRET/B, TECH/01/2017-18).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Namasivayam, S.K.R., Venkatachalam, G. & Bharani, R.S.A. Noteworthy enhancement of wound-healing activity of triphala biomass metabolite-loaded hydroxyapatite nanocomposite. Appl Nanosci 11, 1511–1530 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-021-01813-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-021-01813-8