Abstract
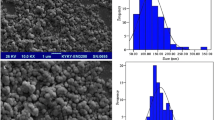
Tacrolimus as an immunosuppressive drug shows poor solubility in aqueous media, accompanied by a low/variable bioavailability in peroral administration due to its high first-pass metabolism. Therefore, in this study, drug-loaded chitosan-coated nanostructured lipid carriers (CCNLCs) were prepared to overcome these limitations. Tacrolimus-loaded NLCs were prepared via solvent displacement technique and were optimized. Stearic acid (SA) and glyceryl mono stearate (GMS) were used as solid lipids, oleic acid (OA) and tween 80 were used as liquid lipid and stabilizer, respectively, in the structure of NLC. The prepared nanoparticles were characterized by size and zeta potential measurements, drug loading determinations, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) analysis. Release profile of tacrolimus from NLCs and CCNLCs was also studied. The results indicated the effect of some preparation parameters on particle size as a dependent parameter. The selected formulations had particle sizes under 100 nm. Conversion of negative zeta potential of NLCs into positive quantities in CCNLCs was attributed to the effect of chitosan coating. SEM images of nanocarriers proved nanoscale dimensions and FTIR analysis showed no unwanted chemical reactions between drug and excipients. NLCs and CCNLCs released the drug in a sustained release pattern. However, chitosan-coating attenuated the burst effect and caused more extended release. The results of this study demonstrated formation of tacrolimus-loaded NLCs and coating them with chitosan with desirable characteristics. These findings suggested that this carrier is a good candidate to overcome serious bioavailability problems of common peroral formulations of tacrolimus.







Similar content being viewed by others
Code availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- NLC:
-
Nanostructured lipid carriers
- CCNLCs:
-
Chitosan-coated nanostructured lipid carriers
- SA:
-
Stearic acid
- GMS:
-
Glyceryl mono stearate
- OA:
-
Oleic acid
- SEM:
-
Scanning electron microscopy
- FTIR:
-
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy
- BCS:
-
Biopharmaceutical classification system
- PEG:
-
Polyethylene glycol
- DLE:
-
Drug-loading efficiency
- EE:
-
Entrapment efficiency
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- HLB:
-
Hydrophilic–lipophilic balance
References
Abdelhamid HN, Wu H-F (2013) Multifunctional graphene magnetic nanosheet decorated with chitosan for highly sensitive detection of pathogenic bacteria. J Mater Chem B 1:3950–3961
Abdelhamid HN, El-Bery HM, Metwally AA et al (2019) Synthesis of CdS-modified chitosan quantum dots for the drug delivery of Sesamol. Carbohydr Polym 214:90–99
Alshamsan A, Binkhathlan Z, Kalam MA et al (2020) Mitigation of tacrolimus-associated nephrotoxicity by PLGA nanoparticulate delivery following multiple dosing to mice while maintaining its immunosuppressive activity. Sci Rep 10:6675. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-63767-1
Andonova V, Peneva P (2017) Characterization methods for solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) and nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC). Curr Pharm Des 23:6630–6642
Arima H, Yunomae K, Hirayama F, Uekama K (2001) Contribution of P-glycoprotein to the enhancing effects of dimethyl-β-cyclodextrin on oral bioavailability of tacrolimus. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 297:547–555
Baghel S, Cathcart H, O’Reilly NJ (2016) Polymeric amorphous solid dispersions: a review of amorphization, crystallization, stabilization, solid-state characterization, and aqueous solubilization of biopharmaceutical classification system class II drugs. J Pharm Sci 105:2527–2544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xphs.2015.10.008
Barbarino JM, Staatz CE, Venkataramanan R et al (2013) PharmGKB summary: cyclosporine and tacrolimus pathways. Pharmacogenet Genom 23:563–585. https://doi.org/10.1097/FPC.0b013e328364db84
Bohrey S, Chourasiya V, Pandey A (2016) Polymeric nanoparticles containing diazepam: preparation, optimization, characterization, in-vitro drug release and release kinetic study. Nano Converg 3:1–7
Brooke D, Washkuhn RJ (1977) Zero-order drug delivery system: theory and preliminary testing. J Pharm Sci 66:159–162
Bunjes H, Koch MHJ, Westesen K (2002) Effects of surfactants on the crystallization and polymorphism of lipid nanoparticles. In: Lagaly G (ed) Molecular organisation on interfaces. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 7–10
Busuttil RW, McDiarmid S, Klintmalm GB, Goldstein R, Miller CM, Schwartz M, Shaw BW (1994) A comparison of tacrolimus (FK 506) and cyclosporine for immunosuppression in liver transplantation. N Engl J Med 331:1110–1115. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199410273311702
Costa P, Lobo JMS (2001) Modeling and comparison of dissolution profiles. Eur J Pharm Sci 13:123–133
Cui Z, Xiang Y, Si J et al (2008) Ionic interactions between sulfuric acid and chitosan membranes. Carbohydr Polym 73:111–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2007.11.009
Dai Y, Zhou R, Liu L et al (2013) Liposomes containing bile salts as novel ocular delivery systems for tacrolimus (FK506): in vitro characterization and improved corneal permeation. Int J Nanomed 8:1921
Dharmala K, Yoo JW, Lee CH (2008) Development of chitosan–SLN microparticles for chemotherapy: in vitro approach through efflux-transporter modulation. J Control Release 131:190–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2008.07.034
Dowaidar M, Nasser Abdelhamid H, Hällbrink M et al (2018) Chitosan enhances gene delivery of oligonucleotide complexes with magnetic nanoparticles–cell-penetrating peptide. J Biomater Appl 33:392–401
Drabczyk A, Kudłacik-Kramarczyk S, Głąb M et al (2020) Physicochemical investigations of chitosan-based hydrogels containing Aloe Vera designed for biomedical use. Materials (Basel) 13:3073
Du Q, Chen J, Yan G et al (2019) Comparison of different aliphatic acid grafted N-trimethyl chitosan surface-modified nanostructured lipid carriers for improved oral kaempferol delivery. Int J Pharm 568:118506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.118506
Ebrahimi HA, Javadzadeh Y, Hamidi M, Jalali MB (2015) Repaglinide-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles: effect of using different surfactants/stabilizers on physicochemical properties of nanoparticles. DARU J Pharm Sci. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40199-015-0128-3
Ebrahimi HA, Javadzadeh Y, Hamidi M, Barzegar Jalali M (2016) Development and characterization of a novel lipohydrogel nanocarrier: repaglinide as a lipophilic model drug. J Pharm Pharmacol. https://doi.org/10.1111/jphp.12537
Fasili Z, Mehri F, Ebrahimi HA et al (2019) Applying nanoparticles in the treatment of viral infections and toxicological considerations. Pharm Biomed Res 5:1–20. https://doi.org/10.18502/pbr.v5i4.2392
Floren LC, Bekersky I, Benet LZ et al (1997) Tacrolimus oral bioavailability doubles with coadministration of ketoconazole. Clin Pharmacol Ther 62:41–49
Fonseca-Santos B, Silva PB, Rigon RB et al (2020) Formulating SLN and NLC as innovative drug delivery systems for non-invasive routes of drug administration. Curr Med Chem 27:3623–3656
Gibaldi M, Feldman S (1967) Establishment of sink conditions in dissolution rate determinations. Theoretical considerations and application to nondisintegrating dosage forms. J Pharm Sci 56:1238–1242. https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.2600561005
Gouda R, Baishya H, Qing Z (2017) Application of mathematical models in drug release kinetics of carbidopa and levodopa ER tablets. J Dev Drugs 6:1–8
Higuchi T (1963) Mechanism of sustained-action medication. Theoretical analysis of rate of release of solid drugs dispersed in solid matrices. J Pharm Sci 52:1145–1149
Hixson AW, Crowell JH (1931) Dependence of reaction velocity upon surface and agitation. Ind Eng Chem 23:923–931
Hu F-Q, Jiang S-P, Du Y-Z et al (2005) Preparation and characterization of stearic acid nanostructured lipid carriers by solvent diffusion method in an aqueous system. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 45:167–173
Jain S, Addan R, Kushwah V et al (2019) Comparative assessment of efficacy and safety potential of multifarious lipid based tacrolimus loaded nanoformulations. Int J Pharm 562:96–104
Kadir MFZ, Aspanut Z, Majid SR, Arof AK (2011) FTIR studies of plasticized poly(vinyl alcohol)–chitosan blend doped with NH4NO3 polymer electrolyte membrane. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 78:1068–1074. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2010.12.051
Kang J-H, Chon J, Kim Y-I et al (2019) Preparation and evaluation of tacrolimus-loaded thermosensitive solid lipid nanoparticles for improved dermal distribution. Int J Nanomed 14:5381
Khan S, Shaharyar M, Fazil M et al (2016a) Tacrolimus-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers for oral delivery—optimization of production and characterization. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 108:277–288
Khan S, Shaharyar M, Fazil M et al (2016b) Tacrolimus-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers for oral delivery-in vivo bioavailability enhancement. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 109:149–157
Khan S, Ganguli M, Aditya A et al (2019) Improved in vivo performance and immunomodulatory effect of novel Omega-3 fatty acid based tacrolimus nanostructured lipid carrier. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 52:138–149
Korsmeyer RW, Gurny R, Doelker E et al (1983) Mechanisms of solute release from porous hydrophilic polymers. Int J Pharm 15:25–35
Kovacevic A, Savic S, Vuleta G et al (2011) Polyhydroxy surfactants for the formulation of lipid nanoparticles (SLN and NLC): effects on size, physical stability and particle matrix structure. Int J Pharm 406:163–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2010.12.036
Kovačević AB, Müller RH, Keck CM (2020) Formulation development of lipid nanoparticles: improved lipid screening and development of tacrolimus loaded nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC). Int J Pharm 576:118918
Lamprecht A, Yamamoto H, Takeuchi H, Kawashima Y (2005) A pH-sensitive microsphere system for the colon delivery of tacrolimus containing nanoparticles. J Control release 104:337–346
Langenbucher F (1972) Letters to the editor: linearization of dissolution rate curves by the Weibull distribution. J Pharm Pharmacol 24:979–981
Ling Tan JS, Roberts CJ, Billa N (2019) Mucoadhesive chitosan-coated nanostructured lipid carriers for oral delivery of amphotericin B. Pharm Dev Technol 24:504–512
Luo Q, Zhao J, Zhang X, Pan W (2011) Nanostructured lipid carrier (NLC) coated with chitosan oligosaccharides and its potential use in ocular drug delivery system. Int J Pharm 403:185–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2010.10.013
Meissner Y, Pellequer Y, Lamprecht A (2006) Nanoparticles in inflammatory bowel disease: particle targeting versus pH-sensitive delivery. Int J Pharm 316:138–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2006.01.032
Nam SH, Ji XY, Park J-S (2011) Investigation of tacrolimus loaded nanostructured lipid carriers for topical drug delivery. Bull Korean Chem Soc 32:956–960
Nasab SH, Amani A, Ebrahimi HA, Hamidi AA (2020) Design and preparation of a new multi-targeted drug delivery system using multifunctional nanoparticles for co-delivery of siRNA and paclitaxel. J Pharm Anal. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpha.2020.04.005
Nassar T, Rom A, Nyska A, Benita S (2009) Novel double coated nanocapsules for intestinal delivery and enhanced oral bioavailability of tacrolimus, a P-gp substrate drug. J Control Release 133:77–84
Natarajan J, Baskaran M, Humtsoe LC et al (2017) Enhanced brain targeting efficacy of olanzapine through solid lipid nanoparticles. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 45:364–371
Noor NM, Sheikh K, Somavarapu S, Taylor KMG (2017) Preparation and characterization of dutasteride-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers coated with stearic acid-chitosan oligomer for topical delivery. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 117:372–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2017.04.012
Osman Z, Arof AK (2003) FTIR studies of chitosan acetate based polymer electrolytes. Electrochim Acta 48:993–999. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0013-4686(02)00812-5
Paul DR, McSpadden SK (1976) Diffusional release of a solute from a polymer matrix. J Membr Sci 1:33–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0376-7388(00)82256-5
Pyo Y-C, Tran P, Kim D-H, Park J-S (2020) Chitosan-coated nanostructured lipid carriers of fenofibrate with enhanced oral bioavailability and efficacy. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 196:111331
Rangaraj N, Pailla SR, Shah S et al (2020) QbD aided development of ibrutinib-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers aimed for lymphatic targeting: evaluation using chylomicron flow blocking approach. Drug Deliv Transl Res 10:1476–1494
Ryšánek P, Grus T, Šíma M, Slanař O (2020) Lymphatic transport of drugs after intestinal absorption: impact of drug formulation and physicochemical properties. Pharm Res 37:1–17
Sakai M, Hobara N, Hokama N et al (2004) Increased bioavailability of tacrolimus after rectal administration in rats. Biol Pharm Bull 27:1480–1482
Salem SG, Gardouh AR, Gad S (2020) Parameter optimization of solid lipid nanoparticles formulation. Rec Pharm Biomed Sci 4:1–7. https://doi.org/10.21608/rpbs.2020.23041.1050
Savić V, Ilić T, Nikolić I et al (2019) Tacrolimus-loaded lecithin-based nanostructured lipid carrier and nanoemulsion with propylene glycol monocaprylate as a liquid lipid: formulation characterization and assessment of dermal delivery compared to referent ointment. Int J Pharm 569:118624
Shah P, Chavda K, Vyas B, Patel S (2020) Formulation development of linagliptin solid lipid nanoparticles for oral bioavailability enhancement: role of P-gp inhibition. Drug Deliv Transl Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13346-020-00839-9
Shazly GA (2017) Ciprofloxacin controlled-solid lipid nanoparticles: characterization, in vitro release, and antibacterial activity assessment. Biomed Res Int 2017
Shin S-B, Cho H-Y, Kim D-D et al (2010) Preparation and evaluation of tacrolimus-loaded nanoparticles for lymphatic delivery. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 74:164–171
Sikma MA, Hunault CC, Van Maarseveen EM et al (2020) High variability of whole-blood tacrolimus pharmacokinetics early after thoracic organ transplantation. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 45:123–134. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13318-019-00591-7
Sznitowska M, Wolska E, Baranska H et al (2017) The effect of a lipid composition and a surfactant on the characteristics of the solid lipid microspheres and nanospheres (SLM and SLN). Eur J Pharm Biopharm 110:24–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2016.10.023
Tan JSL, Roberts C, Billa N (2020) Pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution of an orally administered mucoadhesive chitosan-coated amphotericin B-Loaded nanostructured lipid carrier (NLC) in rats. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed 31:141–154
Trotta M, Debernardi F, Caputo O (2003) Preparation of solid lipid nanoparticles by a solvent emulsification–diffusion technique. Int J Pharm 257:153–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-5173(03)00135-2
Tuteja S, Alloway RR, Johnson JA, Gaber AO (2001) The effect of gut metabolism on tacrolimus bioavailability in renaltransplant recipients1, 2. Transplantation 71:1303–1307
Tyliszczak B, Drabczyk A, Kudłacik-Kramarczyk S et al (2017) Preparation and cytotoxicity of chitosan-based hydrogels modified with silver nanoparticles. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 160:325–330
Tyliszczak B, Drabczyk A, Kudłacik-Kramarczyk S et al (2019) In vitro biosafety of pro-ecological chitosan-based hydrogels modified with natural substances. J Biomed Mater Res Part A 107:2501–2511
Vishwakarma N, Jain A, Sharma R et al (2019) Lipid-based nanocarriers for lymphatic transportation. AAPS PharmSciTech 20:1–13
Wagner JG (1985) Propranolol: pooled Michaelis-Menten parameters and the effect of input rate on bioavailability. Clin Pharmacol Ther 37:481–487
Wang Y, Sun J, Zhang T et al (2011) Enhanced oral bioavailability of tacrolimus in rats by self-microemulsifying drug delivery systems. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 37:1225–1230
Weiss J, Decker EA, McClements DJ et al (2008) Solid lipid nanoparticles as delivery systems for bioactive food components. Food Biophys 3:146–154. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-008-9065-8
Wu Q, Liu D, Zhang X et al (2019) Development and effects of tacrolimus-loaded nanoparticles on the inhibition of corneal allograft rejection. Drug Deliv 26:290–299. https://doi.org/10.1080/10717544.2019.1582728
Yu M, Yuan W, Li D et al (2019) Predicting drug release kinetics from nanocarriers inside dialysis bags. J Control Release 315:23–30
Funding
This work was funded by Dean of Research, Ardabil University of Medical Sciences as a PharmD thesis number 527. The authors would like to appreciate from this support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SD and MA carried out the experiments and collected the data. HAE conceived the idea of this study, supervised the experiments and wrote the manuscript and GB performed the experimental analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
This research was approved by ethical committee of Ardabil University of Medical Sciences under the Approval ID: IR.ARUMS.REC.1398.292.
Availability of data and material
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dasineh, S., Akbarian, M., Ebrahimi, H.A. et al. Tacrolimus-loaded chitosan-coated nanostructured lipid carriers: preparation, optimization and physicochemical characterization. Appl Nanosci 11, 1169–1181 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-021-01744-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-021-01744-4