Abstract
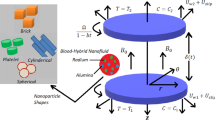
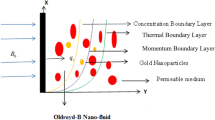
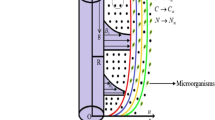
Currently, researchers across the world achieved theoretical and experimental works to investigate the significance of nanofluid due to their diverse application in heat transport phenomena. Nanofluids are actually the suspension of nanoparticles in the base liquid. Embedding nanoparticles in the base fluid enhances thermal conductivity and heat transfer rate. The present article shed light on the influence of gold nanoparticles along with oxytactic microorganisms on radiative Reiner–philippoff fluid due to extendable sheet. Suitable transformation convert the partial differential equations (PDEs) are renovated into nonlinear ordinary differential equations (ODEs) and furthermore tackled these equations numerically via bvp4c Matlab builtin scheme. Further the investigations are carried out in the presence of molecular diffusivity, oxytactic microorganisms and nonlinear thermal radiation. The effect of influential parameters on heat transfer, mass transfer, motile density of microorganisms profile are investigated with the assistance of tables and graphs. Embedding the nanoparticles and nonlinear thermal radiation amplifies the heat transfer process and motile density profile depreciates owing to an augmentation in Peclet number. The novel outcomes of this investigation will advance the field of nanomaterials.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
The data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
Abbreviations
- C :
-
Concentration of fluid
- \(C_{0}\) :
-
Wall concentration
- \(C_{\infty }\) :
-
Ambient concentration
- \(\gamma\) :
-
Bingham number
- \(Sc\) :
-
Schmidt number
- \(Nu _{x}\) :
-
Nusselt number
- \(Pr\) :
-
Prandtl number
- \(\theta _{w}\) :
-
Temperature ratio parameter
- \(\tau\) :
-
Shear stress
- \(\mu _{0}\) :
-
Shear viscosity
- \(\rho _{nf}\) :
-
Bio-nanofluid density
- \(c_{p}\) :
-
Specific heat at constant pressure
- \(\rho _{b}\) :
-
Density of the blood
- \((\rho C_{p})_{b}\) :
-
Heat capacity of blood
- \(k_{b}\) :
-
Thermal conductivity of blood
- \(\sigma ^{*}\) :
-
Stefan-Boltzmann constant
- \(\epsilon\) :
-
Variable molecular diffusivity parameter
- \(D_{B_{\infty }}\) :
-
Ambient Brownian diffusion coefficient
- \(T_{\infty }\) :
-
Ambient temperature
- U(x):
-
Stretching velocity
- \(\lambda\) :
-
Fluid parameter
- \(q_{w}\) :
-
Surface heat flux
- \(Sh _{x}\) :
-
Sherwood number
- Rd :
-
Radiation parameter
- \(q_{r}\) :
-
Radiative heat flux
- \(\tau _{s}\) :
-
Reference shear stress
- \(\mu _{\infty }\) :
-
Limiting viscosity
- \(\alpha _{nf}\) :
-
Bio-nanofluid thermal diffusivity
- \(k_{nf}\) :
-
Bio-nanofluid thermal conductivity
- \(\rho _{g}\) :
-
Densities of the gold
- \((\rho C_{p})_{g}\) :
-
Heat capacity of gold
- \(k_{g}\) :
-
Thermal conductivity of gold
- \(\kappa ^{*}\) :
-
Absorption coefficient
References
Abdelmalek Z, Khan SU, Waqas H, Nabwey HA, Tlili I (2020) Utilization of second order slip, activation energy and viscous dissipation consequences in thermally developed flow of third grade nanofluid with gyrotactic microorganisms. Symmetry 12(2):309
Ahmad A (2016) Flow of reinerphilippoff based nano-fluid past a stretching sheet. J Mol Liquids 219:643–646
Ahmed A, Khan M, Hafeez A, Ahmed J (2020) Thermal analysis in unsteady radiative Maxwell nanofluid flow subject to heat source/sink. Applied Nanoscience. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-020-01431-w
Ahmed A, Khan M, Irfan M, Ahmed J (2020) Transient mhd flow of Maxwell nanofluid subject to nonlinear thermal radiation and convective heat transport. Appl Nanosci https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-020-01375-1
Aladdin NAL, Bachok N, Pop I (2020) \(Cu-Al_{2}O_{3}\)/water hybrid nanofluid flow over a permeable moving surface in presence of hydromagnetic and suction effects. Alexandria Eng J 59:657–666
Al-Khaled Kamel, Khan Sami Ullah, Khan Ilyas (2020) Chemically reactive bioconvection flow of tangent hyperbolic nanoliquid with gyrotactic microorganisms and nonlinear thermal radiation. Heliyon 66(1):e03117
Alzahrani Ebraheem O, Shah Zahir, Dawar Abdullah, Malebary Sharaf J (2019) Hydromagnetic mixed convective third grade nanomaterial containing gyrotactic microorganisms toward a horizontal stretched surfaceHydromagnetic mixed convective third grade nanomaterial containing gyrotactic microorganisms toward a horizontal stretched surface. Alexandria Eng J 58(4):1421–1429
Bhatti MM, Sheikholeslami M, Shahid A, Hassan M, Abbas T (2019) Entropy generation on the interaction of nanoparticles over a stretched surface with thermal radiation. Coll Surf A 570:368–376
Buschmann MH, Azizian R, Kempe T, Julia JE, Martinez-Cuenca R, Sunden B, Wu Z, Seppala A, Ala-Nissila T (2018) Correct interpretation of nanofluid convective heat transfer. Int J Thermal Sci 129:504–531
Chakraborty Tanmoy, Das Kalidas, Kundu Prabir Kumar (2018) Framing the impact of external magnetic field on bioconvection of a nanofluid flow containing gyrotactic microorganisms with convective boundary conditions. Alexandria Eng J 57(1):661–71
Eid MR (2020) Effects of NP shapes on non-Newtonian bio-nanofluid flow in suction/blowing process with convective condition: Sisko model. J Non-Equilibrium Thermodyn 45(2):97–108
Gangadhar K, Vijayakumar D, Chamkha AJ, Kannan T, Sakthivel G (2020) Effects of newtonian heating and thermal radiation on micropolar ferrofluid flow past a stretching surface: Spectral quasi-linearization method. Heat Transfer 49:838–857
Ghosh S, Mukhopadhyay S, Hayat T (2018) Couple stress effects on three dimensional flow of magnetite-water based nanofluid over an extended surface in presence of non-linear thermal radiation. Int J Appl Comput Math 4:11
Gireesha BJ, Archana M, Prasannakumara BC, Gorla RS, Makinde OD (2017) MHD three dimensional double diffusive flow of Casson nanofluid with buoyancy forces and nonlinear thermal radiation over a stretching surface. International Journal of Numerical Methods for Heat and Fluid Flow 27: https://doi.org/10.1108/HFF-01-2017-0022
Hayat T, Khan WA, Abbas SZ, Nadeem S, Ahmad S (2020) Impact of induced magnetic field on second-grade nanofluid flow past a convectively heated stretching sheet. Appl Nanosci 10:3001–3009
Irfan M, Rafiq K, Khan WA, Khan M (2020) Numerical analysis of unsteady Carreau nanofluid flow with variable conductivity. Appl Nanosci 10:3075–3084
Jamshed W, Aziz A (2018) Cattaneo-Christov based study of \({TiO_{2}}/{CuO}/{EG}\) Casson hybrid nanofluid flow over a stretching surface with entropy generation. Appl Nanosci 8:685–698
Jyothi K, Reddy PK, Reddy M, Reddy S, Prabhavathi B (2020) Impact of slip effects on unsteady Sisko nanoliquid heat and mass transfer characteristics over stretching sheet filled with gold nanoparticles. Heat Transfer 49:2103–2130
Khan M, Irfan M, Khan WA (2017) Impact of nonlinear thermal radiation and gyrotactic microorganisms on the magneto-burgers nanofluid. Int J Mech Sci 130:375–382
Khan A, Khan D, Khan I, Ali F, Karim F, Imran M (2018) MHD flow of sodium alginate-based Casson type nanofluid passing through a porous medium with Newtonian heating. Sci Rep 8:8645
Khashi NS, Arifin MD, Pop I, Roslinda Nazar R, Hafidzuddin EH, Wahi N (2020) Three-dimensional hybrid nanofluid flow and heat transfer past a permeable stretching/shrinking sheet with velocity slip and convective condition. Chinese Journal of Physics, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjph.2020.03.032,
Koriko OK, Animasaun IL, Reddy N, Sandeep MG (2017) Scrutinization of thermal stratification, nonlinear thermal radiation and quartic autocatalytic chemical reaction effects on the flow of three-dimensional Eyring-Powell alumina-water nanofluid. Multidiscipline Modeling Materials Struct 14:261–283
Koriko OK, Animasaun IL, Mahanthesh B, Saleem S, Sarojamma G, Sivaraj R (2018) Heat transfer in the flow of Blood-Gold Carreau nanofluid induced by partial slip and buoyancy. Heat Transf-Asian Res 47(6):806–823
Kumar PB, Gireesha BJ, Gorla RSR, Mahanthesh B (2017) Magnetohydrodynamic flow of Williamson nanofluid due to an exponentially stretching surface in the presence of thermal radiation and chemical reaction. J Nanofluids 6(2):264–272
Mabood F, Yusuf TA, Khan WA (2020) \(Cu-Al_{2}o_{3}-H_{2}O\) hybrid nanofluid flow with melting heat transfer, irreversibility analysis and nonlinear thermal radiation. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09720-w
Mahanthesh B, Gireesha BJ, Animasaun IL, Muhammad Taseer, Shashikumar NS (2019) Mhd flow of swcnt and mwcnt nanoliquids past a rotating stretchable disk with thermal and exponential space dependent heat source. Phys Scripta 94(8):085214
Mondal Surya Kanta, Pal Dulal (2020) Computational analysis of bioconvective flow of nanofluid containing gyrotactic microorganisms over a nonlinear stretching sheet with variable viscosity using ham. J Comput Design Eng 7(2):251–267
Myers Tim G, Helena Ribera, Vincent Cregan (2017) Does mathematics contribute to the nanofluid debate? Int J Heat Mass Transf 111:279–288
Nawaz M (2020) Role of hybrid nanoparticles in thermal performance of Sutterby fluid, the ethylene glycol. Phys A 537:122447
Naz R, Noor M, Hayat T, Javed M, Alsaedi A (2020) Dynamism of magnetohydrodynamic cross nanofluid with particulars of entropy generation and gyrotactic motile microorganisms. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf 110:104431
Ogunseye HA, Mondal H, Sibanda P, Mamboundou HM (2020) Lie group analysis of a Powell-Eyring nanofluid flow over a stretching surface with variable properties. SN Appl Sci 2:115
Patel HR (2019) Effects of cross diffusion and heat generation on mixed convective MHD flow of Casson fluid through porous medium with non-linear thermal radiation. Heliyon 5:e01555
Qayyum S, Khan MI, Hayat T, Alsaedi A (2017) A framework for nonlinear thermal radiation and homogeneous–heterogeneous reactions flow based on silver-water and copper-water nanoparticles: A numerical model for probable error. Res Phys 7:1907–1914
Ragupathi P, Hakeem A, Saranya S, Ganga B (2018) Non-darcian three-dimensional flow of \({Fe_{3}}{O_{4}}/{Al{2}}{O_{3}}\) nanoparticles with \({H_{2}}{O}/{Na}{C_{6}}{H_{9}}{O_{7}}\) base fluids past a riga plate embedded in a porous medium. Euro Phys J Plus 228:2571–2600
Reddy MG, Rani S, Kumar KG, Seikh AH, Gorji MR, Sherif EM (2019) Transverse magnetic flow over a Reiner–Philippoff nanofluid by considering solar radiation. Modern Phys Lett B 33:1950449
Sajid T, Sagheer M, Hussain SS (2020) Impact of temperature-dependent heat source/sink and variable species diffusivity on radiative Reiner-Philippoff fluid. Math Prob Eng 4:16
Sajid Tanveer, Sagheer Muhammad, Hussain Shafqat, Shahzad Faisal (2020) Impact of double-diffusive convection and motile gyrotactic microorganisms on magnetohydrodynamics bioconvection tangent hyperbolic nanofluid. Open Phys 18(1):74–88
Sajid T, Sagheer M, Hussain M, annd Bilal S (2018) Darcy-Forchheimer flow of Maxwell nanofluid flow with nonlinear thermal radiation and activation energy. AIP Advances, 8:035102
Sharma B, Kumar S, Paswan MK (2018) Numerical investigation of MHD stagnation-point flow and heat transfer of sodium alginate non-Newtonian nanofluid. Nonlinear Eng 8:179–192
Sheikholeslami M (2019) New computational approach for exergy and entropy analysis of nanofluid under the impact of Lorentz force through a porous media. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 344:319–333
Sivaraj R, Animasaun IL, Olabiyi AS, Saleem S, Sandeep N (2018) Gyrotactic microorganisms and thermoelectric effects on the dynamics of 29 nm \({CuO}\)-water nanofluid over an upper horizontal surface of paraboloid of revolution. Multidiscipline Modeling in Materials and Structures
Uddin I, Ullah I, Ali R, Khan I, Nisar KS (2020) Numerical analysis of nonlinear mixed convective MHD chemically reacting flow of Prandtl-Eyring nanofluids in the presence of activation energy and Joule heating. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09574-2
Vasu B, Gorla RSR, Murthy PVSN, Beg OA (2019) Entropy analysis of a convective film flow of a power-law fluid with nanoparticles along an inclined plate. J Appl Mecha Tech Phys 60:827–841
Waini I, Ishak A, Pop I (2020) Transpiration effects on hybrid nanofluid flow and heat transfer over a stretching/shrinking sheet with uniform shear flow. Alexandria Eng J 59:91–99
Xinhui Si, Li H, Zheng L, Shen Y, Zhang Xi (2017) A mixed convection flow and heat transfer of pseudo-plastic power law nanofluids past a stretching vertical plate. Int J Heat Mass Transfer 105:350–358
Zaib A, Khan U, Wakif A, Zaydan M (2020) Numerical entropic analysis of mixed MHD convective flows from a non-isothermal vertical flat plate for radiative tangent hyperbolic blood biofluids conveying magnetite ferroparticles: dual similarity solutions. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04393-x
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with humans participents or animals performed by the author.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sajid, T., Tanveer, S., Munsab, M. et al. Impact of oxytactic microorganisms and variable species diffusivity on blood-gold Reiner–Philippoff nanofluid. Appl Nanosci 11, 321–333 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-020-01581-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-020-01581-x