Abstract
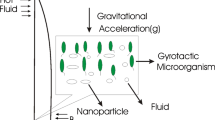
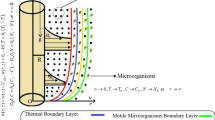
In modern technology, the cooling mechanisms are important for energy storage devices that have been performed with both active and passive heat transfer enhancement techniques. Engineers and scientists have produced various strategies for improving heat transport within thermal process. Nanofluids are the developing consequence of the improvement in heat transfer which has been continuously analyzed. This article discusses the 2D flow of Oldroyd-B nanofluid including swimming gyrotactic motile microorganisms through stretched cylinder. Aspects of Arrhenius activation energy, Cattaneo–Christov heat and mass fluxes and heat source/sink are also considered. The significance of Brownian motion and thermophoresis diffusions is also described to analyze the nanoparticles. Oldroyd-B nanofluid is auspicious for depicting many forms of problems, because this fluid system has the potential to show the features of several rate-type liquids like fluids under the short-chain suspended tiny particles, fluid particles, cleaning products as well as blood in humans. Appropriate similarity variables are used to attain a non-dimensional appearance of problem, and then embedded coupled ODEs have been solved mathematically by using bvp4c solver in the computational software MATLAB. Significance of involved pertinent parameters on flow field like temperature profile, volumetric nanoparticle concentration and microorganism field is also analyzed through graphs. It has been found that the increment in Prandtl number reduces temperature. It is also interesting to observe that temperature field is enhanced for larger temperature ratio and thermophoresis parameters. The outcomes indicate that concentration of nanoparticles is decreasing functions of concentration relaxation parameter and Lewis number. Furthermore, the microorganism field is reduced for larger bioconvection Lewis number while upgraded for bioconvection Rayleigh number.






















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
This manuscript has associated data in a data repository. [Authors’ comment: The data used to support the findings of this study are included within the article.]
References
T. Anwar, P. Kumam, I. Khan, W. Watthayu, Heat transfer enhancement in unsteady MHD natural convective flow of CNTs Oldroyd-B nanofluid under ramped wall velocity and ramped wall temperature. Entropy 22(4), 401 (2020)
T. Hayat, S.A. Khan, M.I. Khan, S. Momani, A. Alsaedi, Cattaneo-Christov (CC) heat flux model for nanomaterial stagnation point flow of Oldroyd-B fluid. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 187, 105247 (2020)
X. Wang, Y. Jiang, Y. Qiao, H. Xu, H. Qi, Numerical study of electroosmotic slip flow of fractional Oldroyd-B fluids at high zeta potentials. Electrophoresis 41, 769–777 (2020)
A. Hafeez, M. Khan, J. Ahmed, Thermal aspects of chemically reactive Oldroyd-B fluid flow over a rotating disk with Cattaneo–Christov heat flux theory. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 144, 793–803 (2020)
A. Hafeez, M. Khan, J. Ahmed, Stagnation point flow of radiative Oldroyd-B nanofluid over a rotating disk. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 27, 105342 (2020)
S.U.S. Choi, J.A. Eastman, Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles. ASME FED. 231/MD 66, 99–105 (1995)
J. Buongiorno, Convective transport in nanofluids. ASME J. Heat Transf. 128, 240–250 (2006)
M. Ali, F. Sultan, W.A. Khan, M. Shahzad, H. Arif, Important features of expanding/contracting cylinder for cross magneto-nanofluid flow. Chaos Solitons Fractals 133, 109656 (2020)
L. Ali, X. Liu, B. Ali, Finite element analysis of variable viscosity impact on MHD flow and heat transfer of nanofluid using the Cattaneo–Christov model. Coatings 10(4), 395 (2020)
S.K. Rawat, H. Upreti, M. Kumar, Comparative study of mixed convective MHD Cu-water nanofluid flow over a cone and wedge using modified Buongiorno’s model in presence of thermal radiation and chemical reaction via Cattaneo-Christov double diffusion model. J. Appl. Comput. Mech. 7, 1383–1402 (2021)
A.S. Dogonchi, M. Waqas, S.M. Seyyedi, M. Hashemi-Tilehnoee, D.D. Ganji, A modified Fourier approach for analysis of nanofluid heat generation within a semi-circular enclosure subjected to MFD viscosity. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 111, 104430 (2020)
K. Muhammad, T. Hayat, A. Alsaedi, B. Ahmad, Melting heat transfer in squeezing flow of basefluid (water), nanofluid (CNTs+ water) and hybrid nanofluid (CNTs+ CuO+ water). J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 143, 1157–1174 (2020)
M. Turkyilmazoglu, On the transparent effects of Buongiorno nanofluid model on heat and mass transfer. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 136(4), 1–15 (2021)
M. Turkyilmazoglu, Exact solutions concerning momentum and thermal fields induced by a long circular cylinder. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 136(5), 1–10 (2021)
T. Muhammad, H. Waqas, S.A. Khan, R. Ellahi, S.M. Sait, Significance of nonlinear thermal radiation in 3D Eyring–Powell nanofluid flow with Arrhenius activation energy. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 143, 929–944 (2020)
C. Cattaneo, Sulla conduzione del calore, Atti Semin. Mat. Fis. Univ. Modena Reggio Emilia 3, 83–101 (1948)
C.I. Christov, On frame indifferent formulation of the Maxwell–Cattaneo model of finite speed heat conduction. Mech. Res. Commun. 36, 481–486 (2009)
V. Tibullo, V. Zampoli, A uniqueness result for the Cattaneo–Christov heat conduction model applied to incompressible fluids. Mech. Res. Commun. 38, 77–79 (2011)
T. Hayat, T. Muhammad, A. Alsaedi, B. Ahmad, Three-dimensional flow of nanofluid with Cattaneo–Christov double diffusion. Results Phys. 6, 897–903 (2016)
A. Tulu, W. Ibrahim, MHD slip flow of CNT-ethylene glycol nanofluid due to a stretchable rotating disk with Cattaneo–Christov heat flux model. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 1–13 (2020)
Z. Shah, E.O. Alzahrani, A. Dawar, W. Alghamdi, M. Zaka Ullah, Entropy generation in MHD second-grade nanofluid thin film flow containing CNTs with Cattaneo–Christov heat flux model past an unsteady stretching sheet. Appl. Sci. 10(8), 2720 (2020)
S.U. Khan, I. Tlili, H. Waqas, M. Imran, Effects of nonlinear thermal radiation and activation energy on modified second-grade nanofluid with Cattaneo–Christov expressions. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 143, 1175–1186 (2020)
J.R. Platt, “Bioconvection patterns” in cultures of free-swimming organisms. Science 133(3466), 1766–1767 (1961)
A. Shahid, H. Huang, M.M. Bhatti, L. Zhang, R. Ellahi, Numerical investigation on the swimming of gyrotactic microorganisms in nanofluids through porous medium over a stretched surface. Mathematics 8(3), 380 (2020)
Y. Li, H. Waqas, M. Imran, U. Farooq, F. Mallawi, I. Tlili, A numerical exploration of modified second-grade nanofluid with motile microorganisms, thermal radiation, and Wu’s slip. Symmetry 12(3), 393 (2020)
M. Aneja, S. Sharma, S. Kuharat, B.O. Anwar, Computation of electroconductive gyrotactic bioconvection under nonuniform magnetic field: simulation of smart bio-nanopolymer coatings for solar energy. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 18, 2050028 (2020)
H. Waqas, S.U. Khan, S.A. Shehzad, M. Imran, I. Tlili, Activation energy and bioconvection aspects in generalized second-grade nanofluid over a Riga plate: a theoretical model. Appl. Nanosci. 20, 1–4 (2020)
H. Waqas, S.U. Khan, M. Hassan, M.M. Bhatti, M. Imran, Analysis on the bioconvection flow of modified second-grade nanofluid containing gyrotactic microorganisms and nanoparticles. J. Mol. Liq. 291, 111231 (2019)
A.A. Siddiqui, M. Turkyilmazoglu, Natural convection in the ferrofluid enclosed in a porous and permeable cavity. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 113, 104499 (2020)
M. Turkyilmazoglu, MHD natural convection in saturated porous media with heat generation/absorption and thermal radiation: closed-form solutions. Arch. Mech. 71(1), 49–64 (2019)
M. Turkyilmazoglu, Thermal radiation effects on the time-dependent MHD permeable flow having variable viscosity. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 50(1), 88–96 (2011)
M. Turkyilmazoglu, Nanoliquid film flow due to a moving substrate and heat transfer. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 135(10), 1–13 (2020)
H. Waqas, S.U. Khan, M. Imran, M.M. Bhatti, Thermally developed Falkner–Skan bioconvection flow of a magnetized nanofluid in the presence of a motile gyrotactic microorganism: Buongiorno’s nanofluid model. Phys. Scr. 94, 115304 (2019)
H. Waqas, S.A. Shehzad, S.U. Khan, M. Imran, Novel numerical computations on flow of nanoparticles in porous rotating disk with multiple slip effects and microorganisms. J. Nanofluids 8, 1423–1432 (2019)
M.I. Khan, F. Haq, S.A. Khan, T. Hayat, M.I. Khan, Development of thixotropic nanomaterial in fluid flow with gyrotactic microorganisms, activation energy, mixed convection. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 187, 105186 (2020)
K. Naganthran, M.F. Basir, M.S. Kasihmuddin, S.E. Ahmed, F.B. Olumide, R. Nazar, Exploration of dilatant nanofluid effects conveying microorganism utilizing scaling group analysis: FDM Blottner. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2, 124040 (2020)
T. Muhammad, S.Z. Alamri, H. Waqas, D. Habib, R. Ellahi, Bioconvection flow of magnetized Carreau nanofluid under the influence of slip over a wedge with motile microorganisms. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 143, 945–957 (2021)
S. Abdelsalam, M.M. Bhatti, Anomalous reactivity of thermo-bioconvective nanofluid towards oxytactic microorganisms. Appl. Math. Mech. 41, 711–724 (2020)
S.U. Khan, H. Waqas, M.M. Bhatti, M. Imran, Bioconvection in the rheology of magnetized couple stress nanofluid featuring activation energy and Wu’s slip. J. Non-Equilib. Thermodyn. 45(1), 81–95 (2020)
M.M. Bhatti, M.I. Marin, A. Zeeshan, R. Ellahi, Swimming of motile gyrotactic microorganisms and movement of nanoparticles in blood flow through anisotropically tapered arteries. Front. Phys. 8, 95 (2020)
M. Irfan, M. Khan, W.A. Khan, M. Sajid, Thermal and solutal stratifications in flow of Oldroyd-B nanofluid with variable conductivity. Appl. Phys. A 124(10), 1–11 (2018)
A. Hafeez, M. Khan, A. Ahmed, J. Ahmed, Rotational flow of Oldroyd-B nanofluid subject to Cattaneo–Christov double diffusion theory. Appl. Math. Mech. 41, 1083–1094 (2020)
A.M. Megahed, Variable fluid properties and variable heat flux effects on the flow and heat transfer in a non-Newtonian Maxwell fluid over an unsteady stretching sheet with slip velocity. Chin. Phys. B 22(9), 094701 (2013)
S.M. Atif, S. Hussain, M. Sagheer, Effect of viscous dissipation and Joule heating on MHD radiative tangent hyperbolic nanofluid with convective and slip conditions. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 41(4), 1–17 (2019)
M. Mustafa, Cattaneo–Christov heat flux model for rotating flow and heat transfer of upper-convected Maxwell fluid. Aip Adv. 5(4), 047109 (2015)
Acknowledgement
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Khalid University, Abha, Saudi Arabia for funding this work through research groups program under grant number R.G.P-2/76/42.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Waqas, H., Muhammad, T., Khan, S.A. et al. Inspection of modified Fourier’s and Fick’s laws in magnetized transport of Oldroyd-B nanofluid with swimming motile microorganisms: a theoretical model. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 136, 860 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-021-01843-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-021-01843-9