Abstract
Impacts of geogenic and anthropogenic sources change seriously quality of groundwater. Inferior groundwater quality directly affects the human health, agricultural output and industrial sector. The aim of the present study is to evaluate the groundwater quality for drinking purpose and also to identify the pollutants responsible for variation of chemical quality of groundwater, using pollution index of groundwater (PIG). Groundwater samples collected from a rural part of Telangana State, India, were analyzed for pH, total dissolved solids (TDS), calcium (Ca2+), magnesium (Mg2+), sodium (Na+), potassium (K+), bicarbonate (\( {\text{HCO}}_{3}^{ - } \)), chloride (\( {\text{Cl}}^{ - } \)), sulfate (\( {\text{SO}}_{4}^{2 - } \)), nitrate (\( {\text{NO}}_{3}^{ - } \)) and fluoride (\( {\text{F}}^{ - } \)). The groundwater is characterized by Na+ and \( {\text{HCO}}_{3}^{ - } \) ions. The values of TDS, Mg2+, Na+, K+, \( {\text{HCO}}_{3}^{ - } \), \( {\text{Cl}}^{ - } \), \( {\text{SO}}_{4}^{2 - } \), \( {\text{NO}}_{3}^{ - } \) and \( {\text{F}}^{ - } \) are more than their threshold limits prescribed for drinking purpose in a few groundwater samples. The computed values of PIG varied from 0.69 to 1.37, which classify the 80% of the present study area into the insignificant pollution zone (PIG: < 1.0) caused by geogenic origin associated with rock-weathering, mineral dissolution, ion exchange and evaporation processes, and the rest (20%) into the low pollution zone (PIG: 1.0 to 1.5) due to influence of anthropogenic source (waste waters and agricultural activities) on the groundwater system, which are proved by ANOVA test. The diagrams (Ca2+ + Mg2+) versus (\( {\text{HCO}}_{3}^{ - } \) + \( {\text{SO}}_{4}^{2 - } \)), Na+ versus (Ca2+ + Mg2+), Na+ versus \( {\text{Cl}}^{ - } \), Ca2+ versus \( {\text{SO}}_{4}^{2 - } \) and Ca2+ versus Mg2+ support the geogenic origin, whereas the diagram TDS with (\( {\text{NO}}_{3}^{ - } \) + \( {\text{Cl}}^{ - } \))/\( {\text{HCO}}_{3}^{ - } \) confirms the impact of anthropogenic activities on the aquifer chemistry, which substantially proved the explanation of PIG. The characterization of geochemical evolution of groundwater, using trilinear diagram, also further supports the assessment of PIG in the variation of groundwater quality. From this study, the TDS, Mg2+, Na+, \( {\text{Cl}}^{ - } \), \( {\text{SO}}_{4}^{2 - } \) and \( {\text{NO}}_{3}^{ - } \) are considered as indicators in assessing the groundwater pollution sources.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Groundwater is a natural replenishable and most precious resource. In arid and semiarid countries like India, especially in rural regions, most population depends on the groundwater for their drinking and irrigation needs. On the other hand, harmony between groundwater resources and human interference is the important aspect to secure the human health, because the chemical quality of water directly affects the human health. Many factors like climate, organic matter decay, soil conditions, lithological characteristics, domestic wastes, agricultural activities and industrial effluents may affect the groundwater quality in a significant way (Barzegar et al. 2016a, b; Nagaraju et al. 2018; Shaji et al. 2018). If the quality of groundwater is suitable for drinking, it can also be consumed for other purposes, including agricultural and industrial uses (Subba Rao et al. 2012, 2017). Thus, the evaluation of groundwater quality and pollution is an important aspect in order to apply water resources management and remediation strategies.
Geochemical processes, occurring within the aquifer system and their chemical reactions, control the changes in groundwater chemistry, and therefore, the study of chemical variations in groundwater can be useful for identifying the hydrogeochemical factors that control the sources of ions in groundwater, which needs water treatment before application (Subba Rao et al. 2012; Nagaraju et al. 2018; Sun and Gui 2015; Selvam et al. 2018).
In recent time, the impacts of geogenic and anthropogenic activities on the aquifer system have been studied and also assessed the groundwater quality and pollution for its sustainable development and protection: Kumar et al. (2006) evaluated the hydrogeochemical processes like dissolution, mixing, weathering of carbonate minerals (CaCO3 concretions), ion exchange and surface water interaction that control the groundwater quality in Delhi, India. Jalali (2009) performed a geochemical characterization of groundwater in an agricultural area of Razan, Hamadan, Iran, and found that the factors such as natural chemical weathering of carbonates, gypsum and anthropogenic activities of fertilizers regulate the groundwater quality. Subba Rao and Surya Rao (2010) stated that the geochemistry of groundwater is mainly controlled by rock-weathering, mineral dissolution, leaching, ion exchange and evaporation, using bivariate diagrams, from a part of Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh, India. Singh et al. (2012) assessed the quality for drinking, domestic and irrigation of groundwater in the village of Lutfullapur Nawada district, Ghaziabad, Uttar Pradesh, India, and observed that the variation of groundwater chemistry is mainly due to ion exchange process. Subba Rao (2012) proposed a pollution index of groundwater (PIG) to evaluate the relative impact of individual chemical parameters on overall chemical quality of groundwater and found that the TDS, Mg2+, Na+, K+, \( {\text{HCO}}_{3}^{ - } \), \( {\text{Cl}}^{ - } \), \( {\text{SO}}_{4}^{2 - } \), \( {\text{NO}}_{3}^{ - } \) and \( {\text{F}}^{ - } \) are considered as pollution indicators for assessment of groundwater quality. Gautam et al. (2015) evaluated the groundwater quality suitability for domestic and irrigation purposes from Chotanagpur plateau region of Subarnarekha river basin, Jharkhand State, India, and stated that the leaching of ions followed by weathering and anthropogenic impact (mainly mining and agricultural activities) control the chemistry of groundwater. Barzegar et al. (2016a, b, 2017a, b) assessed the hydrogeological, hydrogeochemical and water quality properties from different parts of Iran, and the results of Piper diagram and bivariate diagrams showed the hydrochemical processes such as weathering and dissolution of rocks, evaporation and ion exchange as the primary factors, while the anthropogenic activities as secondary factors that are responsible for variation of groundwater quality. Ghalib (2017) carried out a study on evaluation of groundwater chemistry for drinking and irrigation utilities in east Wasit province, Central Iraq and found that the differences in the groundwater chemistry from place to place are due to variation in lithological characteristics as well as in rock-weathering and evaporation processes. Nag and Das (2017) assessed the quality of groundwater from a part of Bankura district of West Bengal, India, and also evaluated the groundwater chemistry as controlled by lithology, using Gibbs and Piper diagrams. Priyanka et al. (2017) evaluated the seasonal variation of groundwater quality, using analysis of variance (ANOVA) test, in rural areas of Jaipur district, Rajasthan, India. Selvakumar et al. (2017) studied the hydrogeochemical characteristics and groundwater contamination from a part of Coimbatore, India, and stated that the groundwater contamination is mainly caused by anthropogenic activities such as population growth, industrial effluents and irrigation return flows. Su et al. (2017) evaluated the groundwater quality and health risks from contamination due to intensive industrial and agricultural activities in the north edge of the loess plateau, Yulin City, Northwest China. Subba Rao et al. (2017) used the bivariate diagrams, trilinear diagram and geochemical modeling to discuss the variation in chemistry of groundwater from a part of Guntur district, Andhra Pradesh, India, and found that the soil–rock–water interactions, mineral weathering and dissolution, ion exchange and evaporation are the prime responsible factors, while the agrochemicals are the supplementary factors that control the groundwater chemistry. Nishi et al. (2018) characterized the hydrogeochemistry, using bivariate diagrams, and groundwater quality from a part of Precambrian Terrain, Eastern India and observed that the groundwater chemistry is controlled by geogenic origin (carbonate and silicate weathering and dissolution, ion exchange and evaporation) and anthropogenic sources. Ramyapriya and Elango (2018) evaluated the impacts of geogenic and anthropogenic sources on quality of surface water and groundwater, using water quality index, along Cauvery River, India. Subba Rao (2018) studied the groundwater quality from a part of Prakasam district, Andhra Pradesh, India, and the results showed that the groundwater chemistry is regulated by rock-weathering, ion exchange and evaporation processes and also interference of human activities such as drainage wastes and agricultural chemicals.
From the above literature, it is clear that the variation of aquifer chemistry from place to place depends upon the influences of geogenic origin associated with soil–rock–water interactions, mineral weathering and dissolution, ion exchange and evaporation as the main controlling processes, while the impact of anthropogenic activities like domestic wastes, agrochemicals and irrigation return flows as the secondary regulating factors. These basic concepts can be helpful for assessing the groundwater quality and contamination in the present study area.
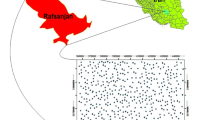
In India, the usage of groundwater is 80% in rural area and 50% in urban area for domestic purposes. More than 33% of the country’s groundwater resources are unfit for drinking due to geogenic and anthropogenic pollution (Chakraborti et al. 2011). According to WHO (2015), about 38 million people are affected by water borne diseases each year in India so that the groundwater quality and its pollution effects on aquifer system is crucial factor for protection of groundwater resources. However, no detailed attempt has so far been made on study of groundwater quality from many rural parts of India. The present study located in a rural part of Wanaparthy district, Telangana State is no exception from it (Fig. 1). Thus, the objective of the present study is to evaluate the quality of groundwater for drinking, meeting the standard drinking water quality limits, and to unhide the sources responsible for variation of quality of groundwater, using pollution index of groundwater (PIG).
Study area
The present study area is a part of Wanaparthy district, Telangana State, India (Fig. 1). It covers an area of 432 km2. The area experiences a semiarid climate. The average annual temperature is 16.9 °C in winter (December–February) and 41.5 °C in summer (March–May). The recorded average annual rainfall is 605 mm. Southwest monsoon contributes 61% of the total rainfall.
Topographically, the slope of the study area is toward southwest. Sandy soils, black cotton soils and sandy loamy soils are the important soil varieties occurring in the study area. Calcium carbonate (CaCO3) concretions occur in soil zone, indicating the prevailing condition of dry climate. The important geomorphic features include moderately weathered pediplain, shallow weathered pediplain, pediment, residual hills, denudational hills and flood plains. The small River Sarala vagu drains the area (Fig. 1). The drainage pattern is semi-dendritic type.
Geologically, the present study area is underlain by Precambrian rocks (Fig. 2). Recent formations, including soils and alluvium, occur over the basement rocks. The granite and granite gneiss are the dominant verities of the Precambrian rocks. Dykes, pegmatites and quartzite veins are associated with the country rocks. They are medium to coarse grained and equigranular in texture, which are composed of quartz, feldspar, apatite, biotite and hornblende. The typical grey color in the country rocks is due to presence of plagioclase feldspar and quartz. The potash feldspars include the orthoclase and microcline varieties. The rocks show N–S or E–W direction, with deviation toward E–W, NW–SE and NE–SW. They show a dip of 55° to 70° southeast.
Geological formations (after CGWB 2013)
Groundwater exists under unconfined conditions in the weathered rocks as well as under semi-confined conditions in the fractured rocks. Groundwater is extracted through shallow depth (dug wells) and deep depth (bore wells). Depth to water level varies from 5.1 to 19.5 m below ground surface. Relatively, the depth to water level is shallow at topographic-lows and is deep at topographic-highs. The yields of the wells vary from 250 to 350 cubic meters per day (m3/day) (CGWB 2013). Storage coefficient varies from 0.002 to 0.020. The transmissivity of aquifer ranges from 4.50 to 150 m2/day.
Agricultural land is occupied by 48.85%, waste land by 43.75%, built-up land by 3.93% and the remaining 3.4% land associated with water bodies of the total study area. Local residents depend upon their income on agriculture. Intensive and long-term irrigation practice is a common phenomenon. Uncontrolled usage of agrochemicals is normal practice for the improvement of soil permeability as well as for higher crop yields. The principal crops grown include cotton, chilly, paddy, pulses and millets. Hygienic conditions are poor due to disposal of domestic wastes on the ground as well as leakage of drainage structures and septic tanks into the sub-surface.
Methodology
Sample collection and chemical analysis
A total of 30 dug wells were observed during summer (May) 2015 (Fig. 1). Groundwater samples were collected in half liter clean plastic containers. The containers were soaked in 1:1 HCl for 24 h and rinsed with distilled water, following the deionized water. They were cleaned before the collection of groundwater samples.
The groundwater samples collected from the field were immediately used to measure hydrogen ion concentration (pH) and electrical conductivity (EC), using their portable meters. The EC, a measure of material’s ability to conduct an electric current, was used to compute the concentration of total dissolved solids (TDS; Eq. 1), as per the procedure of Hem (1991). All chemical parameters were analyzed, following the methods suggested by American Public Health Association (APHA 2012). The total hardness (TH as CaCO3) and calcium (Ca2+) were estimated by EDTA titration method. The magnesium (Mg2+) was computed, taking the difference value between TH and Ca2+. A flame photometer was used for determination of sodium (Na+) and potassium (K+) ions. The bicarbonate (\( {\text{HCO}}_{3}^{ - } \)) was analyzed by HCl volumetric method. The chloride (\( {\text{Cl}}^{ - } \)) was estimated by AgNO3 titration method. \( {\text{SO}}_{4}^{2 - } \), \( {\text{NO}}_{3}^{ - } \) and \( {\text{F}}^{ - } \) were measured, using UV-spectrophotometer. The concentrations of hydrochemical parameters were expressed in milligrams per liter (mg/L), excepting pH (unit less). The computed ionic balance error (IBE) was within the standard limit of ± 5% (Domenico and Schwartz 1990).
Pollution index of groundwater
For assessment of variation in groundwater quality caused by geogenic and anthropogenic sources, pollution index of groundwater (PIG) proposed by Subba Rao (2012) was used in the present study, which quantifies the status of relative impact of individual chemical variables (pH, TDS, Ca2+, Mg2+, Na+, K+, \( {\text{Cl}}^{ - } \), \( {\text{SO}}_{4}^{2 - } \), \( {\text{NO}}_{3}^{ - } \) and \( {\text{F}}^{ - } \)) on overall quality of groundwater (Table 1). Five steps were involved in computation of the PIG. In first step, the relative weight (Rw) from 1 to 5 was assigned for each chemical parameter, according to its relative impact on human health. For example, minimum weight (1) was given to K+ and maximum weight (5) to pH, TDS, \( {\text{SO}}_{4}^{2 - } \), \( {\text{NO}}_{3}^{ - } \) and \( {\text{F}}^{ - } \). In second step, the weight parameter (Wp) was computed for each chemical variable to assess its relative share on overall quality of water (Eq. 2). In third step, the status of concentration (Sc) was estimated by dividing the each chemical variable content of each water sample by its respective drinking water quality threshold limit (Ds; Eq. 3). In fourth step, overall chemical quality of water (Ow) was computed by multiplying the Wp with the Sc (Eq. 4). In final step, pollution index of groundwater (PIG) was calculated by adding all Ow values (ΣOw; Eq. 5), which contribute all chemical variables of each water sample, to get a clear scenario on the influence of contamination on aquifer system.
In assessment of PIG, the relative contribution of chemical variables from each groundwater sample will be taken into account. If the overall chemical quality of water (Ow) is more than 0.1, it accounts for 10% of value of 1.0 of the PIG. This gives clear cut information on the influence of contamination of groundwater body (Subba Rao 2012). The PIG has been classified as an insignificant pollution, if it is less than 1.0; low pollution, if it is in between 1.0 and 1.5; moderate pollution, if it varies from 1.5 to 2.0; high pollution, if it is from 2.0 to 2.5; very high pollution, and if it is more than 2.5 (Table 2), considering the additional concentrations of chemical variables, which specify the inflowing of foreign matter into an aquifer system gradually.
Analysis of variance
One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used for hypothesis test, whether it is significant or not (Priyanka et al. 2017). It compares the variance (variability in scores) between the different groups with the variability within each of the group, which is called F test (Eq. 6). This test has been carried out in the present study area between the insignificant pollution zone and the low pollution zone to examine, whether the experimental results are at accepted level or not, using Statistica version 6.
If the calculated value of F is more than the critical value of F (tabulated value), then the null hypothesis (Ho) will be rejected at α level (significance level). That means the experimental assumption will be accepted or null hypothesis is significant. If the calculated value of F is less than the critical value of F, then the null hypothesis (Ho) will not be rejected at α level. That means the experimental assumption will not be accepted or null hypothesis is insignificant.
Bivariate and trilinear diagrams
Bivariate diagrams were used here to evaluate the geogenic source (rock-weathering, mineral dissolution, ion exchange and evaporation) and anthropogenic activities (waste water, agrochemicals and irrigation return flow) on groundwater quality (Barzegar et al. 2017a, b). Trilinear diagram was also adopted to evaluate the geochemical characteristics of groundwater (Piper 1944).
Results and discussion
Groundwater quality and chemistry
The results of chemical composition of groundwater of the present study area are presented in Table 3. The groundwater contains neutral to alkaline condition, with measured pH in the field varying from 7.1 to 8.6 with an average of 7.56, which is caused by both \( {\text{HCO}}_{3}^{ - } \) and \( {\text{CO}}_{ 3}^{{ 2 { - }}} \) ions (Hem 1991). The degree of groundwater quality in terms of TDS showed a wide range from 200 to 2106, and its average was 583.60 mg/L, which gives information on total dissolved salts present in the groundwater system. Generally, the lower TDS may be a result of natural origin, while the higher TDS specifies the influence of anthropogenic source on aquifer system (Subba Rao 2017a).
The concentrations of cations (Ca2+, Mg2+, Na+ and K+) and anions (\( {\text{HCO}}_{3}^{ - } \), \( {\text{Cl}}^{ - } \), \( {\text{SO}}_{4}^{2 - } \), \( {\text{NO}}_{3}^{ - } \) and \( {\text{F}}^{ - } \)) can explain the causes of variations in the quality of groundwater and also determine the basic hydrogeochemical characteristics of groundwater (Subba Rao 2017a). The Na+ was observed to be in higher concentration among the cations, varying from 33 to 434 with an average of 117.87 mg/L (Table 3). This is caused by rock-weathering, mineral dissolution, evaporation and anthropogenic activities (irrigation return flows, poor drainage conditions, etc.) on the groundwater system (Stallard and Edmond 1983; Drever 1997; Subba Rao et al. 2017). The occurrence of ferromagnesium minerals in the basement rocks and disposal of waste waters on the ground are the main sources of higher concentration of Mg2+, which was from 19 to 119, and its average was 41.63 mg/L, while the concentration of Ca2+ showed the values from 18 to 67 with an average of 39.30 mg/L, which is caused by calcium feldspars (Todd 1980; Hem 1991; Subba Rao et al. (2012). The lowest concentration of K+ (1 to 18 with an average of 4.10 mg/L) among the cations in the present study is a result of its greater resistant to chemical weathering and also its adsorption on clay products (Subba Rao et al. 2012).
The \( {\text{HCO}}_{3}^{ - } \) had the highest concentrations among the anions, which varied from 13 to 453, and its average was 137.87 mg/L (Table 3). This indicates dissolution of feldspar minerals (Stumm and Morgan 1996). The higher concentration of \( {\text{HCO}}_{3}^{ - } \) is also a result of decay of organic matter and root respiration that combines with rainwater (H2O) to form \( {\text{HCO}}_{3}^{ - } \) (Eqs. 7 and 8), which controls the pH. The concentration of \( {\text{Cl}}^{ - } \) was from 20 to 680 with an average of 119.27 mg/L. The clays formed by highly weathered rocks are the prime source, and the anthropogenic activities (irrigation return flows and poor drainage conditions) are the secondary source for the concentration of \( {\text{Cl}}^{ - } \) in the groundwater (Subba Rao et al. 2017). The \( {\text{SO}}_{4}^{2 - } \) content varied from 14 to 200, and its average was 51.53 mg/L. No sulfide-bearing minerals are present in the present study area so that the application of uncontrolled gypsum used for the improvement of soil conditions appears to be the main source of \( {\text{SO}}_{4}^{2 - } \) in the groundwater system. The concentration of \( {\text{NO}}_{3}^{ - } \) was from 0.10 to 59 with an average of 7.50 mg/L in the groundwater of the present study, and its higher content (> 10 mg/L) indicates the influences of disposal of waste waters and application of nitrogen fertilizers on the aquifer system (Cushing et al. 1973; Subba Rao et al. 2012, 2017). The \( {\text{F}}^{ - } \) content was from 0.26 to 2.30 (with an average of 0.99) mg/L in the present study area. The country rocks, containing the \( {\text{F}}^{ - } \) bearing minerals (apatite, biotite and hornblende), and the occurrence of clays are the main responsible for the \( {\text{F}}^{ - } \) content in the present study area, as also suggested by Rao et al. (2014) and Subba Rao et al. (2017b). The extensive use of phosphate fertilizers for higher crop yields is the secondary source for enrichment of \( {\text{F}}^{ - } \) in the groundwater (Subba Rao 2017b).
Overall, Na+ is the dominant ion, among the cations, followed by Mg2+, Ca2+ and K+, while \( {\text{HCO}}_{3}^{ - } \) is the abundant ion among the anions, followed by \( {\text{Cl}}^{ - } \), \( {\text{SO}}_{4}^{2 - } \), \( {\text{NO}}_{3}^{ - } \) and \( {\text{F}}^{ - } \) (Table 3). Therefore, the groundwater belongs to Na+- \( {\text{HCO}}_{3}^{ - } \) type. The concentrations of TDS, Mg2+, Na+, K+, \( {\text{HCO}}_{3}^{ - } \), \( {\text{Cl}}^{ - } \), \( {\text{SO}}_{4}^{2 - } \), \( {\text{NO}}_{3}^{ - } \) and \( {\text{F}}^{ - } \) exceed their recommended limits of 500, 30, 200, 10, 300, 250, 150, 45 and 1.5 mg/L permitted for drinking water purpose in about 33, 60, 20, 7, 7, 20, 7, 7 and 20% of the total groundwater samples, respectively (Fig. 3), which may cause health disorders (BIS 2012).
Groundwater pollution zones
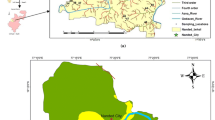
The computed values of PIG varied from 0.69 to 1.37 (Table 4). As per the classification of PIG (Table 2), 80% of the total groundwater samples fall in the insignificant pollution zone (PIG: 0.69) and the rest (20%) in the low pollution zone (PIG: 1.37). The groundwater samples (5, 8, 16, 22 and 28) of the low pollution zone spread mainly from central side to eastern side (Fig. 4). The pH (0.13) and TDS (0.12) show the values of Ow more than 0.1 in the insignificant pollution zone, while the Ca2+ (0.04), Mg2+ (0.06), Na+ (0.04), K+ (0.02), \( {\text{HCO}}_{3}^{ - } \) (0.03), \( {\text{Cl}}^{ - } \) (0.04), \( {\text{SO}}_{4}^{2 - } \) (0.04), \( {\text{NO}}_{3}^{ - } \) (0.07) and \( {\text{F}}^{ - } \) (0.10) have the values of Ow less than 0.1. These values are considered as natural contributors of groundwater quality. On the other hand, the pH (0.13), TDS (0.39), Mg2+ (0.17), Na+ (0.15), \( {\text{Cl}}^{ - } \) (0.11), \( {\text{SO}}_{4}^{2 - } \) (0.11) and \( {\text{NO}}_{3}^{ - } \) (0.14) show the values of Ow higher than 0.1 in the low pollution zone, which are more than the natural contributors of groundwater quality. Thus, they obviously indicate the influence of anthropogenic source rather than the geogenic origin on the groundwater system.
In order to verify the role of geogenic and anthropogenic origins as sources of dissolved salts on the aquifer system, it is imperative to consider the difference in the values of Ow between the insignificant pollution zone and the low pollution zone. From Table 4, it is significant to note that there is no much difference in the values of Ow in the cases of pH, Ca2+, K+, \( {\text{HCO}}_{3}^{ - } \) and \( {\text{F}}^{ - } \) between the insignificant pollution zone and the low pollution zone. Further, it is also observed that the Ow values of Na+ (0.04), \( {\text{HCO}}_{3}^{ - } \) (0.03) and \( {\text{Cl}}^{ - } \) (0.04) are more or less the same in the insignificant pollution zone, whereas the \( {\text{HCO}}_{3}^{ - } \) (0.04) is less than \( {\text{Cl}}^{ - } \) (0.11) and the Na+ (0.15) is more than \( {\text{Cl}}^{ - } \) (0.11) in the low pollution zone. This difference could be due to variation in the source of pollution in the groundwater system.
To further confirm the experimental results between the insignificant pollution zone and the low pollution zone, one-way ANOVA test was conducted at different significant levels (α = 0.01, 0.025 and 0.05), using Statistica version 6. The results of ANOVA and F tests are presented in Tables 5 and 6. The critical values of F (α, 1, 20) are 8.10, 5.87 and 4.35 at α level of 0.01, 0.025 and 0.05, respectively. The calculated value of F is observed to be 2.778, which is less than the critical value of F at significant levels of 50%, 75% and 95%, respectively. Since the difference being tested is statistically significant at all levels of α, the experimental results of Ow observed between the insignificant pollution zone and the low pollution zone are at accepted level, which supports the above hypothesis.
To assess the processes controlling the groundwater chemistry, bivariate diagrams such as (Ca2+ + Mg2+) versus (\( {\text{HCO}}_{3}^{ - } \) + \( {\text{SO}}_{4}^{2 - } \)), Na+ versus (Ca2+ + Mg2+), Na+ versus \( {\text{Cl}}^{ - } \), Ca2+ versus \( {\text{SO}}_{4}^{2 - } \), Ca2+ versus Mg2+ and TDS versus (\( {\text{NO}}_{3}^{ - } \) + \( {\text{Cl}}^{ - } \))/\( {\text{HCO}}_{3}^{ - } \) are widely used (Subba Rao and Surya Rao 2010; Marghade et al. 2012; Barzegar et al. 2016a, b; Li et al. 2018). The dominance of (\( {\text{HCO}}_{3}^{ - } \) + \( {\text{SO}}_{4}^{2 - } \)) over (Ca2+ + Mg2+) indicates the feldspar-bearing rock-weathering, whereas the abundance of (Ca2+ + Mg2+) over (\( {\text{HCO}}_{3}^{ - } \) + \( {\text{SO}}_{4}^{2 - } \)) is an indicative of reverse ion exchange (Barzegar et al. 2016b, 2017a). In the present study area, most groundwater samples fall below the equiline (1:1; Fig. 5a). Thus, the groundwater chemistry is mainly controlled by reverse ion exchange process. However, the groundwater samples are observed on both sides of 1:1 line of Na+ versus (Ca2+ + Mg2+; 5b), which indicate the ion exchange as well as reverse ion exchange processes, taking place in the present study area. In the plot of Na+ versus \( {\text{Cl}}^{ - } \), most groundwater samples fall below the equiline 1:1 (Fig. 5c). It demonstrates not only the mineral weathering (Eq. 9) but also the ion exchange (10) processes taking place in the present study area. As a result, the relation of Na+ with \( {\text{Cl}}^{ - } \) indicates the effective processes of silicate weathering and ion exchange (Li et al. 2016a; Barzegar et al. 2017b; Subba Rao et al. 2017). The higher concentration of \( {\text{HCO}}_{3}^{ - } \) (Table 3) indicates the mineral dissolution (Stumm and Morgan 1996). Also, the groundwater samples are observed on both sides of the equiline (1:1) of Ca2+ and \( {\text{SO}}_{4}^{2 - } \) (Fig. 5d), which reflect the dissolution of gypsum/anhydrite (Barzegar et al. 2016b). However, the dissolved gypsum in the groundwater is sourced from the used gypsum for the improvement of the soil in the present study area. Further, most groundwater samples fall toward Mg2+ content rather than toward Ca2+ content in the plot of Mg2+ versus Ca2+ (Fig. 5e), which is due to a result of precipitation of CaCO3. Datta and Tyagi (1996) stated that the formation of calcareous (CaCO3) concretions infers a long history of evaporation caused by semiarid climate so that the occurrence of CaCO3 concretions in soil zone of the present study area supports the above hypothesis. Thus, these observations clearly indicate the mineral weathering and dissolution, ion exchange and evaporation as the major regulating factors of chemical quality of groundwater.
Correlation between a (Ca2+ + Mg2+) and (\( {\text{HCO}}_{3}^{ - } \) + \( {\text{SO}}_{4}^{2 - } \)), b Na+ and (Ca2+ + Mg2+), c Na+ and \( {\text{Cl}}^{ - } \), d Ca2+ and \( {\text{SO}}_{4}^{ 2- } \), e Ca2+ and Mg2+, and f TDS and (\( {\text{NO}}_{3}^{ - } \) + \( {\text{Cl}}^{ - } \))/\( {\text{HCO}}_{3}^{ - } \)
Moreover, the values of Ow of Mg2+ (0.17), Na+ (0.15), \( {\text{Cl}}^{ - } \)(0.11), \( {\text{SO}}_{4}^{2 - } \)(0.11) and \( {\text{NO}}_{3}^{ - } \)(0.14) are more than 0.1 in the low pollution zone (Table 4). As pointed out by Subba Rao (2012), the values of Ow more than 0.1 are an indication of pollution. The higher values of Ow with respect to Mg2+, Na+, \( {\text{Cl}}^{ - } \), \( {\text{SO}}_{4}^{2 - } \) and \( {\text{NO}}_{3}^{ - } \) can be taken as pollution indicators, as these chemical parameters also exceed their drinking water quality limits of 30, 200, 250, 150 and 45 mg/L (BIS 2012) in 19%, 20%, 20%, 7% and 7% of the total groundwater samples in the present study area (Fig. 4). Since most of the study area comes under the agricultural land (48.85%), the sources of \( {\text{Cl}}^{ - } \) and \( {\text{NO}}_{3}^{ - } \) are substantially supporting the influence of anthropogenic source on the aquifer system (Cushing et al. 1973; Subba Rao et al. 2012, 2017).
Human interference affects the groundwater chemistry, especially agrochemicals, which contaminate the groundwater body. As a result, the groundwater shows the higher concentrations of Na+, \( {\text{HCO}}_{3}^{ - } \), \( {\text{Cl}}^{ - } \) and \( {\text{NO}}_{3}^{ - } \) (Jalali 2009). It further causes the higher TDS in the groundwater. Therefore, a relation between TDS and (\( {\text{NO}}_{3}^{ - } \) + \( {\text{Cl}}^{ - } \))/\( {\text{HCO}}_{3}^{ - } \) is widely used to examine the role of influence of anthropogenic activity on the aquifer chemistry (Han and Liu 2004; Jalali 2009; Marghade et al. 2012; Barzegar et al. 2016b; Li et al. 2016b, 2018). Generally, a positive relation of TDS with (\( {\text{NO}}_{3}^{ - } \) + \( {\text{Cl}}^{ - } \))/\( {\text{HCO}}_{3}^{ - } \) can be considered as an indicator to assess the influence of agrochemical inputs on the aquifer system. The chemical composition of groundwater samples of the present study area is plotted in diagram TDS versus (\( {\text{NO}}_{3}^{ - } \) + \( {\text{Cl}}^{ - } \))/\( {\text{HCO}}_{3}^{ - } \) (Fig. 5f). A positive relation is between TDS and (\( {\text{NO}}_{3}^{ - } \) + \( {\text{Cl}}^{ - } \))/\( {\text{HCO}}_{3}^{ - } \). This suggests the impact anthropogenic source on the groundwater chemistry. Consequently, the TDS shows the three times higher value of Ow (0.39) in the low pollution zone compared to that in the insignificant pollution zone (0.12; Table 4). Thus, the anthropogenic source seems to be a secondary origin, which enriches the various dissolved salts content in the groundwater system by masking the groundwater quality caused by geogenic origin.
For characterization of geochemical evolution of groundwater, which supports the assessment in the variation of groundwater quality by PIG, a trilinear diagram (Piper 1944) was also adopted here to classify the overall chemical water quality as (1) Ca2+–\( {\text{HCO}}_{3}^{ - } \) type (zone-5), (2) Ca2+–\( {\text{Cl}}^{ - } \) type (zone-6), (3) Na+–\( {\text{Cl}}^{ - } \) type (zone-7), (4) Na+–\( {\text{HCO}}_{3}^{ - } \) type (zone-8) and (5) mixed type (zone-9). In the present study area, thirty percent of the total groundwater samples are observed from the zone-5 (Fig. 6). This is a result of more concentrations of Ca2+ + Mg2+ and \( {\text{HCO}}_{3}^{ - } \) + \( {\text{CO}}_{3}^{2 - } \) than that of Na+ + K+ and \( {\text{Cl}}^{ - } \) + \( {\text{SO}}_{4}^{2 - } \)(Table 7). About 23% of the groundwater samples fall in the zone-7. This is caused by higher concentrations of Na+ + K+ and \( {\text{Cl}}^{ - } \) + \( {\text{SO}}_{4}^{2 - } \) ions than that of Ca2+ + Mg2+ and \( {\text{HCO}}_{3}^{ - } \) + \( {\text{CO}}_{ 3}^{{ 2 { - }}} \) ions. The remaining 47% of the groundwater samples are observed from the zone-9, which shows a mixed water type, namely no ion-pairs, exceeding 50% of the total ions. From Fig. 6, it can be clearly said that the fresh water type (zone-5) of geogenic origin gradually changes to saline water type (zone-7) through the mixed water type (zone-9) due to impact of anthropogenic activities on the aquifer system. Thus, the characterization of geochemical evolution of groundwater is also further supported by the PIG’s assessment in the variation of groundwater quality.
Characterization of geochemical evolution of groundwater (after Piper 1944)
After discussion, the groundwater quality and the impacts of geogenic and anthropogenic sources on the groundwater system, using PIG, the TDS, Mg2+, Na+, \( {\text{Cl}}^{ - } \), \( {\text{SO}}_{4}^{2 - } \) and \( {\text{NO}}_{3}^{ - } \), are considered as indicators for assessing the pollution sources in the present study area.
Conclusions
The following important conclusions were drawn from the rural part of Telangana State, India:
-
Groundwater quality is characterized by Na+ and \( {\text{HCO}}_{3}^{ - } \) ions.
-
The concentrations of TDS, Mg2+, Na+, K+, \( {\text{Cl}}^{ - } \), \( {\text{SO}}_{4}^{2 - } \), \( {\text{NO}}_{3}^{ - } \) and \( {\text{F}}^{ - } \) exceed their recommended limits prescribed for drinking purpose in a few groundwater samples.
-
The values of pollution index of groundwater (PIG) vary from 0.69 to 1.37, which classify the 80% of the area into insignificant pollution zone (PIG: < 1.0) and the rest (20%) into low pollution zone (PIG: 1.0 to 1.5). They are caused by geogenic (rock-weathering, mineral dissolution, ion exchange and evaporation) and anthropogenic (waste waters and irrigation activities) sources, respectively.
-
ANOVA test conducted between the insignificant pollution zone and the low pollution zone, the value of F is less than that of critical F at significant levels of 0.01, 0.025 and 0.05, which accept the experimental results.
-
The diagrams (Ca2+ + Mg2+) versus (\( {\text{HCO}}_{3}^{ - } \) + \( {\text{SO}}_{4}^{2 - } \)) and Na+ versus (Ca2+ + Mg2+) support the reverse ion exchange and ion exchange processes controlling the groundwater chemistry.
-
The relation between Na+ and \( {\text{Cl}}^{ - } \) is explained the role of rock-weathering, mineral dissolution and evaporation processes in regulating the groundwater quality.
-
The groundwater samples falling toward Mg2+ over Ca2+ indicate the precipitation of CaCO3 due to higher rate of evaporation, which is also supported by the occurrence of calcium carbonate concretions in the soil zone.
-
A positive relation of TDS with (\( {\text{NO}}_{3}^{ - } \) + \( {\text{Cl}}^{ - } \))/\( {\text{HCO}}_{3}^{ - } \) confirms the influence of anthropogenic activities on the aquifer chemistry.
-
The characterization of geochemical evolution of groundwater, using trilinear diagram, also further supports the assessment of PIG in the variation of groundwater quality.
-
The TDS, Mg2+, Na+, \( {\text{Cl}}^{ - } \), \( {\text{SO}}_{4}^{2 - } \) and \( {\text{NO}}_{3}^{ - } \) are considered as indicators in assessing the pollution sources.
References
APHA (2012) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 22nd edn. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC
Barzegar R, Moghaddam AA, Najib M, Kazemian N, Adamowski J (2016a) Characterization of hydrogeologic properties of the Tabriz plain multi-layer aquifer system, NW Iran. Arab J Geosci 9:147. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-2229-1
Barzegar R, Moghaddam AA, Tziritis E (2016b) Assessing the hydrogeochemistry and water quality of the Aji-Chay River, northwest of Iran. Environ Earth Sci 75:1486. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-6302-1
Barzegar R, Moghaddam AA, Tziritis E (2017a) Hydrogeochemical features of groundwater resources in Tabriz plain, northwest of Iran. Appl Water Sci 7:3997–4011
Barzegar R, Moghaddam AA, Tziritis E, Fakhri MS, Soltani S (2017b) Identification of hydrogeochemical processes and pollution sources of groundwater resources in the Marand plain, northwest of Iran. Environ Earth Sci 76:297. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6612-y
BIS (2012) Drinking water specifications. Bureau of Indian Standards, IS 10500, New Delhi, India
CGWB (2013) Groundwater brochure, Prakasam district. Central Ground Water Board, Government of India, New Delhi
Chakraborti D, Das B, Murrill MT (2011) Examining India’s groundwater quality management. Environ Sci Technol 45:27–33
Cushing EM, Kantrowitz IH, Taylor KR (1973) Water resources of the Delmarva Peninsular. U. S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 822, Washington, p 58
Datta PS, Tyagi SK (1996) Major ion chemistry of groundwater in Delhi area: chemical weathering processes and groundwater flow regime. J Geol Soc India 47:179–188
Domenico PA, Schwartz FW (1990) Physical and chemical hydrogeology. Wiley, New York, p 824
Drever JI (1997) The geochemistry of natural waters. Prentice Hall, Englewood, p 379
Gautam SK, Maharana C, Sharma D, Singh AK, Tripathi JK, Singh SK (2015) Evaluation of groundwater quality in the chotanagpur plateau region of the Subarnarekha river basin, Jharkhand State, India. Sustain water Qual Ecol 6:57–74
Ghalib HB (2017) Groundwater chemistry evaluation for drinking and irrigation utilities in east Wasit province, Central Iraq. Appl Water Sci 7:3447–3467. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-017-0575-8
Han G, Liu C-Q (2004) Water geochemistry controlled by carbonate dissolution: a study of the river waters draining karst-dominated terrain, Guizhou province, China. Chem Geol 204:1–21
Hem JD (1991) Study and interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural water: USGS Professional Paper Book 2254. Scientific Publishers, Jodhpur, p 263
Jalali M (2009) Geochemistry characterization of groundwater in an agricultural area of Razan, Hamadan, Iran. Environ Geol 56:1479–1488
Kumar M, Ramanathan AL, Rao MS, Kumar B (2006) Identification and evaluation of hydrogeochemical processes in the groundwater environment of Delhi, India. Environ Geol 50:1025–1039
Li P, Wu J, Qian H (2016a) Hydrochemical appraisal of groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation purposes and the major influencing factors: a case study in and around Hua County, China. Arab J Geosci 9:15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-2059-1
Li P, Wu J, Qian H (2016b) Preliminary assessment of hydraulic connectivity between river water and shallow groundwater and estimation of their transfer rate during dry season in the Shidi River, China. Environ Earth Sci 75(2):99. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4949-7
Li P, Wu J, Tian R, He S, He X, Xue Ch, Zhang K (2018) Geochemistry, hydraulic connectivity and quality appraisal of multilayered groundwater in the Hongdunzi coal mine, Northwest China. Mine Water Environ 37:222–237. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-017-0507-8
Marghade D, Malpe DB, Zade AB (2012) Major ion chemistry of shallow groundwater of a fast growing city of Central India. Environ Monit Assess 184:2405–2418
Nag SK, Das Sh (2017) Assessment of groundwater quality from Bankura I and II Blocks, Bankura district, West Bengal, India. Appl Water Sci 7:2787–2802. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-017-0530-8
Nagaraju A, Balaji E, Sun LH, Thejaswi A (2018) Processes controlling groundwater chemistry from Mulakalacheruvu area, Chittoor district, Andhra Pradesh, South India: a statistical approach based on hydrochemistry. J Geol Soc India 91:425–430
Nishi K, Singh PK, Kumar B (2018) Hydrogeochemical characterization and groundwater quality of Jamshedpur urban agglomeration in Precambrian Terrain, Eastern India. J Geol Soc India 92:67–75
Piper AM (1944) A graphical procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water analysis. Trans Am Geophys Union 25:914–928
Priyanka S, Smita S, Gayatri D (2017) Seasonal variation of groundwater quality in rural areas of Jaipur district, Rajasthan. Ind J Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.17485/ijst/2017/v10i30/115534
Ramyapriya R, Elango L (2018) Evaluation of geogenic and anthropogenic impacts on spatio-temporal variation in quality of surface water and groundwater along Cauvery River, India. Environ Earth Sci 77:2. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-7176-6
Rao PN, Rao AD, Bhargav JS, Siva Sankar K, Sudarshan G (2014) Regional appraisal of the fluoride occurrence in groundwaters of Andhra Pradesh. J Geol Soc India 84:483–493
Selvakumar S, Chandrasekhar N, Kumar G (2017) Hydrogeochemical characteristics and groundwater contamination in the rapid urban development areas of Coimbatore, India. Water Resour Ind 17:23–33
Selvam S, Singaraja C, Venkatramanan S, Chung SY (2018) Geochemical appraisal of groundwater quality in Ottapidaram taluk, Thoothukudi district, Tamilnadu, using graphical and numerical method. J Geol Soc India 92:313–320
Shaji E, Gomez A, Hussein S, Deepu TR, Anilkumar Y (2018) Salinization and deterioration of groundwater quality by nitrate and fluoride in the Chittur block, Palakkad, Kerala. J Geol Soc India 92:337–345
Singh VK, Bikundia DS, Sarswat A, Mohan D (2012) Groundwater quality assessment in the village of Lutfullapur Nawada, Loni, district Ghaziabad, Uttar Pradesh. India Environ Monit Assess 184:4473–4488
Stallard RE, Edmond JM (1983) Geochemistry of Amazon River: the influence of the geology and weathering environment on the dissolved load. J Geophys Res 88:9671–9688
Stumm W, Morgan JJ (1996) Aquatic chemistry. Wiley, New York, p 1022
Su H, Kang W, Xu Y, Wang J (2017) Evaluation of groundwater quality and health risks from contamination in the north edge of the loess plateau, Yulin City, Northwest China. Environ Earth Sci 76:467. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6781-8
Subba Rao N (2012) PIG: a numerical index for dissemination of groundwater contamination zones. Hydrol Process 26:3344–3350
Subba Rao N (2017a) Hydrogeology: problems with solutions. Prentice Hall of India, New Delhi, India, p 265
Subba Rao N (2017b) Controlling factors of fluoride in groundwater in a part of South India. Arab J Geosci 10:524. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-3291-7
Subba Rao N (2018) Groundwater quality from a part of Prakasam district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Appl Water Sci 8:30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-018-0665-2
Subba Rao N, Surya Rao P (2010) Major ion chemistry of groundwater in a river basin: a study from India. Environ Earth Sci 61:757–775
Subba Rao N, Surya Rao P, Venktram Reddy G, Nagamani M, Vidyasagar G, Satyanarayana NLVV (2012) Chemical characteristics of groundwater and assessment of groundwater quality in Varaha River Basin, Visakhapatnam district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ Mon Assess 184:5189–5214
Subba Rao N, Marghade D, Dinakar A, Chandana I, Sunitha B, Ravindra B, Balaji T (2017) Geochemical characteristics and controlling factors of chemical composition of groundwater in a part of Guntur district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ Earth Sci 76:747. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-7093-8
Sun LH, Gui HR (2015) Source quantification of major ions in groundwater and hydrological implications: Liuqiao case study. Electron J Geotech Eng 20:1791–1800
Todd DK (1980) Groundwater hydrology. Wiley, New York, p 535
WHO (2015) Guidelines for drinking water quality. World Health Organization, Geneva
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the reviewers and editor of the journal for their valuable and constructive suggestions to improve the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Rao, N.S., Sunitha, B., Rambabu, R. et al. Quality and degree of pollution of groundwater, using PIG from a rural part of Telangana State, India. Appl Water Sci 8, 227 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-018-0864-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-018-0864-x