Abstract
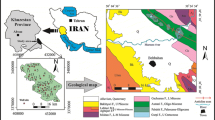
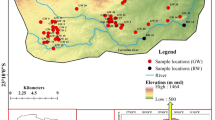
Chittur block represents a mid-land region of Palakkad district, Kerala and the block differs from the rest of the blocks in its climate and availability of groundwater. About 75% of the people depend on agriculture for their livelihood. Results showed that groundwater salinity levels (up to 1,963 mg/L TDS),fluoride (up to 6.3 mg/L) and nitrate (up to 141 mg/L) contents have increased significantly in tandem with the increase in groundwater abstraction. Before human intervention the chemical weathering of gneisses and granites was the main process impinging on the chemical signature of groundwater. The initial chemical equilibrium conditions change with increasing groundwater withdrawal rates and fertilizer input, in a milieu of lower natural groundwater recharge. The appearance of higher levels of bicarbonate, linked to denitrification processes, and the decrease in calcium, due to calcite precipitation, can lead to increased content of sodium and fluoride in groundwater. In this scenario the use of groundwater resources for human consumption and agriculture represents a public health risk if water management actions do not change the trend in water use in the near future. The potential loss of fertile soil by groundwater salinization must also be considered when planning sustainable policies in a region with over dependence on groundwater resources.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Apello, C.A.J. and Postma, D. (2005) Geochemistry, groundwater and pollution, 2nd edition, A.A. Balkema Publishers, Leiden, 536p.
APHA-AWWA-WEF (1998) Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20, Washington, American Public Health Association.
Ayoob, S. and Gupta, A.K. (2006) Fluoride in drinking water: a review on the status and stress effects. Critical Reviews in Environ. Sci. Tech., v.36, pp.433–487.
Bell, M.C. and Ludwig, T.G. (1970) The supply of fluoride to man: ingestion from water. Fluorides and Human Health, WHO Monograph Series, v.9, pp.18–32.
Benson, V.S., Van Leeuwen, J.A., Sanchez, J., Dohoo, I.R. and Somers, G.H. (2006) Spatial analysis of land use impact on ground water nitrate concentrations. Jour. Environ. Quality, v.35, pp.421–432.
BGS (2003). Water quality Fact Sheet: Nitrate.Water Aid. London.
BIS (2009) Draft Indian Standard. Drinking Water Specification (2nd Revision of IS 10500). ICS No 13.060.20.Bureau of Indian Standards. Manak Bhawan, 9 Bahadur Shah Zafar Marg. New Delhi, 24p.
Brindha, K. and Elango, L. (2012).Groundwater quality zonation in a shallow weathered rock aquifer using GIS. Geo-spatial Information Science, v.15, pp.95–104.
Brindha, K. and Elango, L. (2013) Geochemistry of fluoride rich groundwater in a weathered granitic rock region, Southern India. Water Quality, Exposure and Health, v.5, pp.127–138.
Brown, D.W. and Roberson, C.E. (1977). Solubility of natural fluorite at 25°C. USGS, Jour. Res., v.5, pp.509–517.
CGWB (2007) Dynamic groundwater resources of India as on 31st March 2004. Central Ground Water Board (CGWB), Ministry of Water Resources Government of India, Faridabad, India.
CGWB (2009) District Groundwater Management Studies Palghat District. Unpublished Report, Central Ground Water Board, Kerala region.
CGWB (2010)Ground water quality in shallow aquifers of India. Central Ground Water Board, Ministry of Water Resources Government of India, Faridabad, India.
CGWB (2015) Dynamic groundwater resources of India as on March 2013. Central Ground Water Board (CGWB), Ministry of Water Resources Government of India, Kerala Region, 30p.
De Andrade, E.M., Palácio, H.A.Q., Souza, I.H., de Oliveira Leão, R.A. and Guerreiro, M.J. (2008). Land use effects in groundwater composition of an alluvial aquifer (Trussu River, Brazil) by multivariate techniques. Environmental research, v.106, pp.170–177.
De Roos, A. J., Ward, M. H., Lynch, C. F. and Cantor, K. P. (2003). Nitrate in public water supplies and the risk of colon and rectum cancers. Epidemiology, v.14, pp.640–649.
Deepu, T.R. and Shaji, E. (2011) Fluoride contamination in groundwater resources of Chittur block, Palghat district, Kerala, India—a health risk. In: Disaster, Risk and Vulnerablity Conference, pp.12–14.
Dhiman, S.D. and Keshari, A.K. (2006) Hydrogeochemical evaluation of highfluoride groundwaters: a case study from Mehsana District, Gujarat, India. Hydrolog. Sci. Jour., v.51, pp.1149–1162.
Flowers, T.J. (1999). Salinisation and horticultural production. Scientia Horticulturae, v.78, pp.1–4.
Freeze, R.A. and Cherry, J.A. (1979) Groundwater, 604p.
Gómez, P. and Turrero, M.J. (1994). Unarevisión de los procesosgeoquímicas de bajatemperatura en la interacciónagua-roca. Estudios Geológicos, v.50, pp.345–357.
Gulis, G., Czompolyova, M. and Cerhan, J. R. (2002). An ecologic study of nitrate in municipal drinking water and cancer incidence in Trnava District, Slovakia. Environ. Res., v.88, pp.182–187.
Handa, B.K. (1975). Geochemistry and genesis of Fluoride Containing ground waters in india. Groundwater, v.13, pp.275–281.
Hasegawa, P. M., Bressan, R. A., Zhu, J. K. and Bohnert, H. J. (2000). Plant cellular and molecular responses to high salinity. Annual Review of Plant Biology, v.51, pp.463–499.
Jacks, G., Bhattacharya, P., Chaudhary, V. and Singh, K. P. (2005). Controls on the genesis of some high-fluoride groundwaters in India. Appld. Geochemistry, v.20, pp.221–228.
Jadhav, S.V., Bringas, E., Yadav, G.D., Rathod, V.K., Ortiz, I. and Marathe, K.V. (2015) Arsenic and fluoride contaminated groundwaters: a review of current technologies for contaminants removal. Jour. Environ. Managmt., v.162, pp.306–325.
Jalali, M. (2009). Geochemistry characterization of groundwater in an agricultural area of Razan, Hamadan, Iran. Environ. Geol., v.56, pp.1479–1488.
Jiang, Y., Zhang, C., Yuan, D., Zhang, G. and He, R. (2008) Impact of land use change on groundwater quality in a typical karst watershed of southwest China: a case study of the Xiaojiang watershed, Yunnan Province. Hydrogeol. Jour., v.16, pp.727–735.
Jones, B. F., Vengosh, A., Rosenthal, E. and Yechieli, Y. (1999) Chapter 3; Geochemical investigations. In: Bear, J., Cheng, A. H. D., Sorek, S., Ouazar, D., & Herrera, I., (Eds.), Seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers—concepts, methods and practices Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp.51–72.
Korom, S. F. (1992) Natural denitrification in the saturated zone: a review. Water Resour. Res., v.28, pp.1657–1668.
Mahramanlioglu, M., Kizilcikli, I. and Bicer, I.O. (2002) Adsorption of fluoride from aqueous solution by acid treated spent bleaching earth. Jour. Fluorine Chemistry, v.115, pp.41–47.
Martinez-Beltran, J. and Manzur, C. L. (2005) Overview of salinity problems in the world and FAO strategies to address the problem. In: Proceedings of the international salinity forum, Riverside, California USDA-ARS Salinity Lab Riverside, pp.311–313.
Martín-Queller, E., Moreno-Mateos, D., Pedrocchi, C., Cervantes, J. and Martínez, G. (2010) Impacts of intensive agricultural irrigation and livestock farming on a semi-arid Mediterranean catchment. Environ. Monit. Assess., v.167, pp.423–435.
Mengis, M., Schif, S. L., Harris, M., English, M. C., Aravena, R., Elgood, R. J. and MacLean, A. (1999) Multiple geochemical and isotopic approaches for assessing ground water NO3–elimination in a riparian zone. Groundwater, v.37, pp.448–457.
Piper, A. M. (1944). A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water analyses. Eos, Trans. AGU, v.25, pp.914–928.
Rafique, T., Naseem, S., Usmani, T.H., Bashir, E., Khan, F.A. and Bhanger, M.I. (2009) Geochemical factors controlling the occurrence of high fluoride groundwater in the Nagar Parkar area, Sindh, Pakistan. Jour. Hazardous Materials, v.171, pp.424–430.
Raj, D. and Shaji, E. (2017) Fluoride contamination in groundwater resources of Alleppey, southern India. Geoscience Frontiers, v.8(1), pp.117–124.
Raju, N. J., Dey, S., Gossel, W. and Wycisk, P. (2012). Fluoride hazard and assessment of groundwater quality in the semi-arid Upper Panda River basin, Sonbhadra district, Uttar Pradesh, India. Hydrological Sci. Jour., v.57, pp.1433–1452.
Reddy, A.G.S., Reddy, D.V., Rao, P.N. and Prasad, K.M. (2010). Hydrogeochemical characterization of fluoride rich groundwater of Wailpalli watershed, Nalgonda District, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ. Monit. Assess., v.171, pp.561–577.
Rivett, M. O., Buss, S.R., Morgan, P., Smith, J.W. and Bemment, C.D. (2008) Nitrate attenuation in groundwater: a review of biogeochemical controlling processes. Water Res., v.42, pp.4215–4232.
Saxena, V. and Ahmed, S. (2003) Inferring the chemical parameters for the dissolution of fluoride in groundwater. Environ. Geol., v.43, pp.731–736.
Shaji, E., Viju, J. and Thambi, D.S. (2007) High fluoride in groundwater of Palghat District, Kerala. Curr. Sci., pp.240–245.
Shaji, E. (2009). Ground water scenario for Chittur block, Palghat district, Unpublished technical report, CGWB, Kerala Region.
Shaji, E. (2012). Source Characterization And Remediation Of Fluoride Contamination In Groundwater Resource Of Chittur Block, Palghat District, Kerala. Project report submitted to KSCSTE, Govt of Kerala.
Singh, C. K. and Mukherjee, S. (2015). Aqueous geochemistry of fluoride enriched groundwater in arid part of Western India. Environ. Sci.Pollution Res., v.22, pp.2668–2678.
Susheela, A.K., Kumar, A., Bhatnagar, M. and Bahadur, R. (1993) Prevalence of endemic fluorosis with gastrointestinal manifestations in people living in some north-Indian villages. Fluoride, v.26, pp.97–104.
Suthar, S., Bishnoi, P., Singh, S., Mutiyar, P.K., Nema, A.K. and Patil, N.S. (2009). Nitrate contamination in groundwater of some rural areas of Rajasthan, India. Jour. Hazardous Materials, v.171, pp.189–199.
Vengosh, A. (2003). Salinization and saline environments. Treatise on Geochemistry, v.9, pp.333–365.
Ward, M.H., De Kok, T.M., Levallois, P., Brender, J., Gulis, G., Nolan, B.T. and VanDerslice, J. (2005). Workgroup report: Drinking-water nitrate and health-recent findings and research needs. Environ. Health Perspectives, v.113, pp.1607–1614.
Yang, C.Y., Wu, D.C. and Chang, C.C. (2007) Nitrate in drinking water and risk of death from colon cancer in Taiwan. Environ. Internat., v.33, pp.649–653.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shaji, E., Gómez-Alday, J., Hussein, S. et al. Salinization and Deterioration of Groundwater Quality by Nitrate and Fluoride in the Chittur Block, Palakkad, Kerala. J Geol Soc India 92, 337–345 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-018-1017-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-018-1017-4