Abstract
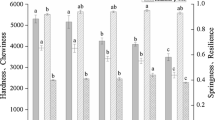
This work aimed to evaluate the microstructural, physicochemical and sensorial properties of buffalo meat patties produced using different mixing equipment (bowl cutter, universal mixer, and meat mixer). Scanning electron microscopy revealed a more homogenize emulsion, cohesive structure and smaller pore size of patties produced using the bowl cutter, which significantly reduced the total fluid release, water release, fat release and cooking loss as compared to the universal mixer and meat mixer. Production of the buffalo meat patties using bowl cutter also improved the moisture retention and gel strength of the patties. The patties produced using bowl cutter had the significantly highest lightness and yellowness values, while the redness was the lowest. Lower hardness, gumminess and chewiness also were observed from the patties produced using bowl cutter. Quality of the microstructural and physicochemical properties of the patties produced using different equipment can be organized as bowl cutter > universal mixer > meat mixer. Nevertheless, the sensory evaluation demonstrated a higher preference on aroma, flavour and overall acceptability of patties produced using meat mixer due to coarser and meaty texture, while the colour, tenderness, juiciness and springiness did not differ against using bowl cutter and universal mixer.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Naeem HHS, Mohamed HMH (2016) Improving the physico-chemical and sensory characteristics of camel meat burger patties using ginger extract and papain. Meat Sci 118:52–60
Allais I (2010) Emulsification. In: Handbook of meat processing, 1st edn. Wiley-Blackwell, Iowa, USA, pp 143–168
AOAC (2000) Official Methods of Analysis, 17th edn. Association of Official Analytical Chemists
Asghar A, Samejima K, Yasui T, Henrickson RL (1985) Functionality of muscle proteins in gelation mechanisms of structured meat products. CRC Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 22(1):27–106
Aslinah LNF, Yusoff MM, Ismail-Fitry MR (2018) Simultaneous use of adzuki beans (Vigna angularis) flour as meat extender and fat replacer in reduced-fat beef meatballs (bebola daging). J Food Sci Technol 55(8):3241–3248
Brennan JG (2012) Mixing, emulsification and size reduction. In: Food processing handbook, 2nd ed. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, Germany, pp 513–558
Cofrades S, López-López I, Solas MT, Bravo L, Jiménez-Colmenero F (2008) Influence of different types and proportions of added edible seaweeds on characteristics of low-salt gel/emulsion meat systems. Meat Sci 79(4):767–776
Devatkal SK, Manjunatha M, Narsaiah K, Patil RT (2014) Evaluation of quality characteristics of chicken meat emulsion/nuggets prepared by using different equipment. J Food Sci Technol 51(3):511–518
Ducept F, De Broucker T, Souli JM, Trystram G, Cuvelier G (2012) Influence of the mixing process on surimi seafood paste properties and structure. J Food Eng 108(4):557–562
El-Magoli SB, Laroia S, Hansen PMT (1996) Flavor and texture characteristics of low fat ground beef patties formulated with whey protein concentrate. Meat Sci 42(2):179–193
Gordon A, Barbut S (1992) Effect of chemical modifications on the stability, texture and microstructure of cooked meat batters. Food Struct 11(2):133–146
Gurikar AM, Lakshmanan V, Gadekar YP, Sharma BD, Anjaneyulu ASR (2014) Effect of meat chunk size, massaging time and cooking time on quality of restructured pork blocks. J Food Sci Technol 51(7):1363–1369
Habib H, Siddiqi RA, Dar AH, Dar MA, Gul K, Rashid N, Siddiqi US (2018) Quality characteristics of carabeef nuggets as affected by pomegranate rind powder. J Food Meas Charact 12(3):2164–2173
Heinz G, Hautzinger P (2007) Meat processing technology for small to medium-scale producers. FAO Regional Office for Asia and the Pacific
Heydari F, Varidi MJ, Varidi M, Mohebbi M (2016) Study on quality characteristics of camel burger and evaluating its stability during frozen storage. J Food Meas Charact 10(1):148–155
Hollenbeck JJ, Apple JK, Yancey JWS, Johnson TM, Kerns KN, Young AN (2019) Cooked color of precooked ground beef patties manufactured with mature bull trimmings. Meat Sci 148:41–49
Krzywdzińska-Bartkowiak M, Piatek M, Dolata W (2014) A comparative quality appraisal of finely comminuted batters produced using three types of knives. Meat Sci 96(1):429–435
Kuraishi C, Sakamoto J, Yamazaki K, Susa Y, Kuhara C, Soeda T (1997) Production of restructured meat using microbial transglutaminase without salt or cooking. J Food Sci 62(3):488–490
Lachowicz K, Sobczak M, Gajowiecki L, Zych A (2003) Effects of massaging time on texture, rheological properties, and structure of three pork ham muscles. Meat Sci 63(2):225–233
Lytras GN, King RD, Ledward DA (2000) Prediction of the soluble myoglobin content of cooked burgers. Meat Sci 55(2):247–250
Pietrasik Z (1999) Effect of content of protein, fat and modified starch on binding textural characteristics, and colour of comminuted scalded sausages. Meat Sci 51:17–25
Serdaroğlu M, Öztürk B, Urgu M (2016) Emulsion characteristics, chemical and textural properties of meat systems produced with double emulsions as beef fat replacers. Meat Sci 117:187–195
Suman SP, Sharma BD (2003) Effect of grind size and fat levels on the physico-chemical and sensory characteristics of low-fat ground buffalo meat patties. Meat Sci 65(3):973–976
Sun XD, Holley RA (2011) Factors influencing gel formation by myofibrillar proteins in muscle foods. Comp Rev Food Sci Food Saf
Thomas R, Anjaneyulu ASR, Kondaiah N (2006) Quality and shelf life evaluation of emulsion and restructured buffalo meat nuggets at cold storage (4 ± 1 °C). Meat Sci 72(3):373–379
Tornberg E (2005) Effects of heat on meat proteins—implications on structure and quality of meat products. Meat Sci 70(3):493–508
Vasanthi C, Venkataramanujam V, Dushyanthan K (2007) Effect of cooking temperature and time on the physico-chemical, histological and sensory properties of female carabeef (buffalo) meat. Meat Sci 76(2):274–280
Youssef MK, Barbut S (2009) Effects of protein level and fat/oil on emulsion stability, texture, microstructure and color of meat batters. Meat Sci 82(2):228–233
Youssef MK, Barbut S, Smith A (2011) Effects of pre-emulsifying fat/oil on meat batter stability, texture and microstructure. Int J Food Sci Technol 46(6):1216–1224
Zhou F, Dong H, Shao JH, Zhang JL, Liu DY (2018) Effect of chopping time and heating on 1H nuclear magnetic resonance and rheological behavior of meat batter matrix. Anim Sci J 89(4):695–702
Acknowledgements
Authors gratefully acknowledge the fund provided by Geran Putra—Insentif Putra Muda (GP-IPM/2016/9514500), Universiti Putra Malaysia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ismail, M.A., Chong, G.H. & Ismail-Fitry, M.R. Comparison of the microstructural, physicochemical and sensorial properties of buffalo meat patties produced using bowl cutter, universal mixer and meat mixer. J Food Sci Technol 58, 4703–4710 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-020-04960-y
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-020-04960-y