Abstract
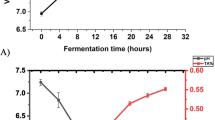
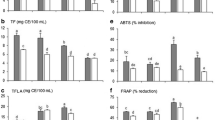
In this study, the changes of anthocyanin content, total phenols, antioxidant capacity, microbiota composition before and after digestion and intestine fermentation in stomach and intestine were studied. The results indicated that after simulated gastrointestinal digestion, compared with the original sample, the total phenol content and anthocyanin content of intestinal digestion group for 2 h (ID 2 group) decreased by 53.64% and 70.45%, respectively, DPPH inhibition rate was 32.75% and T-AOC values of the extracts decreased to 62.89U/mg. The anthocyanins were identified to be composed of cyanidin-3-arabinoside, cyanidin-3-galactoside, cyanidin-3-xyloside, and cyanidin-3-glucoside. Black Chokeberry (Aronia melanocarpa (Michx.) Elliot) anthocyanins significantly increased the relative richness of Bacteroides, promoted the growth of Bifidobacterium, Blautia, Faecalibacterium, and inhibited the growth of Prevotella, Megamonas, Escherichia/Shigella, etc. Anthocyanins have a positive regulatory effect on intestinal flora. These studies also provide essential information for the development of anthocyanin related health care products and drug products.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alara OR, Abdurahman NH, Mudalip SKA, Olalere OA (2017) Characterization and effect of extraction solvents on the yield and total phenolic content from Vernonia amygdalina leaves. J Food Meas Charact 12:311–316
Appel K, Meiser P, Millan E, Collado JA, Rose T, Gras CC (2015) Chokeberry (Aronia melanocarpa (Michx.) Elliot) concentrate inhibits NF-kappa B and synergizes with selenium to inhibit the release of pro-inflammatory mediators in macrophages. Fitoterapia 105:73–82
Azm SAN, Djazayeri A, Safa M, Azami K, Ahmadvand B, Sabbaghziarani F (2018) Lactobacilli and bifidobacteria ameliorate memory and learning deficits and oxidative stress in β-amyloid (1–42) injected rats. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 43:718–726
Burapan S, Kim M, Han J (2017) Demethylation of polymethoxyflavones by human gut bacterium, Blautia sp. MRG-PMF1. J Agr Food Chem 65:1620–1629
Bursać Kovačević D, Barba FJ, Granato D, Galanakis CM, Herceg Z, Dragović-Uzelac V (2018) Pressurized hot water extraction (PHWE) for the green recovery of bioactive compounds and steviol glycosides from Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni leaves. Food Chem 254:150–157
Chen J, Chen Q, Xie C, Ahmad W, Zhao L (2019) Effects of simulated gastric and intestinal digestion on chitooligosaccharides in two in vitro models. Int J Food Sci Technol 1:1–10
Chena G, Xiea M, Peng W, Dan C, Hong Y (2017) Digestion under saliva, simulated gastric and small intestinal conditions and fermentation in vitro by human intestinal microbiota of polysaccharides from Fuzhuan brick tea. Food Chem 244:331–339
Colin D (2006) Aspects of anthocyanin absorption, metabolism and pharmacokinetics in humans. Nutr Res Rev 19:137–146
Correa J, Allen E, Mcdonald J, Schroeter K, Corredig M, Paliyath G (2014) Stability and biological activity of wild blueberry (Vaccinium angustifolium) polyphenols during simulated in vitro gastrointestinal digestion. Food Chem 165:522–531
Dai J, Gupte A, Gates L, Mumper RJ (2009) A comprehensive study of anthocyanin-containing extracts from selected blackberry cultivars: extraction methods, stability, anticancer properties and mechanisms. Food Chem Toxicol 47:837–847
Daniel AO, Lovie M, Malak AH, Reza T (2018) Application of protein-based edible coatings for fat uptake reduction in deep-fat fried foods with an emphasis on muscle food proteins. Trends Food Sci Technol 80:167–174
Fazenda PP, Fonseca M, Carlier J, Leitão J (2019) Identification and validation of microsatellite markers in strawberry tree (Arbutus unedo L.). Turk J Agric For 43:430–436
Finotti A, Treves S, Zorzato F, Gambari R, Feriotto G (2009) Upstream stimulatory factors are involved in the P1 promoter directed transcription of the A β H-J-J locus. BMC Mol Biol 9:110–119
Galanakis MC (2015) Separation of functional macromolecules and micromolecules: from ultrafiltration to the border of nanofiltration. Trends Food Sci Technol 42:44–63
Galanakis CM (2018) Phenols recovered from olive mill wastewater as additives in meat products. Trends Food Sci Technol 79:98–105
Galanakis CM, Tsatalas P, Galanakis IM (2018) Implementation of phenols recovered from olive mill wastewater as UV booster in cosmetics. Ind Crop Prod 111:30–37
Halasz JA (2010) S-genotyping supports the genetic relationships between Turkish and Hungarian apricot germplasm. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 135:410–417
Gill SR, Pop M, Deboy RT, Eckburg PB, Turnbaugh PJ, Samuel BS (2006) Metagenomic analysis of the human distal gut microbiome. Science 312:1355–1359
Huang Z, Hua Y, Tian Y, Qin C, Gu M (2018) High expression of fructose-bisphosphate aldolase A induces progression of renal cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep 39:2996–3006
Jamar G, Estadella D, Pisani LP (2017) Contribution of anthocyanin-rich foods in obesity control through gut microbiota interactions. BioFactors 43:507–516
Ji B (2014) Stability and absorption of anthocyanins from blueberries subjected to a simulated digestion process. Int J Food Sci Nutr 65:440–448
Jung H, Lee HJ, Cho H, Lee K, Kwak HK, Hwang KT (2015) Anthocyanins in Rubusfruits and antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities in RAW 264.7 cells. Food Sci Biotechnol 24:1879–1886
Kulling S, Rawel H (2008) Chokeberry (Aronia melanocarpa)—a review on the characteristic components and potential health effects. Planta Med 74:1625–1634
Lee KM, Min K, Choi O, Kim KY, Woo HM, Kim Y (2015) Electrochemical detoxification of phenolic compounds in lignocellulosic hydrolysate for Clostridium fermentation. Bioresour Technol 187:228–234
Liang G, Malmuthuge N, Bao H, Stothard P, Griebel PJ, Guan LL (2016) Transcriptome analysis reveals regional and temporal differences in mucosal immune system development in the small intestine of neonatal calves. BMC Genom 17:602–611
Lonneke O, Richard D, Karolien VD, Celine DM, Karen V, Freddy H (2015) Steering endogenous butyrate production in the intestinal tract of broilers as a tool to improve gut health. Fron Vet Sci 2:75–76
Moroz VM (2002) Roles of the caudate nuclei, cerebellum, and caudato-cerebellar interconnections in the control and coordination of ballistic food-procuring movements. Neurophysiol 34:395–405
Nagarajan J, Krishnamurthy NP, Nagasundara Ramanan R, Raghunandan ME, Galanakis CM, Ooi CW (2019) A facile water-induced complexation of lycopene and pectin from pink guava byproduct: extraction, characterization and kinetic studies. Food Chem 296:47–55
Nilufer-Erdil D (2014) Investigating the effects of food matrix and food components on bioaccessibility of pomegranate (Punica granatum) phenolics and anthocyanins using an in-vitro gastrointestinal digestion model. Food Res Int 62:1069–1079
Oh SY, Youn SY, Park MS, Baek NI, Ji GE (2018) Synthesis of stachyobifiose using bifidobacterial α-galactosidase purified from recombinant Escherichia coli. J Agric Food Chem 66:1184–1190
Park GS, Min HP, Shin W, Zhao C, Kim HJ (2017) Emulating host-microbiome ecosystem of human gastrointestinal tract in vitro. Stem Cell Rev 13:1–14
Park SN, Lim YK, Shin JH, Jo E, Kook JK (2019) Prevotella koreensis sp. nov., isolated from human subgingival dental plaque of periodontitis lesion. Curr Microbiol 76:1055–1060
Puupponen-Pimia R, Nohynek L, Hartmann SS, Heinonen M, Oksman KM (2005) Berry phenolics selectively inhibit the growth of intestinal pathogens. J Appl Microbiol 98:991–1000
Rivière J (1997) Differentiation between naproxen, naproxen-protein conjugates, and naproxen-lysine in plasma via micellar electrokinetic capillary chromatography—a new approach in the bioanalysis of drug targeting preparations. Clin chem 43:2083
Rosacmillán J, OronaPadilla JL, Florescmoreno VM, SernaSaldivar SO (2020) Effect of Jet-cooking and hydrolyses with amylases on the physicochemical and in vitro digestion performance of whole chickpea flours. Pediatr Res 32:145–148
Ryu D, Koh E (2018) Stability of anthocyanins in bokbunja (Rubus occidentalis L.) under in vitro gastrointestinal digestion. Food Chem 30:157–162
Şahin S, Elhussein E, Bilgin M, Lorenzo JM, Barba FJ, Roohinejad S (2018) Effect of drying method on oleuropein, total phenolic content, flavonoid content, and antioxidant activity of olive (Olea europaea) leaf. J Food Process Preserv 42:e13604
Sangkanu S, Rukachaisirikul V, Suriyachadkun C, Phongpaichit S (2017) Evaluation of antibacterial potential of mangrove sediment-derived actinomycetes. Microb Pathog 112:303–312
Senica MS, Mikulic PM (2019) Different extraction processes affect the metabolites in blue honeysuckle (Lonicera caerulea L. subsp. edulis) food products. Turk J Agric For 43:576–585
Sun D, Huang S, Cai S, Cao J, Han P (2015) Digestion property and synergistic effect on biological activity of purple rice (Oryza sativa L.) anthocyanins subjected to a simulated gastrointestinal digestion in vitro. Food Res Int 78:114–123
Suzihaque MUH, Ibrahim UK, Hashib SA, Asri NASM (2017) Antioxidant determination of fiber-enriched milk powder. Adv Sci Lett 23:3897–3902
Swer TL, Mukhim C, Bashir K, Chauhan K (2018) Optimization of enzyme aided extraction of anthocyanins from Prunus nepalensis L. LWT Food Sci Technol 91:382–390
Tanaka A (2001) Chemical components and characteristics of black chokeberry. Nip Sho Kogyo Gak 48:606–610
Turroni F, Milani C, Duranti S, Ferrario C, Ventura M (2017) Bifidobacteria and the infant gut: an example of co-evolution and natural selection. Cell Mol Life Sci 75:1–16
Wang M-L, Shen X, Ge L, He M, He F (2018) A preliminary study of the difference in composition of intestinal bifidobacteria between healthy infants and infants with allergic diseases. Chin J Contemp Pediatr 20:746–752
Wang Y, Zhao F, Zhang H, Fk D, Gao QT, Yu Y (2019) Contribution of digestive enzymes in simulated digestion of small intestine to digestibility of gross energy and crude protein of feed for pigs. Chin J Anim Nutr 37:3242–3250
Weller R, Glöckner FO, Amann R (2000) 16S rRNA-targeted oligonucleotide probes for the in situ detection of members of the phylum Cytophaga-Flavobacterium-Bacteroides. Syst Appl Microbiol 23:107–114
Worsztynowicz P, Napierala M, Bialas W, Grajek W, Pancreatic OM (2014) Pancreatic α-amylase and lipase inhibitory activity of polyphenolic compounds present in the extract of black chokeberry (Aronia melanocarpa L.). Process Biochem 49:1457–1463
Yabe S, Sakai Y, Abe K, Yokota A (2017) Diversity of Ktedonobacteria with actinomycetes-like morphology in terrestrial environments. Microbes Environ 32:61–70
Yang JY, Lee YS, Kim Y, Lee SH, Ryu S, Fukuda S (2016) Gut commensal Bacteroides acidifaciens prevents obesity and improves insulin sensitivity in mice. Mucosal Immunol 1:104–116
Yoon S, Yu J, Mcdowell A, Kim SH, Ko GP (2017) Bile salt hydrolase-mediated inhibitory effect of Bacteroides ovatus on growth of Clostridium difficile. J Microbiol 55:892–899
Yuki S, Tadashi S, Koji N, Hirokazu T (2018) Identification of phenol- and p-cresol-producing intestinal bacteria by using media supplemented with tyrosine and its metabolites. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 94:1–11
Zhang S, Zhao J, Xie C, Tan M, Li H (2018) Analysis and development proposals of Aronia mealnocarpa planting industry in Heilongjiang province. Asian Agric Res 10:28–30
Zhang L, Fan G, Ammar Khan M, Yan Z, Beta T (2020) Ultrasonic-assisted enzymatic extraction and identification of anthocyanin components from mulberry wine residues. Food Chem 63:214–225
Zinoviadou KG, Galanakis CM, Grimi N, Boussetta N, Mota MJ, Saraiva JA (2015) Fruit juice sonication: implications on food safety and physicochemical and nutritional properties. Food Res Int 77:743–752
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by "Liaoning Talent Program" Project in Liaoning Province (XLYC1902081).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Ethical approval
This experiment strictly abides by the ethical principles of human experiments, and the experimental methods and purposes conform to the ethical standards and international practices of human beings.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, W., Gao, J., Hao, R. et al. Effects of simulated digestion on black chokeberry (Aronia melanocarpa (Michx.) Elliot) anthocyanins and intestinal flora. J Food Sci Technol 58, 1511–1523 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-020-04664-3
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-020-04664-3