Abstract
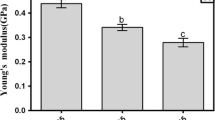
A new type of biodegradable film was formulated and characterized when based on the water-soluble-phase of Persian gum (SPG). The edible film was formulated optimally by using different concentrations of SPG (2.0, 2.5, 3.0, 3.5 and 4%) and glycerol as plasticizer (25, 35, and 35% based on dried SPG). Further examinations involved evaluating the manufactured films in terms of the barrier and physical properties, mechanical qualities, optical indices, microstructural properties and Fourier transform. The results showed that the increase in SPG and plasticizer content caused increases in thickness, moisture uptake, water vapor permeability and density of films (p < 0.05). Water solubility increased in response to higher concentrations of glycerol but decreased by higher amounts of dry matter (p < 0.05). The highest levels of the tensile strength (59.95%) and elongation at break (40.3 MPa) were obtained by SPG (3.5%) + 35% glycerol treatment. The L*, a* and opacity values decreased, while there was an increase in the b* value, as a result of increasing the plasticizer content (p < 0.05). A reduction occurred in the L* value of films, while the a* and b* values increased when using higher amounts of dry matter (p < 0.05). By analyzing the samples with field emission scanning electron microscopy, no cracks were observed on films when the contents of glycerol and dry matter were higher than 30% and 2.5%, respectively. The findings demonstrated that creating edible films from SPG can be an effective approach to the production of edible films.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi S (2017a) Challenges towards characterization and applications of a novel hydrocolloid: Persian gum. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 28:37–45
Abbasi S (2017b) Persian gum: a novel natural hydrocolloid. Nutr Food Sci Res 4:1–2
Arham R, Mulyati MT, Metusalach M, Salengke S (2016) Physical and mechanical properties of agar based edible film with glycerol plasticizer. Int Food Res J 23:1669–1675
ASTM (1995) Standard test methods for water vapour transmission of materials. In standards designations: E96–95. Annual book of ASTM standards. Philadelphia, Pa: American society for testing and materials.
ASTM (2001) Standard test method for tensile properties of thin plastic sheeting. Standard D882 ASTM, Annual book of ASTM, pp 162–170.
Beristain-Bauza SC, Mani-López E, Palou E, López-Malo A (2016) Antimicrobial activity and physical properties of protein films added with cell free supernatant of Lactobacillus rhamnosus. Food Control 62:44–51
Bourtoom T (2008) Edible films and coatings: characteristics and properties. Int Food Res J 15:237–248
Chevalier E, Assezat G, Prochazka F, Oulahal N (2018) Development and characterization of a novel edible extruded sheet based on different casein sources and influence of the glycerol concentration. Food Hydrocoll 75:182–191
Dabestani M, Kadkhodaee R, Phillips GO, Abbasi S (2018) Persian gum: a comprehensive review on its physicochemical and functional properties. Food Hydrocoll 78:92–99
Daza LD, Homez-Jara A, Solanilla JF, Váquiro HA (2018) Effects of temperature, starch concentration, and plasticizer concentration on the physical properties of ulluco (Ullucustuberosus Caldas)-based edible films. Int J Biol Macromol 120:1834–1845
Dick M, Costa TMH, Gomaa A, Subirade M, Rios ADO, Flôres SH (2015) Edible film production from chia seed mucilage: effect of glycerol concentration on its physicochemical and mechanical properties. Carbohydr Polym 130:198–205
Ekrami M, Emam-Djomeh Z (2014) Water vapor permeability, optical and mechanical properties of Salep-based edible film. J Food Process Preserv 38:1812–1820
Farhan A, Hani NM (2017) Characterization of edible packaging films based on semi-refined kappa-carrageenan plasticized with glycerol and sorbitol. Food Hydrocoll 64:48–58
Ghasemlou M, Aliheidari N, Fahmi R, Shojaee-Aliabadi S, KeshavarzB CMJ, Khaksar R (2013) Physical, mechanical and barrier properties of corn starch films incorporated with plant essential oils. Carbohydr Polym 98:1117–1126
Haq MA, Hasnain A, Jafri FA, Akbar MF, Khan A (2016) Characterization of edible gum cordia film: effects of beeswax. LWT - Food Sci Technol 68:674–680
Heidari M, Rahemi M, Daneshvar MH (2008) Effects of mechanical, chemical scarification and stratification on seed germination of Prunusscoparia (Spach) and Prunuswebbii (Spach) Vierh. Am Eurasian J Agric Environ Sci 3:114–117
Iamareerat B, Singh M, Sadiq MB, Anal AK (2018) Reinforced cassava starch based edible film incorporated with essential oil and sodium bentonite nanoclay as food packaging material. J Food Sci Technol 55:1953–1959
Kibar EAA, Ferhunde US (2017) starch-cellulose ether films: microstructure and water resistance. J Food Process Eng 40:1–8
Liang T, Wang L (2018) Preparation and characterization of a novel edible film based on Artemisia sphaerocephala Krasch. gum: effects of type and concentration of plasticizers. Food Hydrocoll 77:502–5018
Liu WG, Yao KD (2001) What causes the unfrozen water in polymers: hydrogen bonds between water and polymer chains? Polymer 42:3943–3947
Mohammadi S, Abbasi S, Scanlon MG (2016) Development of emulsifying property in Persian gum using octenylsuccinic anhydride (OSA). Int J Biol Macromol 89:396–405
Nafchi AM, Olfat A, Bagheri M, Nouri L, Karim AA, Ariffin F (2017) Preparation and characterization of a novel edible film based on Alyssum homolocarpum seed gum. J Food Sci Technol 54:1703–1710
Nur- Hanani ZA, Mc-Namara J, Roos YH, Kerry JP (2013) Effect of plasticizer content on the functional properties of extruded gelatine-based composite films. Food Hydrocoll 31:264–269
Osés J, Niza S, Ziani K, Maté JI (2009) Potato starch edible films to control oxidative rancidity of polyunsaturated lipids: effects of film composition, thickness and water activity. Int J Food Sci Technol 44:1360–1366
Ploypetchara T, Gohtani S (2018) Effect of sugar on starch edible film properties: plasticized effect. J Food Sci Technol 9:3757–3766
Raoufi N, Fang Y, Kadkhodaee R, Phillips GO, Najaf-Najafi M (2017) Changes in turbidity, zeta potential and precipitation yield induced by Persian gum-whey protein isolated interactions during acidification. J Food Process Preserv 41:1–8
Sadeghi-Varkani A, Emam-Djomeh Z, Askari G (2018) Physicochemical and microstructural properties of a novel edible film synthesized from Balangu Seed Mucilage. Int J Biol Macromol 108:1110–1119
Singh TP, Chatli MK, Sahoo J (2015) Development of chitosan based edible films: process optimization using response surface methodology. J Food Sci Technol 52:2530–2543
Sothornvit R, Pitak N (2007) Oxygen permeability and mechanical properties of banana films. Food Res Int 40:365–370
Soukoulis C, Singh P, Macnaughtan W, Parmenter C, Fisk I (2016) Compositional and physicochemical factors governing the viability of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG embedded in starch-protein based edible films. Food Hydrocoll 52:876–878
Tajik S, Maghsoudlou Y, Khodaiyan F, Jafari SM, Ghasemlou M, Aalami M (2013) Soluble soybean polysaccharide: a new carbohydrate to make a biodegradable film for sustainable green packaging. Carbohydr Polym 97:817–824
Tong DW, Mauer LJ, Wongruong S, Sriburi P, Rachtanapun P (2011) Effect of carboxymethyl cellulose concentration on physical properties of biodegradable cassava starch-based films. Chem Cent J 5:6
Vargas M, Albors A, Chiralt A, González-Martínez C (2011) Water interactions and microstructure of chitosan-methylcellulose composite films as affected by ionic concentration. LWT - Food Sci Technol 44:2290–2295
Wang X, Guo C, Hao W, Ullah N, Chen L, Li Z, Feng X (2018) Development and characterization of agar-based edible films reinforced with nano-bacterial cellulose. Int J Biol Macromol 118:722–730
Zhang P, Zhao Y, Shi Q (2016) Characterization of a novel edible film based on gum ghatti: effect of plasticizer type and concentration. Carbohydr Polym 153:345–355
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pak, E.S., Ghaghelestani, S.N. & Najafi, M.A. Preparation and characterization of a new edible film based on Persian gum with glycerol plasticizer. J Food Sci Technol 57, 3284–3294 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-020-04361-1
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-020-04361-1