Abstract
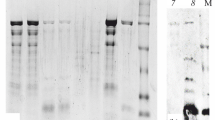
Allergy to seafood mainly fish and shellfish has been reported. Tropomyosin is recognized as a major allergen in many crustaceans especially shrimps. A study was carried out to identify the IgE reactive proteins of allergic nature in Flower tail shrimp (Metapenaeus dobsonii), a frequently consumed shrimp in India mainly in dried form. Protein profiling and identification of IgE reactive proteins in raw and cooked extracts of Flower tail shrimp was carried out by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting using sera of 13 patients having allergic reactions on consumption of shrimp and positive to skin prick test. The IgE binding ability was determined by ELISA and it was found higher in the case of cooked extracts ranging from 0.244 to 0.440 at 490 nm. The SDS-PAGE of raw extract revealed many protein bands between 205 and 6.5 KDa, while in the case of cooked extracts bands of 36, 20, 29 and 70 KDa were prominent. Heat resistant protein of 37 KDa, tropomyosin was showing a clear immune reaction both in the case of raw and cooked extracts was identified as the major allergen by all the patient sera. The minor proteins of raw extract identified by immune reaction are 50, 75 and 100 KDa. The identified allergen can be used for the diagnosis and management of shrimp allergy.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
AOAC International (2000) Official methods of analysis of AOAC international, 17th edn. Association of Analytical Communities, Gaithersburg
Ayuso R, Reese G, Leong-Kee S, Plante M, Lehrer SB (2002) Molecular basis of arthropod cross-reactivity: IgE-binding cross-reactive epitopes of shrimp, house dust mite and cockroach tropomyosins. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 129(1):38–48
Ayuso R, Grishina G, Bardina I, Carrillo T, Blanco C, Ibanez MD, Sampson HA, Beyer K (2008) Myosin light chain is a novel shrimp allergen Lit, v 3. J Allergy Clin Immunol 122:795–802
Ayuso R, Sánchez-Garcia S, Lin J, Fu Z, Ibáñez MD, Carrillo T, Blanco C, Goldis M, Bardina L, Sastre J, Sampson HA (2010) Greater epitope recognition of shrimp allergens by children than by adults suggests that shrimp sensitization decreases with age. J Allergy Clin Immunol 125(6):1286–1293
Burney P, Summers C, Chinn S, Hooper R, Van Ree R, Lidholm J (2010) Prevalence and distribution of sensitization to foods in the European community respiratory health survey: a EuroPrevall analysis. Allergy 65(9):1182–1188
Chakraborty RD, Nandakumar G, Maheswarudu G, Chellapan K (2014) Fishery, biology and population dynamics of Metapenaeus dobsoni (Miers 1878) from Kerala, south-west coast of India. Indian J Fish 61(4):42–47
Chuo KH, Wong SH, Leung PSC (2000) Tropomyosin is the major mollusk allergen: reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction, expression and IgE reactivity. Mar Biotechnol 2:499–509
Daul C, Slattery M, Reese G, Lehrer S (1994) Identification of the major brown shrimp (Penaeus aztecus) allergen as the muscle protein tropomyosin. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 105(1):49–55
Emoto A, Ishizaki S, Shiomi K (2009) Tropomyosins in gastropods and bivalves: identification as major allergens and amino acid sequence features. Food Chem 114:634–641
FAO (2014) World aquaculture and fisheries statistics. FAO Publication, Rome
Gill BV, Rice TR, Cartier A, Gautrin D, Neis B, Horth-Susin L, Jong M, Swanson M, Lehrer SB (2009) Identification of crab proteins that elicit IgE reactivity in snow crab-processing workers. J Allergy Clin Immunol 124:1055–1061
Gornall AG, Bardawill CJ, David MM (1949) Determination of serum proteins by means of biuret reaction. J Biol Chem 177(2):751–766
Hashimoto K, Watabe S, Kono M, Skiro K (1979) Muscle protein composition of sardine and mackerel. Bull Jpn Soc Sci Fish 45:1435–1441
Ishikawa M, Shimakura K, Nagashima Y, Shiomi K (1997) Isolation and properties of allergenic proteins in the oyster Crassostrea gigas. Fish Sci 63:610–614
Karakoltsidis PA, Zotos A, Constantinides SM (1995) Composition of the commercially important Mediterranean finfish, crustaceans, and mollusks. J Food Compos Anal 8:258–273
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head ofbacteriophageT4. Nature 227:680–685
Lehrer SB, Ayuso R, Reese G (2003) Seafood allergy and allergens: a review. Mar Biotechnol (NY) 5:339–348
Leung PSC, Chow WK, Duffey S, Kwan HS, Gershwin ME, Chu KH (1996) IgE reactivity against a cross-reactive allergen in crustacea and mollusca: evidence for tropomyosin as the common allergen. J Allergy Clin Immunol 98:954–961
Liang Y, Cao M, Su W, Zhang L, Huang Y, Liu G (2008) Identification and characterisation of the major allergen of Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis). Food Chem 111(4):998–1003
Lopata A, O'hehir R, Lehrer S (2010) Shellfish allergy. Clin Exp Allergy 40(6):850–858
Motoyama K, Ishizaki S, Nagashima Y, Shiomi K (2006) Cephalopod tropomyosins: identification as major allergens and molecular cloning. Food Chem Toxicol 44:1997–2002
Motoyama K, Suma Y, Ishizaki S, Nagashima Y, Shiomi K (2007) Molecular cloning of tropomyosins identified as allergens in six species of crustaceans. J Agric Food Chem 55:985–991
Motoyama K, Suma Y, Ishizaki S, Nagashima Y, Lu Y, Ushio H, Shiomi K (2008) Identification of tropomyosins as major allergens in Antarctic Krill and Mantis Shrimp and their amino acid sequence characteristics. Mar Biotechnol 10:709–718
Nakano S, Yoshinuma T, Yamada T (2008) Reactivity of shrimp allergy-related IgE antibodies to krill tropomyosin. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 145:175–181
Peng J, Gygi SP (2001) Proteomics: the move to mixtures. Int J Mass Spectrom 36:1083–1091
Reese G, Ayuso R, Lehrer SB (1999) Tropomyosin an invertebrate panallergen. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 119(4):247–258
Samson KT, Chen FH, Miura K, Odajima Y, Iikura Y, Naval Rivas M et al (2004a) IgE binding to raw and boiled shrimp proteins in atopic and nonatopic patients with adverse reaction to shrimp. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 133(3):225–232
Samson KTR, Chen FH, Miura K, Odajima Y, Iikura Y, Rivas MN, Minoguchi K, Adachi M (2004b) IgE binding to raw and boiled shrimp proteins in atopic and nonatopic patients with adverse reactions to shrimp. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 133:225–232
Sathe SK, Teuber SS, Roux KH (2005) Effects of food processing on the stability of food allergens. Biotechnol Adv 23(6):423–429
Shamsundar BA, Prakash V (1994) Physicochemical and functional properties of proteins from prawns (Metapenaeus dobsoni). J Agric Food Chem 42:169–174
Shanti KN, Martin BM, Nagpal S, Metcalfe DD, Rao PV (1993) Identification of tropomyosin as the major shrimp allergen and characterization of its IgE-binding epitopes. J Immunol 151(10):5354–5363
Shimakura K, Tonomura Y, Hamada Y, Nagashima Y, Shiomi K (2005) Allergenicity of crustacean extractives and its reduction by protease digestion. Food Chem 91(2):247–253
Shioni K, Sato Y, Hamamoto S, Mita H, Shimakura K (2008) Sarcoplamic calcium-binding protein: identification of a new allergen of the black tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 146:91–98
Sicherer SH (2011) Epidemiology of food allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol 127(3):594–602
Sicherer SH, Sampson HA (2010) Food allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol 125(2):S116–S125
Sriket Pisal, Benjakul Soottawat, Visessaguan Wonnop, Kijroongrojana Kongkarn (2007) Comparative studies on chemical composition and thermal properties of black tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon) and white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) meats. Food chem 103:1199–1207
Yadzir ZHM, Misnan R, Abdullah N, Bakhtiar F, Arip M, Murad S (2012) Identification of the major allergen of Macrobrachium rosenbergii (giant freshwater prawn). Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 2(1):50–54
Yanar Y, Celik M (2006) Seasonal amoni acid profiles and mineral contents of green tiger shrimp (Penaeus semisulcatus De Haan, 844) and speckled shrimp (Metapenaeus monoceros Fabricus, 1789) from the Eastern Mediterranean. Food Chem 94:33–36
Yu CJ, Lin YF, Chiang BL, Chow LP (2003) Proteomics and immunological analysis of a novel shrimp allergen, Pen m 2. J Immunol 170:445–453
Acknowledgements
This research work was completed with the support of Indian Council of Agricultural Research, New Delhi, India. The authors are extremely thankful to the Director, Indian council of Agriculture Research-Central Institute of Fisheries Technology (ICAR-CIFT), Cochin for providing facilities and support to undertake this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Laly, S.J., Sankar, T.V. & Panda, S.K. Identification of allergic proteins of Flower tail shrimp (Metapenaeus dobsonii). J Food Sci Technol 56, 5415–5421 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-019-04012-0
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-019-04012-0