Abstract
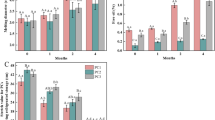
The functional properties (shredability, meltability, fat leakage, stretchability) of Mozzarella Cheese Analogue (MCA) prepared using acid casein (ACMCA), rennet casein (RCMCA) and their admixture (ARCMCA) were monitored with those of Natural Mozzarella Cheese (NMC) during refrigerated storage. The shredability of analogues was superior over such attribute of NMC. The MCAs had good shredability up to 28 days, while that of NMC started deteriorating from 21 days onwards. The meltability of both NMC and MCAs improved with advancement of storage; the extent of increase in meltability during span of 35 days period was 2.65, 2.85, 2.78 and 2.63 for NMC, ACMCA, RCMCA and ARCMCA respectively. The stretch value of the MCAs exhibited an increase up to 21 days of refrigerated storage followed by decline up to 35 days, whereas NMC exhibited a linear increase in stretch value with advancement of storage till 35 days. There was a steady decline in the fat leakage in case of any of the MCAs with advancement in storage period; the difference in the values of fat leakage up to 35 days was to the tune of 1.50 cm2, 1.39 cm2 and 1.43 cm2 for ACMCA, RCMCA and ARCMCA respectively. Conversely, NMC exhibited linear increase in fat leakage with progressive storage up to 35 days. It is concluded that MCAs had better functional stability as compared to NMC during refrigerated storage. Amongst MCAs, ARCMCA performed better in terms of baking qualities than those prepared using AC or RC alone. MCAs had better storage stability as compared to NMC.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Badem A, Ucar G (2016) Cheese analogues. Res Rev J Food Dairy Technol 4:44–48
Chavan RS, Jana A (2007) Cheese substitutes: an alternative to natural cheese—a review. Int J Food Sci Technol Nutr 2:25–39
Chaves VW, Grosso CRF (1999) Proteolysis and functional properties of Mozzarella cheese as affected by refrigerated storage. J Food Sci 64:202–205
Childs JL, Daubert CR, Stefanski L, Foegeding EA (2007) Factors regulating cheese shredability. J Dairy Sci 90:2163–2174
Cortez MA, Furtado MM, Gigante ML, Kindstedt PS (2008) Effect of pH on characteristics of low moisture mozzarella cheese during refrigerated storage. J Food Sci 73:S443–S448
Dave RI, Mc Mahon DJ, Oberg CJ, Broadbent JR (2003a) Influence of coagulant level on proteolysis and functionality of mozzarella cheeses made using direct acidification. J Dairy Sci 86:114–126
Dave RI, Sharma P, Mc Mahon DJ (2003b) Melt and rheological properties of Mozzarella cheese as affected by starter culture and coagulating enzymes. Le Lait 83:61–77
Dave RI, Sharma P, Muthukumarappan K (2003c) Effects of starter culture and coagulating enzymes on viscoelastic behaviour and melt of Mozzarella cheese. J Food Sci 68:1404–1410
El-Bakry M, Duggan E, O’ Riordan ED, O’ Sullivan M (2010) Effects of emulsifying salts reduction on imitation cheese manufacture and functional properties. J Food Eng 100:596–603
El-Bakry M, Duggan E, O’ Riordan ED, O’ Sullivan M (2011) Effect of chelating salt type on casein hydration and fat emulsification during manufacture and functionality of imitation cheese. J Food Eng 102:145–153
FSSA (2015) Manual of methods of analysis of foods. Milk and milk products. Ministry of health and family welfare, Government of India, New Delhi, p 57, 88, 171
Guinee TP, Mulholland EO, Mullins C, Corcoran MO (1997) Functionality of low-moisture Mozzarella cheese during ripening. In: 5th Symposium, 11–13 March, 1997. Cogan TM, Fox PF, Ross RP (eds.) Dublin Irish Republic. pp. 15–23. Cited in Dairy Science Abstracts, 59:6002
Guinee TP, Harrington D, Corcoran M, Mulholland EO, Mujllins C (2000) The compositional and functional properties of commercial mozzarella, Cheddar and analogue pizza cheeses. Int J Dairy Technol 53:51–56
Guinee TP, Feeney EP, Fox PF (2001) Effect of ripening temperature on low moisture Mozzarella cheese: 2. Texture and functionality. Lait 81:475–485
Guinee TP, Caric M, Kalab M (2004) Pasteurized processed cheese and substitute/imitation cheese products. In: Fox PF, Mc Sweeney PLH, Cogan TM, Guinee TP (eds) Cheese—chemistry, physics and microbiology, vol 2, 3rd edn. Elsevier Academic Press, London, pp 349–394
Gunasekaran S, Ak MM (eds) (2003) Chapter 10: Factors affecting functional properties of cheese. In: Cheese rheology and texture. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 399–428
Jana AH, Tagalpallewar GP (2017) Functional properties of mozzarella cheese for its end use application. J Food Sci Technol 54:3766–3778
Jana AH, Upadhyay KG (2001) Development of a formulation and process standardization for mozzarella cheese analogue. Ind J Dairy Sci 54:1–7
Kuo MI, Gunasekaran S (2003) Effect of frozen storage on physical properties of pasta filata and non-pasta filata mozzarella cheeses. J Dairy Sci 86:1108–1117
Ma X, James B, Zhang L, Emanuelsson-Patterson EAC (2012) The stretchability of Mozzarella cheese evaluated by temperature-controlled 3-prong hook test. J Dairy Sci 95(10):5561–5568
McMahon DJ, Fife RL, Oberg CJ (1996) Measuring stretch of Mozzarella cheese. Paper presented at 12th Utah State Biennial Cheese Industry Conference, The United States.http://www.digitalcommons.usu.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1029&context=wdc_conference. Accessed 12 Aug 2017
McMahon DJ, Fife RL, Oberg CJ (1999) Water partitioning in mozzarella cheese and its relationship to cheese meltability. J Dairy Sci 82:1361–1369
Muthukumarappan K, Wang YC, Gunasekaran S (1999) Modified Schreiber test for evaluation of Mozzarella cheese meltability. J Dairy Sci 82:1068–1071
O’ Malley AM, Mulvihill DM, Singh TK (2000) Proteolysis in rennet casein based cheese analogues. Int Dairy J 10:743–753
Rudan MA, Barbano DM, Kindstedt PS (1998) Effect of fat replacer (Salatrim®) on chemical composition, proteolysis, functionality, appearance, and yield of reduced fat Mozzarella cheese. J Dairy Sci 81:2077–2088
Shah R, Jana AH, Aparnathi KD, Prajapati PS (2010) Process standardization for rennet casein based Mozzarella cheese analogue. J Food Sci Technol 47:574–578
Soni T (2014) Technological aspects of formulation of Mozzarella cheese analogue using a blend of rennet and acid casein. M.Tech. thesis submitted to Anand Agricultural University, Anand, Gujarat, India. http://krishikosh.egranth.ac.in/handle/1/5810003020 Accessed 14 Dec 2017
Steel RGD, Torrie JH (1980) Principles and procedure of statistics—a biometrical approach, 2nd edn. Mc-Graw Hill, Columbus, pp 137–167
USDA (2007) United States Department of Agriculture Commodity requirements, MCD4 Mozzarella cheese for use in domestic programs. United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), Washington DC, USA. http://www.fsa.usda.gov/Internet/FSA_File/dmoz3.pdf Accessed 11 Dec 2017
Zedan IA, Abou-Shaloue Z, Zaky SM (2014) Quality evaluation of mozzarella cheese from different milk types. Alex Sci Exch J 35:162–177
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dharaiya, C.N., Jana, A.H. & Aparnathi, K.D. Functionality of Mozzarella cheese analogues prepared using varying protein sources as influenced by refrigerated storage. J Food Sci Technol 56, 5243–5252 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-019-03993-2
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-019-03993-2