Abstract
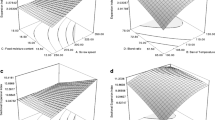
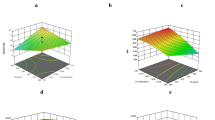
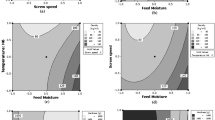
This study investigated the influence of extrusion operating condition [barrel temperature (BT) (50–90 °C), feed moisture content (FM) (25–35%, w.b.), feeder speed (FS) (8–16 rpm) and screw speed to feeder speed ratio (SS:FS) (8–12)] on quality of pearl millet pasta [cooking time (CT), cooking loss (CL), hydration capacity (HC), swelling capacity (SC), hardness, springiness (SP), chewiness (CH) through response surface methodology (CCRD design)]. The results indicated that raising BT and FM reduced CT, CL, but increased HC, SC, hardness, SP, CH of pearl millet based pasta. HC, SC, hardness, SP and CH of pasta were increased as FS and SS:FS increased, whereas, CT and CL showed decreasing trend. The optimum operating conditions for pear millet based pasta was obtained at BT of 70 °C, FM of 30% (w.b.), FS of 12 rpm and SS:FS ratio of 10 with low CT (≤ 5.25 min), CL (≤ 7.45%) and high HC (≥ 2.30 g g−1), SC (≥ 3.14 ml g−1), good hardness (≥ 11.11 N), SP (≥ 1.24 N) and CH (≥ 6.09 N mm).


Similar content being viewed by others
References
AACC (2003) Approved methods of the AACC, 10th edn. American Association of Cereal Chemists, St. Paul
Abecassis J, Abbou R, Chaurand M, Morel MH, Vernoux P (1994) Influence of extrusion conditions on extrusion speed, temperature and pressure in the extruder and on pasta quality. Cereal Chem 71(3):247–253
Abecassis J, Autran JC, Feillet P (2000) Durum wheat, semolina and pasta quality: recent achievements and new trends. Editions Quae, Montpellier, p 42
Akdogan H (1996) Pressure, torque, and energy responses of a twin screw extruder at high moisture contents. Food Res Int 29:423–429
Anonymous (2016) www.indiastat.com. Department of Agriculture and Co-operation, Govt. of India. Accessed 12 April 2016
Bagdi A, Szabo F, Gere A, Kokai Z, Sipos L, Tomoskozi S (2014) Effect of aleurone-rich flour on composition, cooking, textural, and sensory properties of pasta. LWT Food Sci Technol 59:996–1002
Bergman C, Gualberto D, Weber C (1994) Development of high-temperature dried soft wheat macaroni supplemented with cowpea (Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp). Cooking quality, colour and sensory evaluation. Cereal Chem 71:523–527
BIS 1485 (2010) Macaroni, spaghetti, vermicelli and egg noodles-specification. Second revision. Bureau of Indian Standards, New Delhi
Carvalho CWP, Mitchell JR (2000) Effect of sugar on the extrusion of maize grits and wheat flour. Int J Food Sci Technol 35:569–576
de la Pena E, Manthey FA (2017) Effect of formulation and dough hydration level on extrusion, physical and cooked qualities of nontraditional spaghetti. J Food Eng 40:1–12
De Noni I, Pagani MA (2010) Cooking properties and heat damage of dried pasta as influenced by raw material characteristics and processing conditions. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 50:465–472
Debbouz A, Doetkott C (1996) Effect of process variables on spaghetti quality. Cereal Chem 73:672–676
D’Egidio MG, De Stefanis E, Fortini S, Galterio G, Nardi S, Sgrulletta D, Bozzini A (1982) Standardization of cooking quality analysis in macaroni and pasta products. Cereal Foods World 27:367–368
D’Egidio MG, Mariani BM, Nardi S, Novaro P, Cubadda R (1990) Chemical and technological variables and their relationships: a predictive equation for pasta cooking quality. Cereal Chem 67:275–281
Donnelly BJ, Ponte JG (2000) Pasta: raw materials and processing. In: Kulp K, Ponte JG (eds) Handbook of cereal science and technology, 2nd edn. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 647–665
Feillet P, Dexter JE (1996) Quality requirement of durum wheat for semolina milling and pasta production. In: Kruger JE, Matsuo RR, Dick JW (eds) Pasta and noodle technology. AACC International, St. Paul, pp 95–131
Galvez FCF, Resurreccion AVA (1992) Reliability of the focus group technique in determining the quality characteristics of mungbean [Vigna radiate (L.) (Wilczec)] noodles. J Sens Stud 7:315–326
Gimenez MA, Gonzalez RJ, Wagner J, Torres R, Lobo MO, Samman NC (2013) Effect of extrusion conditions on physicochemical and sensorial properties of corn-broad beans (Vicia faba) spaghetti type pasta. Food Chem 136:538–545
Gopalakrishnan J, Menon R, Padmaja G, Sanjeev MS, Moorthy SN (2011) Nutritional and functional characteristics of protein-fortified pasta from sweet potato. Food Nutr Sci 2:944–955
Gopalan C, Rama Sastri BV, Balasubramanian SC (2004) Nutritive value of Indian foods, 2nd edn. National Institute of Nutrition, ICMR, Hyderabad, p 47
Guo G, Jackson DS, Graybosch RA, Parkhurst AM (2003) Wheat tortilla quality: impact of amylose content adjustments using waxy wheat flour. Cereal Chem 80:427–436
Hagenimana A, Ding X, Fang T (2006) Evaluation of rice flour modified by extrusion cooking. J Cereal Sci 43:38–46
Ilo S, Tomschik U, Berghofer E, Mundigler N (1996) The effect of extrusion operating conditions on the apparent viscosity and the properties of extrudates in twin-screw extrusion cooking of maize grits. LWT Food Sci Technol 29:593–598
Jalgaonkar K, Jha SK (2016) Influence of particle size and blend composition on quality of wheat semolina–pearl millet pasta. J Cereal Sci 71:239–245
Jalgaonkar K, Jha SK, Mahawar MK (2018) Influence of die size and drying temperature on quality of pearl millet based pasta. Int J Chem Stud 6(6):979–984
Kaur P, Singh N, Pal P, Kaur A (2018) Traditional and improved paddy varieties: composition, protein, pasting, and gluten-free chapati making properties. Cereal Chem 95:666–678
Lamacchia C, Di Luccia A, Baiano A, Gambacorta G, La Gatta B, Pati S, La Notte E (2007) Changes in pasta proteins induced by drying cycles and their relationship to cooking behaviour. J Cereal Sci 46:58–63
Lawton BT, Hendeson BA, Derlatka EJ (1972) The effects of extruder variables on the gelatinization of corn starch. Can J Chem Eng 50:168
Limroongreungrat K, Huang YW (2007) Pasta products made from sweet potato fortified with soy protein. LWT Food Sci Technol 40:200–206
Lintas CD, Appolonia BD (1973) Effect of spaghetti processing on semolina carbohydrates. Cereal Chem 50:563–570
Manthey FA, Yalla SR, Dick TJ, Badaruddin M (2004) Extrusion properties and cooking quality of spaghetti containing buckwheat bran flour. Cereal Chem 81:232–236
Medvedev GM, Malandeeva NI, Kovalskaja LP (1987) Changes in the properties of the component of dough for pasta during its thermal processing. Tecnica Molitoria 38:796–874
Meng X, Threinen D, Hansen M, Driedger D (2010) Effects of extrusion conditions on system parameters and physical properties of a chickpea flour based snack. Food Res Int 43:650–658
Milatovic L, Mondelli G (1991) Pasta technology today. Chiriotti Editori, Pinerolo
Nasehi B, Mortazavi SA, Razavi SM, Tehrani MM, Karim R (2009) Effects of processing variables and full fat soy flour on nutritional and sensory properties of spaghetti using a mixture design approach. Int J Food Sci Nutr 60:112–125
Nwabueze TU, Anoruoh GA (2011) Evaluation of flour and extruded noodles from eight cassava mosaic disease (CMD)-resistant varieties. Food Bioprocess Technol 4:80–91
Pagani MA, Resmini P, Dalbon G (1989) Influence of the extrusion process on characteristics and structure of pasta. Food Microstruct 8:173–182
Petitot M, Brossard V, Barron C, Larre C, Morel MH, Micard V (2009) Modification of pasta structure induced by high drying temperatures. Effects on the in vitro digestibility of protein and starch fractions and the potential allergenicity of protein hydrolysates. Food Chem 116:401–412
Sozer A, Dalgic AC, Kaya A (2007) Thermal, textural and cooking properties of spaghetti enriched with resistant starch. J Food Eng 81:476–484
Van Den Einde R, Van Der Goot A, Boom R (2003) Understanding molecular weight reduction of starch during heating-shearing processes. J Food Sci 68:2396–2404
Walsh DE, Ebeling KA, Dick JW (1971) A linear programming approach to spaghetti processing. Cereal Sci Today 16:385–389
Wang N, Bhirud PR, Sosulski FW, Tyler RT (1999) Pasta-like product from pea flour by twin-screw extrusion. J Food Sci 64(4):671–678
Wang N, Maximiuk L, Toews R (2012) Pea starch noodles: effect of processing variables on characteristics and optimization of twin-screw extrusion process. Food Chem 133:742–753
Wojtowicz A (2006) Influence of extrusion parameters on some texture characteristics of precooked semolina pasta. Acta Agrophys 8:1049–1060
Wojtowicz A (2012) Influence of process conditions on selected texture properties of precooked buckwheat pasta. TEKA Comm Mot Energ Agric 12:315–322
Wojtowicz A, Moscicki L (2008) Energy consumption during extrusion cooking of precooked pasta. TEKA Kom Mot Energ Roln OL PAN 8:311–318
Yadav DN, Balasubramanian S, Kaur J, Anand T, Singh AK (2014a) Non-wheat pasta based on pearl millet flour containing barley and whey protein concentrate. J Food Sci Technol 51(10):2592–2599
Yadav DN, Sharma M, Chikara N, Anand T, Bansal S (2014b) Quality characteristics of vegetable-blended wheat pearl millet composite pasta. Agric Res 3:263–270
Yeh AI, Jaw YM (1999) Effects of feed rate and screw speed on operating characteristics and extrudate properties during single-screw extrusion cooking of rice flour. Cereal Chem 76:236–242
Acknowledgements
The first author is thankful for the financial funding (INSPIRE fellowship) received from Department of Science and Technology (DST), Government of India (Grant No. 10401). NAE (Niche Area of Excellence) project of Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) is also duly acknowledged for providing facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jalgaonkar, K., Jha, S.K., Mahawar, M.K. et al. Pearl millet based pasta: optimization of extrusion process through response surface methodology. J Food Sci Technol 56, 1134–1144 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-019-03574-3
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-019-03574-3