Abstract
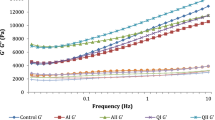
Quality protein maize (QPM) is nutritionally improved maize which has twice the amount of lysine and tryptophan than normal maize. The present study evaluated the effect of different proteins namely egg white proteins (EWP), casein, whey protein isolate, soy protein isolate (SPI) on characteristics of gluten free QPM based muffins. QPM muffins without any added protein served as control and muffins prepared using wheat and EWP served as reference. Effect of addition of different proteins on pasting properties revealed that the thermal stability of QPM flour increased as indicated by decrease in breakdown viscosity. The effect of added proteins on QPM muffin-making properties was evaluated for rheology of batter and physicochemical, texture, color and sensory characteristics of muffins. Dynamic rheology showed that storage modulus (G′) and loss modulus (G″) of batter with SPI was the highest while batter with EWP showed lowest value. QPM–EWP muffins were softer, chewy and springier and had more specific volume than control muffins and were comparable to reference muffins. Inclusion of all proteins increased L* values (lightness) and decreased a* (redness/greenness) and b* (yellow/blueness) values of QPM based muffins. Sensory analysis revealed that gluten free QPM muffin prepared from EWP were acceptable with a sensory score of 7.97 which was comparable to reference muffins (8.03).


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adebowale AA, Sanni LO, Awonarin SO (2005) Effect of texture modifiers on the physicochemical and sensory properties of dried fufu. Food Sci Technol Int 11:373–382
Adeyemi IA, Idowu MA (1990) Evaluation of pregelatinized maize flour in the development of Maissa, a baked product. Niger Food J 8:63–73
AOAC (2000) Official method of analysis of AOAC International, 17th edn. Method 925.09, 969.24, 950.48 and 923.03. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Gaithersburg, MD, USA
Baixauli R, Sanz T, Salvador A, Fiszman SM (2008) Muffins with resistant starch: baking performance in relation to the rheological properties of the batter. J Cereal Sci 47:502–509
BIS (1971) Indian Standard IS: 6273 Part I and Part II. Guide for sensory evaluation of foods. Indian Standard Institution (BIS), Manak Bhawan, New Delhi
Crockett R, Ie P, Vodovotz Y (2011) Effects of soy protein isolate and egg white solids on the physicochemical properties of gluten-free bread. Food Chem 129:84–91
Edema MO, Sanni LO, Sanni A (2005) Evaluation of maize-soybean flour blends for sour maize bread production in Nigeria. Afr J Biotech 4(9):911–918
Flores-Farias R, Martinez-Bustos F, Salinas-Moreno Y, Chang YK, Hernandez JS, Rios E (2000) Physicochemical and rheological characteristics of commercial nixtamalised Mexican corn flours for tortillas. J Sci Food Agric 80:657–664
Francis FJ, Clydesdale FM (1975) Food colorimetry: theory and applications. AVI Publishing Company Inc, Westport
FSSAI (2016) Manual of methods of analysis of foods microbiological testing. Food Safety and Standards Authority of India, Ministry of health and Family Welfare, Government of India, New Delhi
Gallagher E, Gormley TR, Arendt EK (2004) Recent advances in the formulation of gluten-free cereal-based products. Trends Food Sci Technol 15:143–152
Geera B, Reiling JA, Hutchison MA, Rybak D, Santha B, Ratnayake WS (2011) A comprehensive evaluation of egg and egg replacers on the product quality of Muffins. J Food Qual 34:333–342
Giwa EO, Abiodun V (2010) Quality characteristics of biscuits produced from composite flours of wheat and quality protein maize. Afr J Food Sci Technol 5:116–119
Goswami D, Gupta RK, Mridula D, Sharma M, Tyagi SK (2015) Barnyard millet based muffins: physical, textural and sensory properties. LWT Food Sci Technol 64:374–380
Gularte MA, De la Hera E, Gómez M, Rosell CM (2012) Effect of different fibers on batter and gluten-free layer cake properties. LWT Food Sci Technol 48:209–214
Harrigan WF, Mccance MF (1976) Laboratory methods in food and dairy microbiology, Revised edn. Academic Press Inc. Ltd., London
Inglett GE, Xu J, Stevenson DG, Chen D (2009) Rheological and pasting properties of buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum Moench) flours with and without jet-cooking. Cereal Chem 86(1):1–6
Khalil AH (1998) The influence of carbohydrate-based fat replacers and with and without emulsifiers on the quality characteristics of low fat cake. Plant Foods Hum Nutr 52:299–313
Lazaridou A, Duta D, Papageorgiou M, Belc N, Biliaderis CG (2007) Effects of hydrocolloids on dough rheology and bread quality parameters in gluten-free formulations. J Food Eng 79:1033–1047
Man S, Adriana P, Sevastiţa M, Anamaria P (2014) Studies on the formulation and quality characteristics of gluten free muffins. J Agro Aliment Process Technol 20:122–127
Martinez Cervera S, Sanz T, Salvador A, Fiszman SM (2012) Rheological, textural and sensorial properties of low-sucrose muffins reformulated with sucrolase/polydextrose. LWT Food Sci Technol 4:213–220
Matos ME, Sanz T, Rosell CM (2014) Establishing the function of protein on the rheological and quality properties of rice based gluten free muffins. Food Hydrocoll 35:150–158
McWatters KH, Ouedraogo JB, Resurreccion AVA, HungY Phillips RD (2003) Physical and sensory characteristics of sugar cookies containing mixtures of wheat, fonio (Digitaria exilis) and cowpea (Vigna unguiculata) flours. Int J Food Sci Technol 38:403–410
Mishra N, Chandra R (2012) Development of functional biscuit from soy flour and rice bran. Int J Agric Food Sci 2:14–20
Ronda F, Oliete B, Gómez M, Caballero PA, Pando V (2011) Rheological study of layer cake batters made with soybean protein isolate and different starch sources. J Food Eng 102:272–277
Sandhu KS, Singh N (2007) Some properties of corn starches II: physicochemical, gelatinization, retrogradation, pasting and textural properties. Food Chem 101:1499–1507
Sanz T, Salvador A, Baixauli R, Fiszman SM (2009) Evaluation of four types of resistant starch in muffins. II. Effects in texture, colour and consumer response. Eur Food Res Technol 229:197–204
Sarabhai S, Prabhasankar P (2015) Influence of whey protein concentrate and potato starch on rheological properties and baking performance of Indian water chestnut flour based gluten free cookie dough. LWT Food Sci Technol 63:1301–1308
Shevkani K, Singh N (2014) Influence of kidney bean, field pea and amaranth protein isolates on the characteristics of starch-based gluten-free muffins. Int J Food Sci Technol 49:2237–2244
Shevkani K, Kaur A, Singh G, Singh B, Singh N (2014) Composition, rheological and extrusion behaviour of fractions produced by three successive reduction dry milling of corn. Food Bioprocess Technol 7:1414–1423
Shevkani K, Amritpal K, Shresth K, Narpinder S (2015) Cowpea protein isolates: functional properties and application in gluten-free rice muffins. LWT Food Sci Technol 63:927–933
Singh JP, Kaur A, Singh N (2016) Development of eggless gluten-free rice muffins utilizing black carrot dietary fibre concentrate and xanthan gum. J Food Sci Technol 53:1269–1278
Tan Y, Corke H (2002) Factor analysis of physicochemical properties of 63 rice varieties. J Sci Food Agric 82:745–752
Trehan S, Singh N, Kaur A (2018) Characteristics of white, yellow, purple, corn accessions: phenolic profile, textural, rheological properties and muffin making potential. J Food Sci Technol 55:2334–2343
Ziobro R, Witczak T, Juszczak L, Korus J (2013) Supplementation of gluten-free bread with non-gluten proteins. Effect on dough rheological properties and bread characteristic. Food Hydrocoll 32:213–220
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the ICAR-IIMR, Ludhiana for providing QPM grains, help provided for texture analysis by Dr M.S. Alam, College of Agricultural Engineering, PAU, Ludhiana, facilities and financial support extended by the Director, ICAR-CIPHET, Ludhiana, Punjab (India) and Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), New Delhi (India).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bala, M., Arun Kumar, T.V., Tushir, S. et al. Quality protein maize based muffins: influence of non-gluten proteins on batter and muffin characteristics. J Food Sci Technol 56, 713–723 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-018-3529-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-018-3529-8