Abstract
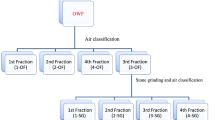
In the present study coarse fraction (CF), medium fine fraction (MFF) and fine fraction (FF) were separated from flours milled from medium-hard and extraordinarily soft wheat varieties and were evaluated for various quality characteristics. Grain hardness of medium-hard and extraordinarily soft wheat varieties varied from 77 to 80 and 17 to 18, respectively. Ash and protein content was the highest for FF and the lowest for CF. Varieties with greater hardness produced higher CF and lower of FF. FF showed higher unextractable polymeric protein (UnEx-PP) and dough stability as compared to MFF and CF. FF showed lower damage starch content as related by lower Sodium SRC (NaSRC) as compared to MFF and FF. CF showed higher paste viscosities than FF and difference were greater amongst fractions from varieties with lower grain hardness. FF with greater proportion of small size particles showed greater accumulation of 98 kDa and 85 kDa PPs than CF. This study demonstrated that fractionation of flours can be employed to produce fractions with varied gluten strength required for production of various products.





Similar content being viewed by others

Abbreviations
- CF:
-
Coarse fraction
- MFF:
-
Medium fine fraction
- FFF:
-
Fine fraction
- GHI:
-
Grain hardness index
- MHW:
-
Medium-hard wheat
- Ex-SW:
-
Extraordinarily soft wheat
- SRC:
-
Solvent retention capacity
- NaSRC:
-
Sodium carbonate SRC
- SuSRC:
-
Sucrose SRC
- LASRC:
-
Lactic acid SRC
- WSRC:
-
Water SRC
- WG:
-
Wet gluten
- DG:
-
Dry gluten
- GI:
-
Gluten index
- PT:
-
Pasting temperature
- PV:
-
Peak viscosity
- BDV:
-
Breakdown viscosity
- FV:
-
Final viscosity
- SBV:
-
Setback viscosity
- WA:
-
Water absorption
- DDT:
-
Dough development time
- DS:
-
Dough stability
- DOS:
-
Degree of softening
- LMW-GS:
-
Low molecular weight glutenins subunits
- HMW-GS:
-
High molecular weight glutenins subunits
References
Ahmed J (2014) Effect of particle size and temperature on rheology and creep behavior of barley β-d-glucan concentrate dough. Carbohydr Polym 111:89–100
Baasandorj T, Ohm JB, Simsek S (2016) Effects of kernel vitreousness and protein level on protein 1 molecular weight distribution, milling, and bread-making quality in hard red spring wheat. Cereal Chem 93:426–434
Bonnand-Ducasse M, Della Valle G, Lefebvre J, Saulnier L (2010) Effect of wheat dietary fibres on bread dough development and rheological properties. J Cereal Sci 52:200–206
De la Hera E, Martinez M, Gomez M (2013) Influence of flour particle size on quality of gluten-free rice bread. LWT Food Sci Technol 54:199–206
Dexter JE, Edwards NM (2001) The implications of frequently encountered grading factors on the processing quality of durum wheat. Tecnica Molitoria 52:553–566
Dobaldo-Maldonado AF, Rose DJ (2013) Particle distribution and composition of retail whole wheat flour separated by sieving. Cereal Chem 90:127–131
Dornez E, Gebruers K, Wiame S, Delcour JA, Courtin CM (2006) Insight into the distribution of arabinoxylans, endoxylanases, and endoxylanase inhibitors in industrial wheat roller mill streams. J Agric Food Chem 54:8521–8529
Every D, Simmons L, Al HJ, Hawkins S, Ross M (2002) Amylase, falling number, polysaccharide, protein and ash relationships in wheat millstreams. Euphytica 126:135–142
Glenn GM, Saunders RM (1990) Physical and structural properties of wheat endosperm associated with grain texture. Cereal Chem 67:176–182
Greffeuille V, Lullien-Pellerin V (2007) Analysis of the milling reduction of bread wheat farina: physical and biochemical characterisation. J Cereal Sci 45:97–105
Greffeuille V, Abecassis J, Bar L’Helgouac’h C, Lullien-Pellerin V (2005) Differences in the aleurone layer fate between hard and soft common wheats at grain milling. Cereal Chem 82:138–143
Gujral HS, Pathak A (2002) Effect of composite flours and additives on the texture of chapatti. J Food Eng 55:173–179
Gupta RB, Khan K, Macritchie F (1993) Biochemical basis of flour properties in bread wheats. 1. Effects of variation in the quantity and size distribution of polymeric protein. J Cereal Sci 18:23–44
Guttieri M, McLean R, Lanning S, Talbert L, Souza E (2002) Assessing environmental influences on solvent retention capacities of two soft white spring wheat cultivars. Cereal Chem 79:880–884
Hayashi M, D’Appolonia BL, Shuey WC (1976) Baking studies on the pin-milled and air-classified flour from four hard red spring wheat varieties. Cereal Chem 53:525–540
Indrani D, Manohar RS, Rajiv J, Venkateswara G (2007) Alveograph as a tool to assess the quality characteristics of wheat flour for parotta making. J Food Eng 78:1202–1206
Johansson E, Malik AH, Hussain A, Rasheed F, Newson WR, Plivelic T, Hedenqvist MS, Gallstedt M, Kuktaite R (2013) Wheat gluten polymer structures: the impact of genotype, environment, and processing on their functionality in various applications. Cereal Chem 90:367–376
Katyal M, Virdi AS, Kaur A, Singh N, Kaur S, Ahlawat AK, Singh AM (2016) Diversity in quality traits amongst Indian wheat cultivars I: flour and protein characteristics. Food Chem 194:337–344
Kaur A, Singh N, Ahlawat AK, Kaur S, Singh AM, Chauhan H, Singh GP (2013) Diversity in grain, flour, dough and gluten properties amongst Indian wheat cultivars varying in high molecular weight subunits (HMW-GS). Food Res Int 53:63–72
Kaur A, Singh N, Kaur S, Katyal M, Virdi AS, Kaur D, Ahlawat AK, Singh AM (2016) Relationship of various flour properties with noodle making characteristics amongst durum wheat varieties. Food Chem 188:517–526
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural protein during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Lazaridou A, Duta D (2007) Effects of hydrocolloids on dough rheology and bread quality parameters in gluten-free formulations. J Food Eng 79:1033–1047
Menkovska M, Knezevic D, Ivanoski M (2002) Protein allelic composition, dough rheology, and baking characteristics of flour mill streams from wheat cultivars with known and varied baking qualities. Cereal Chem 79:720–725
Ng PKW, Bushuk W (1987) Glutenin of marquis wheat as a reference for estimating molecular weights of glutenin subunits by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Cereal Chem 64:324–327
Olkku J, Rha C (1978) Gelatinization of starch and wheat flour starch—a review. Food Chem 3:293–317
Sakhare SD, Inamdar AA, Soumya C, Indrani D, Venkateswara Rao G (2014) Effect of flour particle size on microstructural, rheological and physico-sensory characteristics of bread and south Indian parotta. J Food Sci Technol 51:4108–4113
Schutyser MAI, Goot AJ (2011) The potential of dry fractionation processes for sustainable plant protein production. Trends Food Sci Technol 22:154–164
Singh S, Singh N, MacRitchie F (2011) Relationship of polymeric proteins with pasting, gel dynamic- and dough empirical-rheology in different Indian wheat varieties. Food Hydrocoll 25:19–24
Singh N, Kaur A, Katyal M, Singh AM, Ahlawat AK, Bhinder S (2016) Diversity in quality traits amongst Indian wheat varieties II: paste, dough and muffin making properties. Food Chem 197:316–324
Singh N, Katyal M, Virdi AS, Kaur A, Goyal A, Ahlawat AK, Singh AM (2018) Effect of grain hardness, fractionation and cultivars on protein, pasting and dough rheological properties of different wheat flours. Int J Food Sci Technol 53:2077–2087
Snow RH, Allen T, Ennis BG, Litster JD (1999) Size reduction and size enlargement. In: Perry RH, Green DW (eds) Perry’s chemical engineering handbook. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 20–89
Wang J, Xie A, Zhang C (2013) Feature of air classification product in wheat milling: physicochemical, rheological properties of filter flour. J Cereal Sci 57:537–542
Wu YV, Stringfellow AC, Bietz JA (1990) Relation of wheat hardness to air-classification yields and flour particle size distribution. Cereal Chem 67:421–427
Acknowledgements
NS acknowledges MOFPI, Govt. of India, for providing funds in the form of a research project. MK acknowledges UGC-BSR for providing financial assistance in the form of Fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Katyal, M., Virdi, A.S., Singh, N. et al. Fractionation and grain hardness effect on protein profiling, pasting and rheological properties of flours from medium-hard and extraordinarily soft wheat varieties. J Food Sci Technol 55, 4661–4674 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-018-3433-2
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-018-3433-2