Abstract
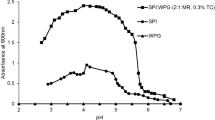
Thermodynamic compatibility and probable interactions between Speckled Sugar been protein (SSBP) and xanthan gum for production of multilayer O/W emulsion (30% oil) were investigated. Different interactions were observed between SSBP and xanthan at different pH (3–7) including electrostatic interactions and hydrogen bonding. These interactions were predominant at pH 3. When low xanthan gum concentration (0.1%) was used, phase separation and complex coacervation observed at this pH (negative effect of interactions). However, at pH 5, only 0.1% xanthan was enough to drastically reduce non-dissolved protein and its precipitation which normally occurs at this pH. In addition, incompatibility or segregative phase behavior which normally occurs when protein and polysaccharide have same charges was not observed (positive effects of interactions). Protein-gum interactions influenced emulsion properties (zeta potential, particle size, PDI, rheology, emulsion capacity, heat stability and creaming rate). Interactions had considerable influence on emulsion shelf life and produced completely stable emulsions at all pH values. Results confirmed that SSBP-xanthan gum mixture has a high potential for production of multilayer emulsions.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azarikia F, Abbasi S (2015) Mechanism of soluble complex formation of milk proteins with native gums (tragacanth and Persian gum). Food Hydrocolloid 59:35–44
Bortnowska G (2015) Multilayer oil in water emulsions: formation, characteristics and application as the carries for lipophilic bioactive food components- a review. Pol J Food Nutr Sci 65:157–166
Chang Y, Hu Y, McClements DJ (2016) Competitive adsorption and displacement of anionic polysaccharides (fucoidan and gum arabic) on the surface of protein-coated lipid droplets. Food Hydrocolloid 52:820–826
Cheng J, Zhou S, Wu D, Chen J, Liu D, Ye X (2009) Bayberry (Myrica rubra Sieb. et Zucc.) kernel: a new protein source. Food Chem 112:469–473
Damodaran S (1997) An overview. In: Damodaran S, Paraf A (eds) Food proteins and their applications. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 1–2
Demetriades K, Coupland JN, McClements DJ (1997) Physical properties of whey protein stabilized emulsions as related to pH and NaCl. J Food Sci 62:342–347
Doublier JL, Garnier C, Renarda D, Sanchez C (2000) Protein-polysaccharide interactions. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 5:202–214
Farshchi A, Ettelaie R (2013) Holmes M, Influence of pH value and locust bean gum concentration on the stability of sodium caseinate-stabilized emulsions. Food Hydrocolloid 32:402–411
Ghorbanian F, Kochaki A, Milani E, Razavi SMA (2015) Effect of xanthan gum on physicochemical properties of grass pea (Lathyrus sativus) isolate stabilized oil in water emulsion (Text in Persian). Food Sci Tech, 115–123
Guo Q, Mu TH (2011) Emulsifying properties of sweet potato protein: effect of protein concentration and oil volume fraction. Food Hydrocolloid 25:98–106
Kaushik PD, Dowling K, Barrow CJ, Adhikari B (2015) Complex coacervation between flaxseed protein isolate and flaxseed gum. Food Res Int 72:91–97
Khouryieh H, Puli G, Williams K, Aramouni F (2015) Effects of xanthan–locust bean gum mixtures on the physicochemical properties and oxidative stability of whey protein stabilised oil-in-water emulsions. Food Chem 167:340–348
Lam RSH, Nickerson MT (2013) Food proteins: a review on their emulsifying properties using a structure–function approach. Food Chem 141:975–984
Long Z, Zhao Q, Liu T, Kuang W, Xu J, Zhao M (2013) Influence of xanthan gum on physical characteristics of sodium caseinate solutions and emulsions. Food Hydrocolloid 32:123–129
Makri EA, Doxastakis GI (2006) Study of emulsions stabilized with Phaseolus vulgaris or Phaseolus coccineus with the addition of Arabic gum, locust bean gum and xanthan gum. Food Hydrocolloid 20:1141–1152
Martínez-Padilla LM, García-Rivera JL, Romero-Arreola V, Casas-Alencáster NB (2015) Effects of xanthan gum rheology on the foaming properties of whey protein concentrate. J Food Eng 156:22–30
McClements DJ (2004) Protein-stabilized emulsions. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 9:305–313
Moosavi- Nasab M, Pashangeh S, Rafsanjani M (2010) Effect of fermentation time on xanthan gum production from sugar beet molasses. Int Scholarl Sci Res Innov 4:8–29
Moschakis T, Murray BS, Biliaderis CG (2010) Modifications in stability and structure of whey protein-coated o/w emulsions by interacting chitosan and gum arabic mixed dispersions. Food Hydrocolloid 24:8–17
Nesterenko A, Alric I, Oise Silvestre F, Durrieu V (2013) Vegetable proteins in microencapsulation: a review of recent interventions and their effectiveness. Ind Crop Product 42:469–479
Noorlaila A, Siti Azah A, Asmeda R, Norizzah AR (2015) Emulsifying properties of extracted okra (Abelmoschus esculentus L.) mucilage of different maturity index and its application in coconut milk emulsion. Int Food Res J 22:782–787
Petsko GA, Ringe D (2004) Protein structure and function. New science Press, London
Qiu C, Zhao M, McClements DJ (2015) Improving the stability of wheat protein-stabilized emulsions: effect of pectin and xanthan gum addition. Food Hydrocolloid 43:377–387
Rahmati NF, Koocheki A, Varidi M, Kadkhodaee R (2017a) Adsorption of Speckled Sugar bean protein isolate at oil-water interface: effect of ionic strength and pH. Int J Biol Macromol 95:1179–1189
Rahmati NF, Koocheki A, Varidi M, Kadkhodaee R (2017b) Structural and functional properties of three genotypes of common bean proteins (Phaseolus vulgaris). Iran Food Sci Tech Res J 13:79–91
Rodríguez Patino JM, Pilosof AMR (2011) Protein-polysaccharide interactions at fluid interfaces. Food Hydrocolloid 25:1925–1937
Siddiq M, Uebersax MA (2013) Dry beans and pulses production and consumption-an overview. In: Siddiq M, Uebersax MA (eds) Dry beans and pulses production, processing and nutrition, 1st edn. Wiley and Blackwell, Iowa, pp 3–22
Wang B, Li D, Wang LJ, Adhikari B, Shi J (2010) Ability of flaxseed and soybean protein concentrates to stabilize oil-in-water emulsions. J Food Eng 100:417–426
Xu BJ, Chang SK (2008) Total phenolic content and antioxidant properties of eclipse black beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) as affected by processing methods. J Food Sci 73:19–27
Yin B, Deng W, Xu K, Huang L, Yao P (2012) Stable nano-sized emulsions produced from soy protein and soy polysaccharide complexes. J Colloid Interface Sci 380:51–59
Zayas J (1997) Functionality of proteins in food. Springer, New York
Zhao Q, Long Z, Kong J, Liu T, Sun-Waterhouse D, Zhao M (2014) Sodium caseinate/flaxseed gum interactions at oil-water interface: effect on protein adsorption and functions in oil-in-water emulsion. Food Hydrocolloid 43:137–145
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rahmati, N.F., Koocheki, A., Varidi, M. et al. Thermodynamic compatibility and interactions between Speckled Sugar bean protein and xanthan gum for production of multilayer O/W emulsion. J Food Sci Technol 55, 1143–1153 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-017-3030-9
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-017-3030-9