Abstract
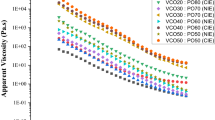
Effects of virgin coconut oil (VCO) at various levels (0–25%) on the properties of croaker surimi gels were studied. As the levels of VCO increased up to 15%, breaking force continuously decreased. No differences in breaking force, deformation and fracture constant were noticeable when VCO of 15–25% was incorporated. Based on texture profile analysis, hardness and chewiness decreased as the level of added VCO increased up to 10%, while no marked changes were observed with the addition of 10–25% VCO. Addition of VCO had no profound impact on springiness, cohesiveness and resilience. No remarkable change in protein pattern among all surimi gel samples was noticed, regardless of VCO levels. Lower elastic (G′) as well as loss moduli (G″) of surimi paste were observed when VCO was added, compared to the control. Nevertheless, there was no marked difference in the moduli among samples containing VCO at all levels. Whiteness of surimi gel increased, whereas expressible moisture content decreased as VCO levels increased. Microstructure study revealed that VCO droplets were distributed uniformly in gel network. Overall likeness of surimi gel was also increased for gel added with VCO. Therefore, VCO addition directly affected textural properties and improved the whiteness as well as sensory property of surimi gel.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arfat YA, Benjakul S (2013) Gel strengthening effect of zinc salts in surimi from yellow stripe trevally. Food Biosci 3:1–9
Benjakul S, Visessanguan W (2003) Transglutaminase mediated setting in bigeye snapper surimi. Food Res Int 36:253–266
Benjakul S, Visessanguan W, Srivilai C (2001) Porcine plasma proteins as gel enhancer in bigeye snapper (Priacanthus tayenus) surimi. J Food Biochem 25:285–305
Benjakul S, Visessanguan W, Kwalumtharn Y (2004) The effect of whitening agents on the gel-forming ability and whiteness of surimi. Int J Food Sci Technol 39:773–781
Bergsson G, Arnfinnsson J, Karlsson SM, Steingrímsson O, Thormar H (1998) In vitro inactivation of Chlamydia trachomatis by fatty acids and monoglycerides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 42:2290–2294
Chang T, Wang C, Wang X, Shi L, Yang H, Cui M (2015) Effects of soybean oil, moisture and setting on the textural and color properties of surimi gels. J Food Qual 38:53–59
Cheret R, Chapleau N, Delbarre-Ladrat C, Verrez-Bagnis V, Lamballerie MD (2005) Effects of high pressure on texture and microstructure of sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.) fillets. J Food Sci 70:477–483
DeJong G, Koppelman S (2006) Transglutaminase catalysed reactions: impact on food applications. J Food Sci 67:2798–2806
Dickinson E, Chen J (1999) Heat-set whey protein emulsion gels: role of active and interactive filler particles. J Dispers Sci Technol 20:197–213
Figura LO, Teixeira AA (2007) Food physics physical properties-measurement and applications. Springer Publishers, Berlin
German JB, Dillard CJ (2004) Saturated fats: What dietary intake? Am J Clin Nutr 80(550):559
Herranz B, Borderias AJ, Solo-de-Zaldívar B, Solas MT, Tovar CA (2012) Thermostability analyses of glucomannan gels. Concentration influence. Food Hydrocoll 29:85–92
Hsu CK, Chiang BH (2002) Effects of water, oil, starch, calcium carbonate and titanium dioxide on the colour and texture of threadfin and hairtail surimi gels. Int J Food Sci Technol 37:387–393
Kaewudom P, Benjakul S, Kijroongrojana K (2013) Properties of surimi gel as influenced by fish gelatin and microbial transglutaminase. Food Biosci 1:39–47
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Lefevre F, Fauconneau B, Ouali A, Culioli J (1998) Thermal gelation of brown trout myofibrils: effect of muscle type, heating rate and protein concentration. J Food Sci 63:299–304
Liu R, Zhao SM, Xiong SB, Xie BJ, Liu HM (2007) Studies on fish and pork paste gelation by dynamic rheology and circular dichroism. J Food Sci 72:399–403
Lowry QH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr LA, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:256–275
Lu R, Abbott JA (2004) Force/deformation techniques for measuring texture. In: Kilcast D (ed) Texture in food: Solid foods. Woodhead Publishing Limited, Cambridge, pp 109–145
Luo YK, Kuwahara R, Kaneniwa M, Murata Y, Yokoyama M (2001) Comparison of gel properties of surimi from Alaska pollock and three freshwater fish species: effects of thermal processing and protein concentration. J Food Sci 66:548–554
Malik MA, Saini CS (2017) Polyphenol removal from sunflower seed and kernel: effect on functional and rheological properties of protein isolates. Food Hydrocoll 63:705–715
Marina A, Man YC, Nazimah S, Amin I (2009) Chemical properties of virgin coconut oil. J Am Oil Chem Soc 86:301–307
Meilgaard M, Civille GV, Carr BT (1999) Sensory evaluation techniques, 3rd edn. CRC Press, Florida
NFI (1991) A manual of standard methods for measuring, specifying the properties of surimi. National Fisheries Institute, Washington, DC
Nolasco NN, Balboa JG, Serrame E, Lim-Sylianco CY (1994) Effect of coconut oil, trilaurin and tripalmitin on the promotion stage of carcinogenesis. Philipp J Sci 123:161–169
Park JW (2000) Ingredient technology and formulation development. In: Park JW (ed) Surimi and surimi seafood. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 343–392
Pietrowski BN, Tahergorabi R, Matak KE, Tou JC, Jaczynski J (2011) Chemical properties of surimi seafood nutrified with ω-3 rich oils. Food Chem 129:912–919
Shi L, Wang X, Chang T, Wang C, Yang H, Cui M (2014) Effects of vegetable oils on gel properties of surimi gels. LWT Food Sci Technol 57:586–593
Shima H, Tanimoto M (2016) Effect of milk fat content on the viscoelasticity of mozzarella-type cheese curds. Eur Food Res Technol 242:157–162
Srivastava Y, Semwal AD, Sajeevkumar VA, Sharma GK (2017) Melting, crystallization and storage stability of virgin coconut oil and its blends by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). J Food Sci Technol 54:45–54
Steel RGD, Torrie JH (1980) Principles and procedures of statistics: a biometrical approach, 2nd edn. McGraw-Hill, New York
Wasson DH (1992) Fish muscle proteases and heat-induced myofibrillar degradation: a review. J Aquat Food Prod Technol 1:23–41
Wu MG, Xiong YL, Chen JY, Tang X, Zhou GH (2009) Rheological and microstructural properties of porcine myofibrillar protein–lipid emulsion composite gels. J Food Sci 74:207–217
Yost RA, Kinsella JE (1992) Microstructure of whey protein isolate gels containing emulsified butterfat droplets. J Food Sci 57:892–897
Zhang F, Fang L, Wang C, Shi L, Chang T, Yang H, Cui M (2013) Effects of starches on the textural, rheological, and color properties of surimi–beef gels with microbial transglutaminase. Meat Sci 93:533–537
Zhou X, Jiang S, Zhao D, Zhang J, Gu S, Pan Z, Ding Y (2017) Changes in physicochemical properties and protein structure of surimi enhanced with camellia tea oil. LWT Food Sci Technol 84:562–571
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Thailand’s Education Hub for Southern Region of ASEAN Countries (TEH-AC, 2015) scholarship. The TRF Distinguished Research Professor Grant was also acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gani, A., Benjakul, S. & Nuthong, P. Effect of virgin coconut oil on properties of surimi gel. J Food Sci Technol 55, 496–505 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-017-2958-0
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-017-2958-0