Abstract
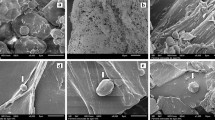
The present study deals with the application of low temperature plasma on basmati rice flour and its effect on functional properties such as gel hydrations properties, flour hydration properties, gelatinization temperatures and antioxidant properties. The water holding capacity and water binding capacity were observed to be increased with increase in plasma power and time of treatment as the air plasma is known to make the surface more hydrophilic. XRD analysis revealed there is no significance difference in the crystalline structure after the plasma treatment. DSC shows a decrease in peak temperatures (Tp) after the treatment. Hot paste viscosities were observed to be decease from 692 to 591 BU was corresponded to decrease in peak temperature. The total polyphenolic content and reducing power was observed to be increased. The effects of plasma treatment on functional groups of polyphenols were observed by changes in absorption intensities using FTIR. This study demonstrates that the low temperature plasma treatmentis capable of improving the functional properties of basmati rice.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdul RA, Lateef SO, Hameed OO, Olayinka KR (2011) Effect of variety and moisture content on some engineering properties of paddy rice. J Food Sci Technol 48(5):551–559
Abu J, Muller K, Duodu KG, Minnaar A (2006) Gamma irradiation of cowpea (Vignaunguiculata L. Walp) flours and pastes: effects on functional, thermal and molecular properties of isolated proteins. Food Chem 95:138–147
Acosta-Estrada BA, Gutierrez-Urib JA, Serna-Saldivar SO (2014) Bound phenolics in foods, a review. Food Chem 152:46–55
Adebowale KO, Lawal OS (2002) Effect of annealing and heat moisture conditioning on the physicochemical characteristics of Bambarra groundnut (Voandzeia Subterranea) starch. Food/Nahrung 46:311–316
Adebowale AA, Sanni LO, Awonorin SO (2005) Effect of texture modifies on the physiochemical and sensory properties of dried fufu. J Food Sci Technol 11:373–385
Adom KK, Liu RH (2002) Antioxidant activity of grains. J Agric Food Chem 50:6182–6187
AOAC (2010) Official methods of analysis. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Washington
Bello MO, Loubes MA, Aguerre RJ, Tolaba MP (2015) Hydrothermal treatment of rough rice: effect of processing conditions on product attributes. J Food Sci Technol 52:5156–5163
Chen HH (2014) Investigation of properties of long-grain brown rice treated by low-pressure plasma. Food Bioproc Technol 6:1–8
Chen HH, Chen Y, Chang CH (2012) Evaluation of physicochemical properties of plasma treated brown rice. Food Chem 135:74–79
Daffalla SB, Mukhtar H, Shaharun MS (2010) Characterization of adsorbent developed from rice husk: effect of surface functional group on phenol adsorption. J Appl Sci 10:1060–1067
de la Hera E, Gomez M, Rosell CM (2013) Particle size distribution of rice flour affecting the starch enzymatic hydrolysis and hydration properties. Carbohydr Polym 98:421–427
Deeyai P, Suphantharika M, Wongsagonsup R, Dangtip S (2013) Characterization of modified tapioca starch in atmospheric argon plasma under diverse humidity by FTIR spectroscopy. Chin Phys Lett. doi:10.1088/0256-307X/30/1/018103
Falade KO, Semon M, Fadairo SO, Oladunjoye AO, Orou KK (2014) Functional and physico-chemical properties of flours and starches of African rice cultivars. Food Hydrocoll 39:41–50
Grzegorzewski F, RohnKroh LW, Geyer M, Schluter O (2010) Surface morphology and chemical composition of lamb’s lettuce (Valerianella locusta) after exposure to low pressure oxygen plasma. Food Chem 122:1145–1152
Harborne JB, Williams CA (2000) Advances in Flavonoid research since 1992. Phytochem 55:481–504
Hinneburg I, Damien Dorman HJ, Hiltunen R (2006) Antioxidant activities of extracts from selected culinary herbs and spices. Food Chem 97:122–129
Ishikawa Y, Ito S (2004) Marketing of value-added rice products in Japan: germinated brown rice and rice bread. FAO Rice Conference 04/CRS.7, Rome
Itagi HN, Singh V (2015) Status in physical properties of coloured rice varieties before and after inducing retro-gradation. J Food Sci Technol. doi:10.1007/s13197-015-1929-6
Juliano BO, Villareal RM, Perez CM, Villareal CP, Takeda V, Hizukuri S (1987) Varietal differences in properties among high amylose rice starches. Starch/Starke 39:390–393
Kalita D, Kaushik N, Mahanta CL (2014) Physicochemical, morphological, thermal and IR spectral changes in the properties of waxy rice starch modified with vinyl acetate. J Food Sci Technol 51:2790–2796
Langmuir I (1928) Oscillations in ionized gases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 14:627–637
Laroussi M (2009) Low-temperature plasmas for medicine? IEEE Trans Plasma Sci 37:714–725
Lii CY, Liao CD, Stobinski L, Tomasik P (2002) Behaviour of granular starches in low-pressure glow plasma. Carbohydr Polym 49:499–507
Misra NN, Han L, Tiwari B, Bourke P, Cullen PJ (2014) Nonthermal plasma technology for decontamination of foods. In: Boziaris IS (ed) Novel food preservation and microbial assessment techniques. CRC Press, New York, pp 155–183
Misra NN, Kaur S, Tiwari BK, Kaur A, Singh N, Cullen PJ (2015) Atmospheric pressure cold plasma (ACP) treatment of wheat flour. Food Hydrocoll 44:115–121
Nemtanu M, Brasoveanu M (2010) Functional properties of some non-conventional treated starches. In: Magdy Elnashar (ed) Biopolymers
Pal P, Kaur P, Singh N, Kaur AP, Misra NN, TiwariBK Cullen PJ, Virdi AS (2016) Effect of nonthermal plasma on physico-chemical, amino acid composition, pasting and protein characteristics of short and long grain rice. Food Res Int 81:50–57
Pandiyaraj KN, Selvarajan V, Deshmukh RR, Gao C (2009) Modification of surface properties of polypropylene (PP) film using DC glow discharge air plasma. Appl Surface Sci 255:3965–3971
Prieto P, Pineda M, Aguilar M (1999) Spectrophotometric quantification of antioxidant capacity through the formation of a phosphomolybdenum complex: specific application of vitamin E. Anal Biochem 269:337–341
Qin-lu L, Hua-xi X, Xiang-jin F, Wei T, Li-hui L, Feng-xiang Y (2011) Physico-chemical properties of flour, starch, and modified starch of tworice varieties. Agric Sci China 10(6):960–968
Rosell CM, Yokoyama W, Shoemaker C (2011) Rheology of different hydrocolloids—rice starch blends effect of successive heating-cooling cycles. Carbohydr Polym 84:373–382
Saleh M, Meullenet JM (2015) Cooked rice texture and rice flour pasting properties; impacted by rice temperature during milling. J Food Sci Technol 52(3):1602–1609
Sarangapani C, Yamuna D, Thirumdas R, Annapure US, Deshmuk RR (2015) Effect of low-pressure plasma on physico-chemical properties of parboiled rice. LWT - Food Sci Technol 63(1):452–460
Sarma SKSS (2005) Electron beam technology in industrial radiation processing. IANCAS Bull 4:128–134
Schutze A, Jeong JY, Babayan SE, Park J, Selwyn GS, Hicks RF (1998) The atmospheric-pressure plasma jet: a review and comparison to other plasma sources. IEEE transactions on plasma science 26:1685–1694
Sood BC, Siddiq EA (1978) A rapid technique for scent determination in rice. Indian J Genet Plant Breed 38:268–271
Sreeramulu D, Reddy VK, Raghunath M (2009) Antioxidant activity of commonly consumed cereals, millets, pulses and legumes in India. Indian J Biochem Biophys 46:112–115
Thirumdas R, Sarangapani C, Annapure US (2015a) Cold plasma: a novel non-thermal technology for food processing. Food Biophys 1:1–11
Thirumdas R, Deshmukh RR, Annapure US (2015b) Effect of low temperature plasma processing on physicochemical properties and cooking quality of basmati rice. Inn Food Sci Emer Technol 31:83–90
Vasudeva S, Bhattacharya KR, Mahadevappa M (1986) A reliable test for the identification of scented rice. Oryza 23:249–251
Wongsagonsup R, Deeyai P, Chaiwat W, Horrungsiwat S, Leejariensuk K, Suphantharika M, Fuongfuchat A, Dangtip S (2014) Modification of tapioca starch by non-chemical route using jet atmospheric argon plasma. Carbohydr Polymers 102:790–798
Yu Y, Ge L, Zhu S, Zhan Y, Zhang Q (2015) Effect of presoaking high hydrostatic pressure on the cookingproperties of brown rice. J Food Sci Technol. doi:10.1007/s13197-015-1901-5
Zaidul ISM, Yamauchi H, Takigawa S, Matsuura-Endo C, Suzuki T, Noda T (2007) Correlation between the compositional and pasting properties of various potato starches. Food Chem 105:164–172
Zhang B, Xiong S, Li X, Li L, Xie F, Chen L (2013) Effect of Oxygen Glow Plasma on Supramolecular and Molecular Structures of Starch and Related Mechanism. Food Hydrocol 37:69–76
Zou JJ, Liu CJ, Eliasson B (2004) Modification of starch by glow discharge plasma. Carbohydr Polym 55:23–26
Acknowledgments
One of the authors Thirumdas Rohit would like to thank the University Grants Commission (UGC), India for financial assistance through UGC-BSR program. We also thank DST [New Delhi (India)] for financially supporting this work vide Project Ref. No. SERB/MOFPI/0047/2012 dated 26/12/2012. We would like to thank Grain Science and Technology, department CFTRI (Mysore) for allowing to use there Microbrabender viscoamylograph facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thirumdas, R., Deshmukh, R.R. & Annapure, U.S. Effect of low temperature plasma on the functional properties of basmati rice flour. J Food Sci Technol 53, 2742–2751 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-016-2246-4
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-016-2246-4