Abstract
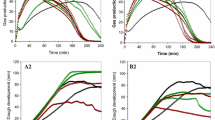
Milk proteins were hydrolyzed by papain and their effect on the rheological, textural and sensory properties of bread were investigated. Water absorption capacity, emulsification capacity, foam volume, foam stability and solubility of Whey and casein protein concentrates and their hydrolysates were determined. The farinograph parameters of wheat flour and blends of wheat flour with casein and whey protein and their hydrolysates were determined to evaluate changes in water absorption capacity, dough development time, dough stability time and mixing tolerance index. The incorporation of WPC, casein and their hydrolysates up to the level of 5 % showed dough properties comparable to control. It was also found that 5 % level incorporation of milk proteins and their hydrolysates have no drastic effect on physical and sensory attributes of bread. The pasting properties showed significant decrease (p ≤ 0.05) when compared with wheat flour at all levels of addition of whey and casein protein concentrates and hydrolysates. Scanning electron microscopy of bread samples shows disruption in the well-defined protein – starch complex of wheat flour bread and the structure of gluten was weak as the concentration of whey protein increases in the wheat flour bread.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
AACC (1983) Approved methods of analysis, 8th edn. American Association of Cereal Chemists, St. Paul
Adler-Nissen J (1986) Enzymic hydrolysis of food proteins. Elsevier 521 Applied Science Publishers, New York
Ahmad A, Baba WN, Wani TA, Gani A et al (2014) Effect of green tea powder on thermal, rheological and functional properties of wheat of wheat flour and physical, nutraceutical and sensory analysis of cookies. J Food Sci Technol. doi:10.1007/s13197-014-1701-3
Ashwar BA, Shah A, Gani A, Rather SA et al (2014) Effect of gamma irradiation on the physicochemical properties of alkali extracted rice starch. Radiat Phys Chem 99:37–44
Axford DWE, Mc Dermott EE, Redman DG (1978) Small scale tests of bread making quality. Milling Feed Fertil 66:18–2
Bera MB, Mukherjee RK (1989) Solubility, emulsifying, and foaming properties of rice bran protein concentrates. J Food Sci 54:142–145
Beuchat LR (1977) Functional and electrophoretic characteristics of succinylated peanut flour protein. J Agric Food Chem 25:258–261
Beuchat LR, Cherry JP, Quinn MR (1975) Physicochemical properties of peanut flour as affected by proteolysis. J Agric Food Chem 23:616–620
Bhagya S, Srinivasan KS (1989) Effect of different methods of drying on functional properties of enzyme treated ground flour. J Food Sci Technol 22:329
Bimlesh M, Malik RC (1996) Studies on some functional characteristics of whey protein polysaccharide complex. J Food Sci Technol 33:202–206
Britten M, Giroux HJ, Gaudin V (1994) Effect of pH during heat processing of partially hydrolyzed whey protein. J Dairy Sci 77:676–684
Caessens PWJR, Visser S, Gruppen H, Voragen AGJ (1999) β-Lactoglobulin hydrolysis. I. Peptide composition and functional properties of hydrolysates obtained by the action of plasmin, trypsin, and Staphylococcus aureus V8 protease. J Agric Food Chem 47:2973–2979
Castimopoolas N, Funk SK, Meyer EW (1970) Thermal aggregation of glycinin subunits. Cereal Chem 47:331
Ceirwyn SJ (1995) Analytical chemistry of foods. Chapman & Hall, London, pp 88–89
Chobert JM, Sitohy MZ, Whitaker JR (1988a) Solubility and emulsifying properties of caseins modified enzymatically by Staphylococcus aureus V8 protease. J Agric Food Chem 36:220–224
Chobert JM, Bertrand HC, Nicolas MG (1988b) Solubility and emulsifying properties of caseins and whey proteins modified enzymatically by trypsin. J Agric Food Chem 36(5):883–892
Crowley PO, Brien CM, Slattery H, Chapman D, Arendt EK, Stanton C (2002) Functional properties of casein hydrolysates in bakery applications. Eur Food Res Technol 215(2):131–137
Day DD, Rogers D (1996) Fourier-based texture measures with application to the analysis of the cell structure of baked products. Digital Signal Process 6:138–144
Erdogdu-Arnoczky N, Czuchzjowska Z, Pomeranz Y (1996) Functionality of whey and casein in bread making by fixed and optimized procedures. Cereal Chem 73:309–316
Finney KF (1984) Optimized, straight dough, bread-making method ofter 44 years. Cereal Chem 61:20–27
Fleming SE, Sosulski FW (1978) Evaluation of bread fortified with concentrated plant proteins. Cereal Chem 55:373–382
Gani A, Broadway AA, Mudasir A, Ashwar BA, Wani AA, Wani SM, Masoodi FA, Khatkar BS (2014) Effect of whey and casein protein hydrolysates on rheological, textural and sensory properties of cookies. J Food Sci Technol. doi:10.1007/s13197-014-1649-3
Gelinas P, Audet J, Lachance O, Vachon M (1995) Fermented dairy ingredients for bread: effects on dough rheology and bread characteristics. Cereal Chem 72(2):151–154
Giami SY (2001) Rheological and bread-making properties of wheat fluted pumpkin seed flour blends. J Dairying Foods Home Sci 20:41–45
Giami SY, Barber LI (2004) Utilization of protein concentrates from ungerminated and germinated fluted pumpkin (Telfairia occidentalis Hook) seeds in cookie formulations. J Sci Food Agric 38:56–60
Greene JL, Bovell-Benjamin AC (2004) Macroscopic and sensory evaluation of bread supplemented with sweet potato flour. J Food Sci 69:167–173
Indrani D, Prabhasankar P, Rajiv J, Venkateswara RG (2007) Influence of whey protein concentrate on the rheological characteristics of dough, microstructure and quality of unleavened flat bread (parotta). Food Res Int 40:1254–1260
Iqbal A, Khalil IA, Ateeq N, Khan MS (2006) Nutritional quality of important food legumes. Food Chem 97:331–335
Kadharmestan C, Baik BK, Czuchajowska Z (1998) Whey protein concentrated with high heat or hydrostatic pressure in wheat-based products. Cereal Chem 75:762–766
Kent NL, Evers AD (1994) Bread made with gluten substitutes. Technol cereal. Pergamon Press, Oxford (pp. 215)
Keuhler CA, Stine CM (1974) Effect of enzymatic hydrolysis on some functional properties of whey protein. J Food Sci 39:379–382
Khoo U, Christianson DD, Inglett GE (1975) Scanning and transmission microscopy of dough and bread. Bakers Digest 49(4):24–26
Kinsella JE, Whitehead DM (1989) Proteins in whey: chemical, physical, and functional properties. Adv Food Nutr Res 33:437–438
Lieske B, Konrad G (1996) Physico-chemical and functional properties of whey protein as affected by limited papain proteolysis and selective ultrafiltration. Int Dairy J 6:13–31
Lorenz K, Dilsaver W, Wolt N (1979) Faba bean flour and protein concentrate in baked goods and in pasta products. Bakers Digest 39–49
Ludwig I, Krause W, Hajos G (1995) Functional properties of enzymatically modified milk proteins. Acta Aliment 24:289–296
Madenci AB, Bilgiçli N (2014) Effect of whey protein concentrate and buttermilk powders on rheological properties of dough and bread quality. J Food Qual 37:117–124
Matthews RH, Sharpe EJ, Clark WM (1970) The use of some oilseed flours in bread. Cereal Chem 47:181–185
Mutilangi WAM, Panyam D, Kilara A (1996) Functional properties of hydrolyzates from proteolysis of heat denatured whey protein isolate. J Food Sci 61:270–274
Peryam DR, Pilgrim FJ (1957) Hedonic scale method of measuring food preferences. Food Technol 11:9–13
Rahma EH, Mostafa MM (1998) Functional properties of peanut fruit as affected by different heat treatment. J Food Sci Technol 25:11–15
Rhicha S, Radha C, Prakash J, Kaul P (2007) Whey protein hydrolysate: functional properties, nutritional quality and utilization in beverage formulation. Food Chem 101:1484–1491
Sekul AA, Vinnett CH, Ory RL (1978) Some functional properties of peanut proteins partially hydrolyzed with papain. J Agric Food Chem 26:855–858
Sidhu JS, Al-Saqer J, Al-Zenki S (1997) Comparison of methods for the assessment of the extent of staling in bread. Food Chem 58:161–167
Sindayikengera S, Xia W (2005) Nutritional evaluation of caseins and whey proteins and their hydrolysates from Protamex. J Zhejiang Univ 7:90–98
Singh B, Bajaj M, Sharma S, Sidhu JS (1993) Studies on the development of high-protein biscuits from composite flours. Plant Foods Hum Nutr 43:181–189
Slattery H, Fitzgerald RJ (1998) Functional properties and bitterness of sodium caseinate hydrolysates prepared with a bacillus proteinase. J Food Sci 63(3):418–422
Tronsmo KM, Faergestad EM, Schofield JD, Magnus S (2003) Wheat protein quality in relation to baking performance evaluated by the Chorleywood bread process and a hearth bread baking test. Cereal Sci 38:205–215
Verbruggen IM, Veraverbeke WS, Delcour JA (2001) Significance of LMW-GS and HMW-GS for dough extensibility: addition versus incorporation protocols. J Cereal Sci 33:253–260
Vrignaud MY (1977) Milk proteins, their properties and applications. CCB Rev Chocolate Confectionery Bak 2:11–13
Wani IA, Sogi DS, Shivhare US, Gill BS (2014) Physico-chemical and functional properties of native and hydrolyzed kidney bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) protein isolates. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2014.08.027
Warren AB, Hnat DL, Michnowski J (1983) Protein fortification of cookies, crackers, and snack bars: uses and needs. Cereal Foods World 28:441–444
Zadow JG (1981) Measurement of the effect of whey protein concentrates on fermenting doughs by the instron tester. Aust J Dairy Technol 36:56–59
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Department of Biotechnology, Govt. of India for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gani, A., Broadway, A.A., Masoodi, F.A. et al. Enzymatic hydrolysis of whey and casein protein- effect on functional, rheological, textural and sensory properties of breads. J Food Sci Technol 52, 7697–7709 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-015-1840-1
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-015-1840-1