Abstract
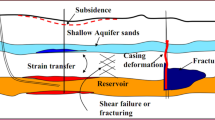
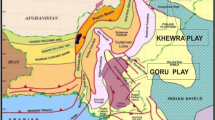
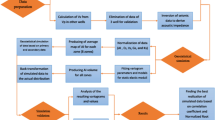
This study strives to analyze a poroelastic media, including water, oil, and gas, of a carbonate formation in southwest Iran. For this purpose, three data sets comprising geochemical, seismic, and geomechanical information from laboratory tests and well-logging operations were employed. In this research, seismic parameters, including P & S—wave velocity, velocity ratio (VP/VS), acoustic impedance (AI) and shear impedance (SI), were directly measured by well-logging data. Dynamic elastic moduli were calculated using the bulk density and seismic velocities. Uniaxial compressive strength (UCS) was calculated by empirical relationships and calibrated with a several laboratory tests. Initially, 41 un-contaminated core samples were tested for the Rock–Eval Pyrolysis (REP) chemical experiment. Simultaneous use of logs and chemical analysis identified three zones (A, B, C), including gas, water, and oil, for the evaluations, proving that hydrocarbon in zone C was migrated from other intervals. The results show that water saturation increases compressional wave velocity and decreases shear wave velocity through porous media. Elasticity is conjugately affected by both shear wave and compressional wave velocity. Accordingly, Young's modulus in the hydrocarbon zones increases while it experiences a decreasing trend in the water zone. On the other hand, the results exhibit a reduction in shear modulus in hydrocarbon zones compared with the water zone. In addition, in hydrocarbon zones, the shear impedance increases while the acoustic impedance decreases, in contrast to the water zone.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data subject to third party restriction
References
Abdollahi R, Haghighi M, Salmachi A (2022) Geo-mechanical modeling of underground hydrogen storage undergoing cyclic injection and production. EAGE GET 2022(1): 1–5. https://doi.org/10.3997/2214-4609.202221094
AbdollahieFard I, Sherkati S, McClay K, Haq BU (2019) Tectono-sedimentary evolution of the Iranian zagros in a global context and its impact on petroleum habitats. Dev Struct Geol Tecton 3:17–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-815048-1.00002-0
Abyat A, Afghah M, Feghhi A (2013) Stratigraphy and foraminiferal biozonation of the upper cretaceous sediments in Southwest Sepid Dasht, Lurestan. Iran World Appl Sci J 28(9):1199–1207. https://doi.org/10.5829/idosi.wasj.2013.28.09.2793
Ali M, Ashraf U, Zhu P, Ma H, Jiang R, Lei G et al (2023) Quantitative characterization of shallow marine sediments in tight gas fields of middle indus basin: a rational approach of multiple rock physics diagnostic models. Processes 11(2):323
Anstey NA (2013) Seismic interpretation: the physical aspects. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 306–393
Baniasad A, Littke R, Froidl F, Grohmann S, Soleimany B (2021) Quantitative hydrocarbon generation and charge risk assessment in the NW Persian Gulf: a 3D basin modeling approach. Mar Petrol Geol 126:104900. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2021.104900
Becker MW, Harris B, Pevzner R (2023) Characterization of Aquifer Poroelastic Response to Impulse and Oscillatory Well Pressure using Distributed Acoustic Sensing. Geophys Res Lett. e2022GL100904. https://doi.org/10.1029/2022GL100904
Biot MA (1956) Theory of propagation of elastic waves in a fluid-saturated porous solid. II. Higher frequency range. J Acoust Soc Am 28(2):179–191. https://doi.org/10.1121/1.1908241
Bordenave ML, Espitalié J, Leplat POJL, Oudin JL, Vandenbroucke M (1993) Screening techniques for source rock evaluation. Appl Petrol Geochem 217–278
Chen Z, Liu X, Jiang C (2017) Quick evaluation of source rock kerogen kinetics using hydrocarbon programs from the regular rock-eval analysis. Energy Fuels 31(2):1832–1841. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.6b01569
Chen X, Eichhubl P, Olson JE, Dewers TA (2019) Effect of water on fracture mechanical properties of shales. J Geophys Res: Solid Earth 124(3):2428–2444. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018JB016479
Daneshfar R, Karimi Nouroddin M, Mousavi Golsefid SZ, Mohammadi-Khanaposhtani M, Davoudi E, Shariati K (2023) Experimental investigation and modeling of fluid and carbonated rock interactions with EDTA chelating agent during EOR process. Energy Fuels. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.2c02702
Elyasi A, Goshtasbi K, Hashemolhosseini H (2016) Coupled solid and fluid mechanics simulation for estimating optimum injection pressure during reservoir CO2-EOR. Struct Eng Mech 59(1):37–57. https://doi.org/10.12989/sem.2016.59.1.037
Fawad M, Hansen JA, Mondol NH (2020) Seismic-fluid detection—a review. Earth-Sci Rev. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103347
Galkin SV, Martyushev DA, Osovetsky BM, Kazymov KP, Song H (2022) Evaluation of void space of complicated potentially oil-bearing carbonate formation using X-ray tomography and electron microscopy methods. Energy Rep 8:6245–6257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2022.04.070
Gassmann F (1951) Elastic waves through a packing of spheres. Geophysics 16:673–685. https://doi.org/10.1190/1.1437718
Ghayeni H, Mahmoudy Gharaie MH, Mousavi Harami R, Vahidinia M, Sharifi J (2022) Sedimentological and geochemical evidence of Aptian–Albian transition in Dezful Embayment, Zagros sedimentary basin. Appl Sedimentol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-07291-0
Gray D, Day S, Schapper S (2015) Rock physics driven seismic data processing for the Athabasca oil sands, Northeastern Alberta. CSEG Rec 32–40
Guo Z, Lv X, Liu C, Chen H, Cai Z (2022) Characterizing gas hydrate–bearing marine sediments using elastic properties—part 1: rock physical modeling and inversion from well logs. J Mar Sci Eng 10:1379
Hashemi SS, Kovscek AR, Zoback MD (2022) Effect of supercritical CO2 on the poroelastic characteristics of poorly cemented sandstone reservoirs during depletion and injection. In: SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition. OnePetro. https://doi.org/10.2118/210228-MS
Hatami M, Bayless D, Sarvestani A (2022) Poroelastic effects on gas transport mechanisms and influence on apparent permeability in shale. Int J Rock Mech Mining Sci 153:105102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2022.105102
Huang L, Stewart RR, Sil S, Dyaur N (2015) Fluid substitution effects on seismic anisotropy. J Geophys Res: Solid Earth: Solid Earth 120(2):850–863. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014JB011246
Li C, Pan JG, Wang HB, Li HZ, Feng C, Zhou JF (2022) Study on seismic petrophysics and dispersion characteristics of carbonate rocks with deep ultra-deep complex pore structure in Tarim Basin. Appl Geophys. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11770-022-0974-y
Liu X, Wen Z, Wang Z, Song C, He Z (2018) Structural characteristics and main controlling factors on petroleum accumulation in Zagros Basin, Middle East. J Nat Gas Geosci 3(5):273–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnggs.2018.11.004
Liu J, Zhang G, Bai J, Ding W, Yang H, Liu Y (2022) Quantitative prediction of the drilling azimuth of horizontal wells in fractured tight sandstone based on reservoir geomechanics in the Ordos Basin, central China. Mar Petrol Geol 136:105439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2021.105439
Lockhart LP, Flemings PB, Nikolinakou M, Germaine J (2023) Velocity-based pore pressure prediction in a basin with late-stage erosion: Delaware Basin, US. Mar Petrol Geol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2023.106159
Makarian E, Elyasi A, Moghadam RH, Khoramian R, Namazifard P (2023) Rock physics-based analysis to discriminate lithology and pore fluid saturation of carbonate reservoirs: a case study. Acta Geophysica 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11600-023-01029-0
Mansourian D, Hamidi A, Makarian E, Namazifard P, Mirhashemi M (2022) Geophysical Surveys for Saltwater Intrusion Assessment Using Electrical Resistivity Tomography and Electromagnetic Induction Methods. 48(4):1–20. https://doi.org/10.22059/jesphys.2022.324755.1007328
Mashhadi ZS, Rabbani AR, Kamali MR, Mirshahani M, Khajehzadeh A (2015) Burial and thermal maturity modeling of the Middle Cretaceous-Early Miocene petroleum system, Iranian sector of the Persian Gulf. Pet Sci 12:367–390. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12182-015-0040-y
Mehmandosti EA, Adabi MH, Woods AD (2013) Microfacies and geochemistry of the Middle Cretaceous Sarvak Formation in Zagros Basin, Izeh Zone, SW Iran. Sed Geol 293:9–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sedgeo.2013.04.005
Miele R, Grana D, Seabra Varella LE, Viola Barreto B, Azevedo L (2023) Iterative geostatistical seismic inversion with rock physics constraints for permeability prediction. Geophysics 88(2):1–51
Mode AW, Willie ES, Eradiri JN, Umeadi MI (2022) Geochemical and mineralogical controls on the geomechanical properties of the Eze-Aku Shale: implications for a potential hydrocarbon reservoir. J Afr Earth Sci 196:104698. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2022.104698
Navidtalab A, Rahimpour-Bonab H, Nazari-Badii A, Sarfi M (2014) Challenges in deep basin sequence stratigraphy: a case study from the Early-Middle Cretaceous of SW Zagros. Facies 60(1):195–215. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10347-013-0377-x
Ni J, Gu H, Wang Y (2022) Seismic wave equation formulated by generalized viscoelasticity in fluid-saturated porous media. Geophysics 87(2):T111–T121. https://doi.org/10.1190/geo2021-0254.1
Norina DA, Stupakova AV, Kiryukhina TA (2014) Depositional environments and the hydrocarbon generative potential of Triassic rocks of the Barents Sea Basin. Mosc Univ Geol Bull 69(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.3103/S0145875214010062
Onyia EC (1988) Relationships between formation strength, drilling strength, and electric log properties. In: 63rd Ann. Tech. Conf. Houston, 2–5 October 1988, TX, USA. SPE 18166. https://doi.org/10.2118/18166-MS
Peters KE, Cassa MR (1994) Applied source rock geochemistry. AAPG Memoir: Petrol Syst From 60(3):93–120. https://doi.org/10.1306/M60585C5
Quintal B, Steeb H, Frehner M, Schmalholz SM, Saenger EH (2012) Pore fluid effects on S-wave attenuation caused by wave-induced fluid flowPore fluid effects on S-wave attenuation. Geophysics 77(3):L13–L23. https://doi.org/10.1190/geo2011-0233.1
Razmjooei MJ, Thibault N, Kani A, Dinarès-Turell J, Pucéat E, Chin S (2020) Calcareous nannofossil response to Late Cretaceous climate change in the eastern Tethys (Zagros Basin, Iran). Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 538:109418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2019.109418
Sabouhi M, Moussavi-Harami R, Kadkhodaie A, Rezaee P, Jalali M, Wood DA (2023) Stratigraphic influences on reservoir heterogeneities of the Mid-Cretaceous carbonates in southwest Iran: Insight from an integrated stratigraphic, diagenetic and seismic attribute study. J Asian Earth Sci 243:105514
Solazzi SG, Guarracino L, Rubino JG, Holliger K (2019) Saturation hysteresis effects on the seismic signatures of partially saturated heterogeneous porous rocks. J Geophys Res: Solid Earth 124(11):11316–11335. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019JB017726
Steiner AP and Hickey KA (2023) Fluid partitioning between veins/fractures and the host rocks in Carlin-type Au deposits: a significant control on fluid-rock interaction and Au endowment. Mineralium Deposita 1–27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00126-022-01159-3
Suriamin F, Pranter MJ (2017) PS petrophysical properties from quantitative multiscale pore-structure characterization in unconventional carbonate reservoir: an example from the mid-continent Mississippian limestones. https://www.searchanddiscovery.com/documents/2017/80598suriamin/ndx_suriamin.pdf
Vafaie A, Kivi IR (2020) An investigation on the effect of thermal maturity and rock composition on the mechanical behavior of carbonaceous shale formations. Mar Petrol Geol 116:104315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2020.104315
Wang H, Wang Z, Ma J, Li L, Wang Y, Tan M, Zhang Y, Cui S, Qu Z (2022) Effective pressure prediction from 4D seismic AVO data during CO2-EOR and storage. Int J Greenhouse Gas Control 113:103525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijggc.2021.103525
Wang Y, Zong Z, Yin X (2022b) Fluid discrimination incorporating amplitude variation with angle inversion and squirt flow of the fluid. Pet Sci 19(4):1592–1604. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petsci.2022.03.007
Zhou X, Ba J, Santos JE, Carcione JM, Fu LY, Pang M (2021) Fluid discrimination in ultra-deep reservoirs based on a double double-porosity theory. Front Earth Sci 9:288. https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2021.649984
Zoback MD (2010) Reservoir geomechanics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511586477
Acknowledgements
The paper's authors express a special thanks to the National Iranian South Oil Company (NISOC) for supplying all data and information to present the research manuscript.
Funding
This research received no specific grant from public, commercial, or not-for-profit funding agencies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
EM: data curation, analysis of the geomechanical data, writing the original draft, revision, and editing of the manuscript. ABMNA: geochemical laboratory tests and REP analysis, methodology, investigation, NSM: discussion and analysis of seismic results, revision, and editing of the manuscript. DM: geophysical studies, writing, revision, and editing of the manuscript. AE: calculating and analyzing the geomechanical results, writing the original draft, and revising and editing. PN: methodology, revision, and editing of the manuscript. DAM: analysis of results, revision, and editing of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Makarian, E., Abad, A.B.M.N., Manaman, N.S. et al. An efficient and comprehensive poroelastic analysis of hydrocarbon systems using multiple data sets through laboratory tests and geophysical logs: a case study in an iranian hydrocarbon reservoir. Carbonates Evaporites 38, 37 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-023-00861-1
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-023-00861-1