Abstract
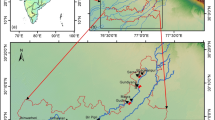
The Arcas pond complex in Cuenca (Spain) develops within an interstratified karst system that affects gypsum deposits of the Cretaceous-Tertiary transition period. The formation of this complex is influenced by fracturing, which acts both as the preferential pathway for groundwater movement and the connecting and upward flow mechanism across aquifer formations. Such fracturing also favors the development of karst morphologies in the form of collapse dolines that are connected to the aquifer and which display a permanent character. Hydrochemical studies have allowed the identification of four types of ponds that show varying degrees of behavior and connection with the confined gypsum aquifer. Evaporation, oversaturation and gypsum and limestone mud precipitation processes take place in the more disconnected ponds. The study of the annual evolution of the water column in two of the ponds that show differing degrees of connection with the groundwater allows for an evaluation of the manner in which groundwater influences the stratification/mixing processes that take place in such ponds, and of the physico-chemical characteristics governed by these processes.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armengol J (1997) Caracterización estructural del zooplancton de las lagunas cársticas de Cuenca, con especial atención a su distribución vertical. Doctoral Thesis. Universitat de Valencia
Calaforra JM, Pulido-Bosch A (2003) Evolution of the gypsum karst of Sorbas (SE Spain). Geomorphology 50:173–180
Camacho A (1997) Ecología de los microorganismos fotosintéticos en las aguas microaerobias y anóxicas de la laguna de Arcas. Doctoral Thesis. Universitat de Valencia
Cooper A (1996) Gypsum karst of Great Britain. In: Klimchouk A, Lowe D, Cooper A, Sauro U (eds). Gypsum karst of the world. Int J Speleology Theme issue 25 (3/4), pp 195–202
Cullimore DR (1993) Practical manual of groundwater microbiology. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton
De la Hera A, Martínez-Parra M, López-Pamo E and Santofimia E (2009) Primeros resultados sobre el estudio hidrogeológico del sinclinal de Fuentes y su relación con los complejos de humedales de Arcas y del río Moscas (Cuenca, España). Póster. Jornadas sobre “El papel del agua subterránea en el funcionamiento de los humedales” Zaragoza 22–23 October 2009. International Association of Hydrogeologists-Spanish Group
Ford DC, Williams PW (1989) Karst geomorphology and hydrology. Unwin Hyman, London
Gutiérrez F, Cooper AH, Johnson KS (2008) Identification, prediction and mitigation of sinkhole hazards in evaporite karst areas. Environ Geol 53:1007–1022
Klimchouk A (1996): The typology of gypsum karst according to its geological and geomorphological evolution. In: Klimchouk A, Lowe D, Cooper A, Sauro U (eds). Gypsum karst of the world. International J Speleol Theme issue 25 (3/4), pp 49–60
Klimchouk A, Aksem SD (2002) Gypsum karst in the Western Ukraine: hydrochemistry and solution rates. Carbonates Evaporites l7(2):142–153
Klimchouk A, Andrejchuk V (1996) Sulphate rocks as an arena for karst development. In: Klimchouk A, Lowe D, Cooper A, Sauro U (eds). Gypsum karst of the world. Int J Speleol Theme issue 25(3/4):9–20
Klimchouk A, Forti P, Cooper A (1996a) Gypsum karst of the world: a brief overwiew. In: Klimchouk A, Lowe D, Cooper A, Sauro U (eds). Gypsum karst of the world. Int J Speleol Theme issue 25(3/4):159–181
Klimchouk A, Cucchi F, Calaforra JM, Aksem S, Finocchiaro F, Forti F. (1996b) Dissolution of gypsum from field observations. In: Klimchouk A, Lowe D, Cooper A, Sauro U (eds). Gypsum karst of the world. Int J Speleol Theme issue 25(3/4):37–48
Martínez-Parra M (2003) Informe hidrogeológico para la mejora del abastecimiento público de agua potable a la localidad de Arcas del Villar (Cuenca). Internal report H2-006/04 Instituto Geológico y Minero de España, Madrid. https://doi.org/www.igme.es/internet/sidPDF/084000/452/84452_0001.pdf. Accessed 28 July 2007
Martínez-Parra M, De la Hera A, López-Pamo E, Moreno MJ, Montero E, Santofimia E (2010) Geomorphological characteristics of the karst-related lakes in gypsum in the Arcas and river Moscas Lake complexes (Cuenca province). In: Andreo B. et al. (eds.) Advances in research in karst media. Environmental Concerns in the 21st Century. Springer, Leipzig, pp 361–365. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-12485-0
Nicod J (2006) Lakes in gypsum karst: some examples in alpine and Mediterranean countries. Acta Carsologica 35(1):69–78
Paskauskas R, Kucinskiene A, Zvikas A (2005) Sulfate-reducing bacteria in gypsum karst lakes of northern Lithuania. Microbiology 74(6):715–721
Rodrigo MA (1997) Limnología comparada de las lagunas de dos sistemas cársticos de Cuenca. Bacterias fotosintéticas de la laguna de la Cruz y la Laguna Arcas-2. Doctoral Thesis. Universitat de Valencia
Rodriguez-Rodriguez M, Benavente J, Julian JJCS et al (2006) Estimation of groundwater exchange with semi-arid playa lakes (Anterquera region, southern Spain). J Arid Environ 66(2):272–289
Sanz E (2002) El karst en yesos en Fuentes. Karst and environment Fundación Cueva de Nerja; Nerja-Málaga. Book of proceedings, pp 351–358
Sauro U (1996) Geomorphological aspects of gypsum karst areas with special emphasis on exponed karsts. In: Klimchouk A, Lowe D, Cooper A, Sauro U (eds). Gypsum karst of the world. Int J Speleol Theme issue 25(3/4):105–114
Soriano MA, Simon JL, Gracia J, Salvador T (1994) Alluvial sinkholes over gypsum in the Ebro basin (Spain): genesis and environmental impact. Hydrol Sci (Journal- des Sciences Hydrologiques) 39(3):257–267
Acknowledgments
This study is part of the activities captured in the Agreement suscribed between IGME and the Excma. Diputación Provincial de Cuenca (Provincial Council of Cuenca) for the years 2008 and 2011. The aforementioned data come from the thesis paper on the Hydrogeology of the Cuenca Range conducted by Marc Martínez-Parra titled “Hidrogeología de la Serranía de Cuenca”. Likewise, isotope analyses carried out at CEDEX fall under the IGME/CEDEX Joint Isotope Hydrology Laboratory agreement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martínez-Parra, M., López-Pamo, E., De la Hera, A. et al. Main characteristics of ponds associated with gypsum karst aquifer in the Arcas pond complex (Cuenca, Spain). Carbonates Evaporites 26, 47–60 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-011-0045-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-011-0045-6