Abstract
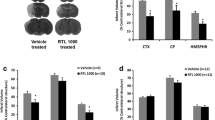
A key target for novel stroke therapy is the regulation of post-ischemic inflammatory mechanisms. Recent evidence emphasizes the role of T lymphocytes of differing subtypes in the evolution is ischemic brain damage. We have recently demonstrated the benefit of myelin antigen-specific immunodulatory agents known as recombinant T cell receptor ligands (RTLs) in a standard murine model of focal stroke. The aim of the current study was to extend this initial observation to RTL treatment in a therapeutically relevant timing after middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) and verify functional benefit to complement histological outcome measures. We observed that the administration of mouse-specific RTL551 reduced infarct size and improved sensorimotor outcome when administered within a 3 h post-ischemic therapeutic window. RTL551 treatment reduced cortical, caudate putamen, and total infarct volume as compared to vehicle-treated mice. Using a standard behavioral testing repertoire, we observed that RTL551 reduced sensorimotor impairment 3 days after MCAO. Humanized RTL1000 (HLA-DR2 moiety linked to hMOG-35-55 peptide) also reduced infarct size in HLA-DR2 transgenic mice. These data indicate that this neuroantigen-specific immunomodulatory agent reduces damage when administered in a therapeutically relevant reperfusion timeframe.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad M, Graham SH. Inflammation after stroke: mechanisms and therapeutic approaches. Transl Stroke Res. 2010;1:74–84.
Burrows GG, Chang JW, Bachinger HP, Bourdette DN, Offner H, Vandenbark AA. Design, engineering and production of functional single-chain T cell receptor ligands. Protein Eng. 1999;12:771–8.
Emsley HC, Smith CJ, Georgiou RF, Vail A, Tyrrell PJ, Barberan EM, et al. Correlation of systemic inflammatory response with infarct volume in acute ischemic stroke patients. Stroke. 2005;36:228–9.
Finn TP, Jones RE, Rich C, Dahan R, Link J, David CS, et al. HLA-DRB1*1501 risk association in multiple sclerosis may not be related to presentation of myelin epitopes. J Neurosci Res. 2004;78:100–14.
Gelderblom M, Leypoldt F, Steinbach K, Behrens D, Choe CU, Siler DA, et al. Temporal and spatial dynamics of cerebral immune cell accumulation in stroke. Stroke. 2009;40:1849–57.
Gonzalez-Gay MA, Zanelli E, Khare SD, Krco CJ, Zhou P, Inoko H, et al. Human leukocyte antigen-DRB1*1502 (DR2Dw12) transgene reduces incidence and severity of arthritis in mice. Hum Immunol. 1996;50:54–60.
Herson PS, Palmateer J, Hurn PD, DeVries AC. Evaluating behavioral outcomes from ischemic brain injury. In: Raber J, editor. Translational animal models of behavioral analysis. New York: Humana; 2010.
Huan J, Kaler LJ, Mooney JL, Subramanian S, Hopke C, Vandenbark AA, et al. MHC class II derived recombinant T cell receptor ligands protect DBA/1LacJ mice from collagen-induced arthritis. J Immunol. 2008;180:1249–57.
Kleinschnitz C, Schwab N, Kraft P, Hagedorn I, Dreykluft A, Schwarz T, et al. Early detrimental T-cell effects in experimental cerebral ischemia are neither related to adaptive immunity nor thrombus formation. Blood. 2010;115:3835–42.
Li X, Blizzard KK, Zeng Z, DeVries AC, Hurn PD, McCullough LD. Chronic behavioral testing after focal ischemia in the mouse: functional recovery and the effects of gender. Exp Neurol. 2004;187:94–104.
Liesz A, Suri-Payer E, Veltkamp C, Doerr H, Sommer C, Rivest S, et al. Regulatory T cells are key cerebroprotective immunomodulators in acute experimental stroke. Nat Med. 2009;15:192–9.
Lloyd-Jones D, Adams RJ, Brown TM, Carnethon M, Dai S, De SG, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2010 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2010;121:e46–e215.
Maeda K, Hata R, Hossmann KA. Differences in the cerebrovascular anatomy of C57black/6 and SV129 mice. Neuroreport. 1998;9:1317–9.
Noskin O, Krakauer JW, Lazar RM, Festa JR, Handy C, O'Brien KA, et al. Ipsilateral motor dysfunction from unilateral stroke: implications for the functional neuroanatomy of hemiparesis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2008;79:401–6.
Offner H, Subramanian S, Parker SM, Afentoulis ME, Vandenbark AA, Hurn PD. Experimental stroke induces massive, rapid activation of the peripheral immune system. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2006;26:654–65.
Offner H, Sinha S, Burrows GG, Ferro AJ, Vandenbark AA. RTL therapy for multiple sclerosis: a phase I clinical study. J Neuroimmunol. 2010;231(1–2):7–14.
Schaefer SY, Haaland KY, Sainburg RL. Ipsilesional motor deficits following stroke reflect hemispheric specializations for movement control. Brain. 2007;130:2146–58.
Sinha S, Subramanian S, Proctor TM, Kaler LJ, Grafe M, Dahan R, et al. A promising therapeutic approach for multiple sclerosis: recombinant T-cell receptor ligands modulate experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by reducing interleukin-17 production and inhibiting migration of encephalitogenic cells into the CNS. J Neurosci. 2007;27:12531–9.
Sinha S, Subramanian S, Emerson-Webber A, Lindner M, Burrows GG, Grafe M, et al. Recombinant TCR ligand reverses clinical signs and CNS damage of EAE induced by recombinant human MOG. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2010;5:231–9.
Smith CJ, Emsley HC, Gavin CM, Georgiou RF, Vail A, Barberan EM, et al. Peak plasma interleukin-6 and other peripheral markers of inflammation in the first week of ischaemic stroke correlate with brain infarct volume, stroke severity and long-term outcome. BMC Neurol. 2004;4:2.
Subramanian S, Zhang B, Kosaka Y, Burrows GG, Grafe MR, Vandenbark AA, et al. Recombinant T cell receptor ligand treats experimental stroke. Stroke. 2009;40:2539–45.
Uchida M, Palmateer JM, Herson PS, DeVries AC, Cheng J, Hurn PD. Dose-dependent effects of androgens on outcome after focal cerebral ischemia in adult male mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2009;29:1454–62.
Zhu W, Wang L, Zhang L, Palmateer JM, Libal NL, Hurn PD, et al. Isoflurane preconditioning neuroprotection in experimental focal stroke is androgen-dependent in male mice. Neuroscience. 2010;169:758–69.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Ms. Kathy Gage, grants and publications writer for the Department of Anesthesiology and Perioperative Medicine, OHSU, for her outstanding editorial work in the preparation of this paper. This material is based upon work supported in part by the Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration, Office of Research and Development, Biomedical Laboratory Research and Development. The contents do not represent the views of the Department of Veterans Affairs or the US government.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akiyoshi, K., Dziennis, S., Palmateer, J. et al. Recombinant T Cell Receptor Ligands Improve Outcome After Experimental Cerebral Ischemia. Transl. Stroke Res. 2, 404–410 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-011-0085-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-011-0085-1