Abstract
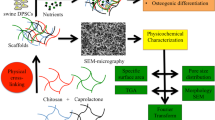
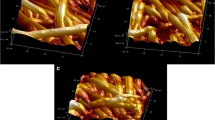
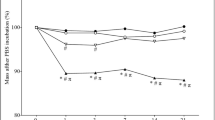
The effect of molecular characteristics and morphology on mechanical performance and biocompatibility of PLA-based spongious scaffolds was studied. PLLA and PDLLA with different molecular weight were studied. It was shown that the structure and the mechanical properties of PLA sponges slightly depend on the molecular mass of the polymer. In the contrary, porosity of the sponge-like material has great effect on its mechanical properties. Biocompatibility tests showed that PLLA provide better matrix behavior compared to PDLLA for the stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xue, J., Lin, H., Bean, A., Tang, Y., Tan, J., Tuan, R., & Wang, B. (2017). One-step fabrication of bone morphogenetic protein-2 gene-activated porous poly-L-lactide scaffold for bone induction. Molecular Therapy — Methods & Clinical Development, 7, 50–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtm.2017.08.008.
Bukharova, T. B., Volkov, A. V., Antonov, E. N., Vihrova, E. B., Popova, A. V., Popov, V. K., & Goldstein, D. V. (2013). Tissue-engineered construction made of adipose derived multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells, polylactide scaffolds and platelet gel. Gene and Cells, 8(4), 61–68.
Lin, X., Bo, W., Yang, G., & Gauthier, M. (2012). Poly (lactic acid)-based biomaterials: synthesis, modification and applications. Biomedical Science, Engineering and Technology, 11, 247–282. https://doi.org/10.5772/23927.
Antonov, E. N., Bukharova, T. B., Dunaev, A. G., Krotova, L. I., Nifant’ev, I. E., Popov, V. K., & Shlyakhtin, A. V. (2017). New “old” polylactides for tissue engineering constructions. Inorganic Materials: Applied Research, 8(5), 704–712. https://doi.org/10.1134/S2075113317050033.
Middleton, J. C., & Tipton, A. J. (2000). Synthetic biodegradable polymers as orthopedic devices. Biomaterials, 21(23), 2335–2346. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0142-9612(00)00101-0.
Ikada, Y., & Tsuji, H. (2000). Biodegradable polyesters for medical and ecological applications. Macromolecular Rapid Communications, 21(3), 117–132. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1521-3927(20000201)21:3<117::AID-MARC117>3.0.CO;2-X.
Sarasua, J. R., Lo’pez-Rodrı’guez, N., Zuza, E., Petisco, S., Castro, B., del Olmo, M., Palomares, T., & Alonso-Varona, A. (2011). Crystallinity assessment and in vitro cytotoxicity of polylactide scaffolds for biomedical applications. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine, 22, 2513–2523. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-011-4425-1.
Yi, Q., Wen, X., Li, L., He, B., Nie, Y., Wu, Y., Zhang, Z., & Gu, Z. (2009). The chiral effects on the responses of osteoblastic cells to the polymeric substrates. European Polymer Journal, 45, 1970–1978. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2009.04.018.
Funding
This work was supported by RSF (grant no. 16-15-00298).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grigoriev, T.E., Bukharova, T.B., Vasilyev, A.V. et al. Effect of Molecular Characteristics and Morphology on Mechanical Performance and Biocompatibility of PLA-Based Spongious Scaffolds. BioNanoSci. 8, 977–983 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-018-0557-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-018-0557-9