Abstract
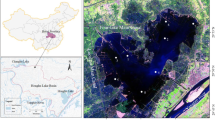
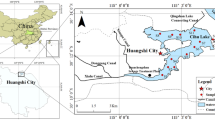
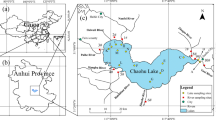
In semiarid areas, closed lakes are essential for maintaining local ecosystem functions. However, many closed lakes are facing continuous deterioration of water quality. To scientifically and comprehensively evaluate the water quality of Daihai Lake (a closed lake in a semiarid region of China) and analyze its spatiotemporal variations and influencing factors, this study analyzed the following nine water quality parameters at five monitoring stations from 2008 to 2017 using the water quality index (WQI) and multivariate statistical techniques: permanganate index (CODMn), biochemical oxygen demand (BOD5), total nitrogen (TN), total phosphorus (TP), fluoride (F−), water temperature (WT), pH, ammonia nitrogen (NH4+-N), and dissolved oxygen (DO). The results showed that the average WQI at the five monitoring stations varies between 45.53 and 46.98, and the water quality of Daihai Lake has improved (2013–2017) after an initial period of pollution (2008–2013), but it remains poor. The main contaminants were identified as CODMn, BOD5, TN, TP, and F−, which showed average concentrations of 13.12, 6.19, 0.98, 0.13, and 2.82 mg/L, respectively. The water quality showed small spatial variability, but distinct variations between the dry and wet seasons. Discriminant analysis showed that 97% of the water quality data can be classified into the correct seasonal with six parameters (WT, pH, CODMn, TN, and NH4+-N). Anthropogenic activities were the main factors driving the variation in water quality. Climatic conditions promoted the release of internal pollutants and aggravated the impact of external pollutants during the dry and wet seasons, respectively. The minimum WQI determined using only key water quality parameters (DO, BOD5, NH4+-N, TP, and TN) could effectively reflect the actual water quality. These results can provide references for lake ecosystem protection and water resources management.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajmal T, Anyachebelu TK, Conrad M, Rawson DM (2019) Evaluating urban surface water quality in Luton. Environ Monit Assess 191:147
Akkoyunlu A, Akiner ME (2012) Pollution evaluation in streams using water quality indices: a case study from Turkey’s Sapanca Lake Basin. Ecol Ind 18:501–511
Alexakis D, Tsihrintzis VA, Tsakiris G, Gikas GD (2016) Suitability of water quality indices for application in lakes in the Mediterranean. Water Resour Manage 30:1621–1633
Alexakis DE (2020) Meta-evaluation of water quality indices. Application into groundwater resources. Water 12:1890
Alexakis DE (2021) Linking DPSIR model and water quality indices to achieve sustainable development goals in groundwater resources. Hydrology 8:90
Ali EM, Khairy HM (2016) Environmental assessment of drainage water impacts on water quality and eutrophication level of Lake Idku. Egypt Environ Pollut 216:437–449
Bekas GK, Alexakis DE, Gamvroula DE (2021) Forecasting discharge rate and chloride content of karstic spring water by applying the Levenberg–Marquardt algorithm. Environ Earth Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09685-5
Caroppo C, Roselli L, Di Leo A (2018) Hydrological conditions and phytoplankton community in the Lesina lagoon (southern Adriatic Sea, Mediterranean). Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 25:1784–1799
Chen JQ, Lv JM, Li N, Wang QW, Wang J (2019) External groundwater alleviates the degradation of closed lakes in semi-arid regions of China. Remote Sens 12:45
Duan WL, He B, Nover D, Yang GS, Chen W, Meng HF, Zou S, Liu CM (2016) Water quality assessment and pollution source identification of the Eastern Poyang Lake Basin using multivariate statistical methods. Sustainability 8:133
El-Serehy HA, Abdallah HS, Al-Misned FA, Al-Farraj SA, Al-Rasheid KA (2018) Assessing water quality and classifying trophic status for scientifically based managing the water resources of the Lake Timsah, the lake with salinity stratification along the Suez Canal. Saudi J Biol Sci 25:1247–1256
Fu XY, Liu HM, Yu XW, Kou X, Wen L, Dong SG, Wang LX (2020) Water sources and use strategies of plants in lake Daihai wetland. J Arid Land Resour Environ 34:42–49
Gamvroula D, Alexakis D, Stamatis G (2012) Diagnosis of groundwater quality and assessment of contamination sources in the Megara basin (Attica, Greece). Arab J Geosci 6:2367–2381
Geng MM, Wang KL, Yang N, Li F, Zou YA, Chen XS, Deng ZM, Xie YH (2021) Evaluation and variation trends analysis of water quality in response to water regime changes in a typical river-connected lake (Dongting Lake). China Environ Pollut 268:115761
Giakoumakis S, Alexakis D, Gotsis D (2013) An approximate method for estimating nutrient loads in drainage water from a coastal irrigated area. Earth Sci Res J 17:115–118
Han Q, Tong RZ, Sun WC, Zhao Y, Yu JS, Wang GQ, Shrestha S, Jin YL (2020) Anthropogenic influences on the water quality of the Baiyangdian Lake in North China over the last decade. Sci Total Environ 701:134929
Horvat M, Horvat Z, Pastor K (2021) Multivariate analysis of water quality parameters in Lake Palic. Serbia Environ Monit Assess 193:410
Jiang ZL, Liu BL, Liu H, Yang J (2013) Trace metals in Daihai Lake sediments, Inner Mongolia, China. Environmental Earth Sciences 71:255–266
Kannel PR, Lee S, Lee YS, Kanel SR, Khan SP (2007) Application of water quality indices and dissolved oxygen as indicators for river water classification and urban impact assessment. Environ Monit Assess 132:93–110
Kukrer S, Mutlu E (2019) Assessment of surface water quality using water quality index and multivariate statistical analyses in Sarayduzu Dam Lake. Turkey Environ Monit Assess 191:71
Lepparanta M, Lewis JE, Heini A, Arvola L (2018) Spatial statistics of hydrography and water chemistry in a eutrophic boreal lake based on sounding and water samples. Environ Monit Assess 190:378
Liang X, Liu HM, Ji MC, Chang M, Wen L, Yu RH, Zhuo Y, Wang LX (2021) Effects of land use/cover change on lake water quality in the semi-arid region of northern China: a case study in Lake Daihai Basin (2000–2018). J Lake Sci 33:727–736
Ma J (2021) Research on the combined effect of daihai ecological water demand and ecological water replenishment. Inner Mongolia University, Hohhot
Ouma H, Mwamburi J (2014) Spatial variations in nutrients and other physicochemical variables in the topographically closed Lake Baringo freshwater basin (Kenya). Lakes Reserv Sci Policy Manag Sustain Use 19:11–23
Pauer JJ, Auer MT (2000) Nitrification in the water column and sediment of a hypereutrophic lake and adjoining river system. Water Resour 34:1247–1254
Pesce SF, Wunderlin DA (2000) Use of water quality indices to verify the impact of Cordoba City (Argentina) on Suquia River. Water Resour 34:2915–2926
Sánchez E, Colmenarejo MF, Vicente J, Rubio A, García MG, Travieso L, Borja R (2007) Use of the water quality index and dissolved oxygen deficit as simple indicators of watersheds pollution. Ecol Ind 7:315–328
Sekaluvu L, Zhang L, Gitau M (2018) Evaluation of constraints to water quality improvements in the Western Lake Erie Basin. J Environ Manage 205:85–98
Sener S, Sener E, Davraz A (2017) Evaluation of water quality using water quality index (WQI) method and GIS in Aksu River (SW-Turkey). Sci Total Environ 584–585:131–144
Shalby A, Elshemy M, Zeidan BA (2020) Assessment of climate change impacts on water quality parameters of Lake Burullus. Egypt Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 27:32157–32178
Shrestha S, Kazama F (2007) Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: a case study of the Fuji river basin, Japan. Environ Model Softw 22:464–475
Sremacki M, Obrovski B, Petrovic M, Mihajlovic I, Dragicevic P, Radic J, Vojinovic Miloradov M (2020) Comprehensive environmental monitoring and assessment of protected wetland and lake water quality in Croatia and Serbia. Environ Monit Assess 192:187
Su XX, He Q, Mao YF, Chen Y, Hu Z (2019) Dissolved oxygen stratification changes nitrogen speciation and transformation in a stratified lake. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 26:2898–2907
Sun YW, Zhang RQ, Ma RP, Zhou HJ, Zhang FJ, Guo GH, Li HX, Lu CW (2021) Distribution, sources, and ecological risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the sediments of Daihai Lake in Inner Mongolia, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 28:23123–23132
Tang L, Duan X, Kong F, Zhang F, Zheng Y, Li Z, Mei Y, Zhao Y, Hu S (2018) Influences of climate change on area variation of Qinghai Lake on Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau since 1980s. Sci Rep 8:7331
Tian C, Pei HY, Hu WR, Xie J (2013) Phytoplankton variation and its relationship with the environmental factors in Nansi Lake, China. Environ Monit Assess 185:295–310
Tian L, Zhu X, Wang L, Du P, Peng F, Pang Q (2020) Long-term trends in water quality and influence of water recharge and climate on the water quality of brackish-water lakes: a case study of Shahu Lake. J Environ Manag 276:111290
Tian LF, Luo GL, Ma YX, Jiang WJ (2019) The causes of water pollution in the Shahu Lake of Ningxia based on migration and transformation characteristics of regional water environment contaminants. Environ Monit China 35:85–92
Wang J (2021) Coupled simulation of climate and hydrological processes in the Daihai Basin in recent 40 years. Inner Mongolia University, Hohhot
Wang JL, Fu ZS, Qiao HX, Liu FX (2019a) Assessment of eutrophication and water quality in the estuarine area of Lake Wuli, Lake Taihu, China. Sci Total Environ 650:1392–1402
Wang SH, Bai MX, Chen JY, Zhao L, Zhang B, Guo YY, Jiang X (2019b) Research on the ecological protection and restoration of mountain-river-forest-farmland-lake-grassland system in typical farming-pastoral ecotone: taking Daihai Lake Basin in Inner Mongolia as an example. J Environ Eng Technol 9:515–519
Wang T, Chen JS, Xu Y, Zhan LC, Huang DW (2017) Isotopes and hydrochemistry of Daihai Lake recharging sources, Northern China. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 312:615–629
Wu L, Han C, Zhu GW, Zhong WH (2019) Responses of active ammonia oxidizers and nitrification activity in eutrophic lake sediments to nitrogen and temperature. Appl Environ Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00258-19
Wu ZS, Wang XL, Chen YW, Cai YJ, Deng JC (2018) Assessing river water quality using water quality index in Lake Taihu Basin, China. Sci Total Environ 612:914–922
Wu ZS, Zhang DW, Cai YJ, Wang XL, Zhang L, Chen YW (2017) Water quality assessment based on the water quality index method in Lake Poyang: the largest freshwater lake in China. Sci Rep 7:17999
Xia M, Dong S, Chen Y, Liu H (2021) Study on evolution of groundwater-lake system in typical prairie open-pit coal mine area. Environ Geochem Health 43:4075–4087
Xu QH, Xiao JL, Li YC, Tian F, Nakagawa T (2010) Pollen-based quantitative reconstruction of holocene climate changes in the Daihai Lake Area, Inner Mongolia, China. J Clim 23:2856–2868
Yang GS, Ma RH, Zhang L, Jiang JH, Yai SC, Zhang M, Zeng HA (2010) Lake status, major problem and protection strategy in China. J Lake Sci 22:799–810
Yang H, Zhao Y, Wang JH, Xiao WH, Jarsjo J, Huang Y, Liu Y, Wu JP, Wang HJ (2020) Urban closed lakes: nutrient sources, assimilative capacity and pollutant reduction under different precipitation frequencies. Sci Total Environ 700:134531
Yang K, Yu Z, Luo Y, Yang Y, Zhao L, Zhou X (2018a) Spatial and temporal variations in the relationship between lake water surface temperatures and water quality - a case study of Dianchi Lake. Sci Total Environ 624:859–871
Yang X, Li CY, Li WB, Shi XH, Zhao SN, Wang XY (2018b) Characteristics of nitrogen accumulation in closed inland lakes in summer: a case study of Dali-Nor Lake, China. J Agro Environ Sci 37:2262–2269
Zhang Q, Yu RH, Jin Y, Zhang ZZ, Liu XY, Xue H, Hao YL, Wang LX (2019) Temporal and spatial variation trends in water quality based on the wpi index in the shallow lake of an arid area: a case study of Lake Ulansuhai, China. Water 11:1410
Zhao L, Chen JY, Jiang X, Zheng SF, Wang SH (2020) Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics and difference analysis of nitrogen and phosphorus in Daihai Lake. Environ Sci 41:1676–1683
Acknowledgements
This study was jointly funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51869014), National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2021YFC3201203), Major Science and Technology Projects of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region (Grant Nos. 2020ZD0009 and ZDZX2018054), Open Project Program of the Ministry of Education Key Laboratory of Ecology and Resources Use of the Mongolian Plateau (Grant No. KF2020006), and Special Funds for Innovation and Entrepreneurship of Postgraduates in Inner Mongolia University (Grant No. 11200-121024). We also thank editors and anonymous reviewers for the constructive suggestions and comments.
Funding
This study was jointly funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51869014), National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2021YFC3201203), Major Science and Technology Projects of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region (Grant Nos. 2020ZD0009 and ZDZX2018054), Open Project Program of the Ministry of Education Key Laboratory of Ecology and Resources Use of the Mongolian Plateau (Grant No. KF2020006), and Special Funds for Innovation and Entrepreneurship of Postgraduates in Inner Mongolia University (Grant No. 11200–121024).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. XR contributed to investigation, formal analysis, software, methodology, writing the original draft, and writing, reviewing, and editing. RY contributed to supervision, conceptualization, and writing, reviewing, and editing. JK contributed to investigation and data curation. CL contributed to writing, reviewing, and editing. RW, YL, and ZZ contributed to investigation. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, X., Yu, R., Kang, J. et al. Water pollution characteristics and influencing factors of closed lake in a semiarid area: a case study of Daihai Lake, China. Environ Earth Sci 81, 393 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-022-10526-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-022-10526-2