Abstract
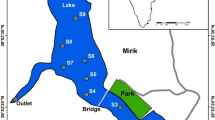
A total of 29 surface sediments were collected from the Daihai Lake, China. Concentrations of metals (Cu, Pb, Zn, and Cd) were determined using HR-ICP-MS after digestion with the mixture of HNO3–HF–HCl (aqua regia), and chemically fractionated according to the modified the European Community Bureau of Reference sequential extraction procedure. Total organic carbon contents and grain size were also analyzed. Average concentrations (ppm) for Cu (39.4 ± 10.6), Pb (29.9 ± 6.1), Zn (102.6 ± 23.3), and Cd (0.21 ± 0.07) were found in the sediments. The concentrations of metals are relatively higher in the central area of lake, while lower nearby the area with a shallower water depth. Sequential extraction results show that Cu and Zn are mainly distributed in the residual fraction, while Cd is dominantly in the non-residual fraction. Enrichment factor values and geoaccumulation indexes suggest that there are not obvious enrichments of Cu, Pb, and Zn in the sediments, but Cd pollution can be found in most of the area of Daihai Lake. The sources for Cu, Pb, and Zn are attributed to atmospheric deposition, which might be mainly associated with coal combustion. Agricultural runoff in polluted soils and coal combustion might be main sources of the Cd pollution in the lake.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvin CR (2002) Methods of multivariate analysis. Wiley, USA
Bordas F, Bourg AM (1998) A critical evaluation of sample pretreatment for storage of contaminated sediments to be investigated for the potential mobility of their trace metal load. Water Air Soil Pollut 103:137–149
Charkhabi AH, Sakizadeh M, Rafiee G (2005) Seasonal fluctuation in trace metal pollution in Iran’s Siahroud River. Environ Sci Pollut Res 12:264–270
China Environmental Monitoring Station (1990) Natural background values of soil elements in China. China Environmental Science Press, Bejing (in Chinese)
Cuong DT, Obbard JP (2006) Metal speciation in coastal marine sediments from Singapore using a modified BCR-sequential extraction procedure. Appl Geochem 21(8):1335–1346
Gallon C, Tessier A, Gobeil C, Alfaro-De La, Torre MC (2004) Modeling diagenesis of lead in sediments of a Canadian shield lake. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 68:3531–3545
Gao XL, Chen CTA, Wang G, Xue QZ, Tang C, Chen SY (2010) Environmental status of Daya Bay surface sediments inferred from a sequential extraction technique. Est Coast Shelf Sci 86:369–378
Gaudette HE, Flight W, Tones L, Folger D (1974) An inexpensive titration method for the determinations of organic carbon in recent sediments. J Sediment Petrol 44:249–253
Graney JR, Eriksen TM (2004) Metals in pond sediments as archives of anthropogenic activities: a study in response to health concerns. Appl Geochem 19:1177–1188
Håkanson L, Jansson M (1983) Principles of lake sedimentology. Springere-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg 316 pp
Han YM, Du PX, Cao JJ, Posmentier ES (2006) Multivariate analysis of trace metal contamination in urban dusts of Xi’an, central China. Sci Total Environ 355:176–186
Han YM, Jin ZD, Cao JJ, Posmentier ES, An ZS (2007) Atmospheric Cu and Pb deposition and transport in lake sediments in a remote mountain area, northern China. Water Air Soil Pollut 179:167–181
Hang XS, Wang HY, Zhou JM, Du CW, Chen XQ (2009) Characteristics and accumulation of trace metals in sediments originated from an electroplating plant. J Hazard Mater 163:922–930
Jin ZD, Zou CJ, Li FC, Wang SM, Shen J, Liang WB (2005) Element distribution in chemical fraction of lake sediment determined by sequential extraction: the case of Lake Daihai (Northern China). J Lake Sci 17(1):47–53
Jin ZD, Li FC, Cao JJ, Wang SM, Yu JM (2006) Geochemistry of Daihai Lake sediments, Inner Mongolia, North China: implications for provenance, sedimentary sorting, and catchment weathering. Geomorphology 80:147–163
Kamenov GD, Brenner M, Tucker JL (2009) Anthropogenic versus natural control on trace element and Sr–Nd–Pb isotope stratigraphy in peat sediments of southeast Florida (USA), ~1500 AD to present. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 73:3549–3567
Liu H, Li L, Yin C, Shan B (2008) Fraction distribution and risk assessment of trace metals in sediments of Moshui Lake. J Environ Sci 20:390–397
Meyers PA, Eadie BJ (1993) Sources, degradation and recycling of organic matter associated with sinking particles in lake Michigan. Org Geochem 20:47–56
Meyers PA, Lallier-Vergès E (1999) Lacustrine sedimentary organic matter records of late quaternary paleoclimates. J Paleolimnol 21:345–372
Mohammed MH, Markert B (2006) Toxicity of trace metals on Scenedesmus quadricauda (Turp.) de Brebisson in batch cultures. Environ Sci Pollut Res 13:98–104
Morillo J, Usero J, Gracia I (2002) Partitioning of metals in sediments from the Odiel river (Spain). Environ Int 28:263–271
Müller G (1969) Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine river. Geo J 142(3):108–118
Olivares-Rieumonta S, Rosaa D, Limaa L, Grahamb DW, Alessandroa K, Borrotoa J, Martíneza F, Sánchez J (2005) Assessment of heavy metal levels in Almendares river sediments—Havana City. Cuba Water Res 39:3945–3953
Qu WC, Mike D, Wang SM (2001) Multivariate analysis of heavy metal and nutrient concentrations in sediments of Taihu lake, China. Hydrobiologia 450:83–89
Ren TJ, Ma YR, Duan LH (1995) Daihai lake in inner Mongolia. In: Jin XC (ed) Lakes in China–research of their environment. Haiyang Press, Beijing, pp 531–559
Salomons W, Forstner U (1984) Metals in the hydrocycle. Springer, Berlin
Shi Q, Thomas L, Peter R, Zhou D, Jan H (2010) Geochemical sources, deposition and enrichment of heavy metals in short sediment cores from the Pearl river estuary, southern China. J Mar Syst 82:S28–S42
Singh KP, Mohan D, Singh VK, Malik A (2005) Studies on distribution and fractionation of trace metals in Gomti river sediments–a tributary of the Ganges, India. J Hydrol 312:14–27
Sly PG (1978) Sedimentary processes in lakes. In: Lerman A (ed) Lakes: chemistry, geology, physics. Springer-Verlag, New York, pp 65–89
Sly PG (1989a) Sediment dispersion: part 1, fine sediments and significance of the silt/clay ratio. Hydorobiologia 176(177):99–110
Sly PG (1989b) Sediment dispersion: part 2, characterisation by size of sand fraction and per cent mud. Hydorobiologia 176(177):111–124
Stoeppler M (1992) Hazardous metals in environment. Elsevier Press, Amsterdam
Suthar S, Nema AK, Chabukdhara M, Gupta SK (2009) Assessment of metals in water and sediments of Hindon river, India: impact of industrial and urban discharges. J Hazard Mater 171:1088–1095
Tessier A, Campbell PGC, Bisson M (1979) Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Anal Chem 51:844–851
Wang SM, Li JR (1990) Lake sediment as an effective tool for historical climate: the case of Qinghai lake and Daihai lake. Chin Sci Bul 35:54–56 (in Chinese)
Wang SF, Jia YF, Wang SY, Wang X, Wang H, Zhao ZX, Liu BZ (2010) Fractionation of trace metals in shallow marine sediments from Jinzhou Bay, China. J Environ Sci 22(1):23–31
Weisz M, Polyak K, Hlavay J (2000) Fractionation of elements in sediment samples collected in rivers and harbors at lake Balaton and its catchment area. Microchem J 67:207–217
Xiao JL, Fan JW, Zhou L, Zhai DY, Wen RL, Qin XG (2012) A model for linking grain-size component to lake level status of a modern clastic lake. J Asian Earth Sci. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.07.003
Xu MH, Yan R, Zheng CG, Qiao Y, Han J, Sheng CD (2003) Status of trace element emission in a coal combustion process: a review. Fuel Process Technol 85:215–237
Xu QH, Li YC, Yang XL, Xiao JL, Liang WD, Peng YJ (2005) Source and distribution of pollen in the surface sediment of Daihai Lake, inner Mongolia. Quatern Int 136:33–45
Yao ZG, Bao ZY, Zhou LF, Gao P (2009) A statistical approach for determining the environment impact of surface sediments from the Dongting lake area, central China. Chin J Geochem 28:97–104
Yu T, Zhang Y, Meng W, Hu XN (2011) Characterization of heavy metals in water and sediments in Taihu Lake, China. Environ Monit Assess 184(7):4367–4382
Yuan C, Shi J, He B, Liu J, Liang L, Jiang G (2004) Speciation of trace metals in marine sediments from the east China sea by ICP-MS with sequential extraction. Environ Int 30:769–783
Zhang M, Xu J, Xie P (2007) Metals in surface sediments of large shallow eutrophic lake Chaohu, China. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 79:242–245
Zhou YK, Jiang JH, Huang Q (2006) Water quality analysis and assessment of Daihai Lake in Inner Mongolia. J Arid Land Res Environ 20(6):74–77 (in Chinese)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41106108), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 2012059 and 2012028), Special Fund for Public Welfare Industrial Research of the Ministry of Land and Resources of China (No. 201011019-05), and Important National Science & Technology Specific Projects (No. 2011ZX05023-002-005). We thank Director Zhang at the Environmental Protection Bureau, Liangcheng City, Inner Mongolia, for his assistance in the fieldwork.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, Z., Liu, B., Liu, H. et al. Trace metals in Daihai Lake sediments, Inner Mongolia, China. Environ Earth Sci 71, 255–266 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2429-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2429-5