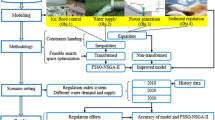
Abstract
The allocation of Limited water resources, water quality, and environmental impacts are issues that necessitate proper planning for the exploitation of water resources. In the present study optimal operation of surface water resources system is studied in the term of quantity and quality simultaneously, using Non-Dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm-II (NSGA-II) algorithm. For this purpose, the WEAP-QUAL2K coupling model was developed for the simulation of water quality and quantity. Dez dam reservoir and Dez dam downstream sub-basin in Dez river-basin, from Dez dam to BandeGhir (Dez river), in Iran is used as study site. The simulation and optimization period is considered to be 5 years (2018–2022). Given that in the verification stage of the QUAL2K and WEAP models, it can be concluded that the model has high accuracy in simulating the parameters of water quality (Temperature, pH, EC, DO, BOD, N–NH4, and N–NO3) and quantity. Two scenarios are considered. The first scenario is used for dynamical coupling of quantity–quality model (reference scenario) and the second is optimization of coupled model (optimal scenario). In optimal scenario, decision variables, environmental flow rate at BandeGhir in different months, are optimized based on multi-objective function within the range of 27.7–86.2 m3/s. The results show that, in the optimal scenario, optimal operation of surface water resources, considering the maximum demand site coverage causes to increase the water supply reliability of all demands in the Dez plain. Average water supply reliability increase from 84.46% in the reference scenario to 92.92% in the optimal scenario. Also, the results of optimal scenario compared with reference scenario show that not only the river water quality was improved, but also in river withdrawal points, especially in the agriculture withdrawal points, there is a least violations of river water quality standards.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azevedo LG, Gates TK, Fontane DG, Labadie JW, Porto RL (2000) Integration of water quantity and quality in strategic river basin planning. J Water Resour Plann Manag 126(2):85–97. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9496(2000)126:2(85)
Campolo M, Andreussi P, Soldati A (2002) Water quality control in the river Arno. Water Res 36(10):2673–2680. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(01)00483-3
Chapra SC, Pelletier GJ, Tao H (2008) QUAL2K: a modeling framework for simulating river and stream water quality, version 2.11: documentation and users manual. Civil and Environmental Engineering Department, Tufts University, Medford, MA, pp 109
Da Silva TD, Albuquerque Alves CD (2016) WEAP and QUAL2K model integration for water quality evaluations as a result of urban expansion scenarios in the Federal District of Brazil. In: World environmental and water resources congress 2016, pp 330–338. https://doi.org/10.1061/9780784479889.035
Deb K, Pratap A, Agarwal S, Meyarivan TA (2002) A fast and elitist multi objective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 6(2):182–197. https://doi.org/10.1109/4235.996017
Froebrich J, Bauer M, Ikramova M, Olsson O (2007) Water quantity and quality dynamics of the THC—Tuyamuyun Hydroengineering complex—and implications for reservoir operation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 14(6):435–442. https://doi.org/10.1065/espr2006.01.012
Guven A, Gunal M (2008) Genetic programming approach for prediction of local scour downstream of hydraulic structures. J Irrig Drain E ASCE 134(2):241–249. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9437(2008)134:2(241)
Guven A, Kisi O (2010) Estimation of suspended sediment yield in natural rivers using machine-coded linear genetic programming. Water Resour Manag 25:691–704. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-010-9721-x
Jaramillo MF, Galvis A, Escobar M, Forni L, Purkey D, Siebel JS, Lozano G, Rodríguez C, Castaño J, Sabas C (2016) Integración de los modelos WEAP y QUAL2K para la simulación de la calidad agua de fuentes superficiales. Caso de estudio: Cuenco del Río la Vieja, Colombia. Aqua-LAC 8(2):14–24
Kaddoura S, El Khatib S (2017) Review of water-energy-food Nexus tools to improve the Nexus modelling approach for integrated policy making. Environ Sci Policy 77:114–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsci.2017.07.007
Kannel PR, Lee S, Lee YS, Kanel SR, Pelletier GJ (2007) Application of automated QUAL2Kw for water quality modeling and management in the Bagmati River, Nepal. Ecol Model 202(3–4):503–517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2006.12.033
Khu ST, Liong SY, Babovic V, Madsen H, Muttil N (2001) Genetic programming and its application in real-time runoff forecasting 1. J Am Water Resour Assoc 37(2):439–451. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1752-1688.2001.tb00980.x
Kileshye Onema JM, Mazvimavi D, Love D, Mul ML (2006) Effects of selected dams on river flows of Insiza River, Zimbabwe. PCE 31(15–16):870–875. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pce.2006.08.022
KWPA (2001) An Assessment of Pollutants in Dez River. A report prepared by the Water Quality Assessment section. Khozestan Water and Power Authority, Ministry of Power, Ahwaz, Iran
Mishra BK, Regmi RK, Masago Y, Fukushi K, Kumar P, Saraswat C (2017) Assessment of Bagmati River pollution in Kathmandu Valley: scenario-based modeling and analysis for sustainable urben development. Sustain Water Qual Ecol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.swaqe.2017.06.001
Orouji H, Bozorg Haddad O, Fallah-Mehdipour E, Marino MA (2013) Estimation of Muskingum parameter by metaheuristic algorithms. Proc Civil Eng Water Manag 166:315–324. https://doi.org/10.1680/wama.11.00068
Piman T, Cochrane TA, Arias ME, Green A, Dat ND (2013) Assessment of flow changes from hydropower development and operations in Sekong, Sesan, and Srepok rivers of the Mekong basin. J Water Resour Plann Manag 139(6):723–732. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)WR.1943-5452.0000286
Rabunal JR, Puertas J, Suarez J, Rivero D (2007) Determination of the unit hydrograph of a typical urban basin genetic programming and artificial neural networks. Hydrol Process 21:476–485. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.6250
Reis J, Culver TB, Lacombe G, Sellamuttu SS (2015) Reservoir operation for recession agriculture in Mekong basin, Laos. J Water Resour Plann Manag 141(7):04014083. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)WR.1943-5452.0000485
Savic DA, Walters GA, Davidson JW (1999) A genetic programming approach to rainfall-runoff modeling. Water Resour Manag 13:219–231. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008132509589
Shirangi E, Kerachian R, Bajestan MS (2008) A simplified model for reservoir operation considering the water quality issues: application of the Young conflict resolution theory. Environ Monit Assess 146(1–3):77–89. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-007-0061-0
Singh KP, Malik A, Sinha S (2005) Water quality assessment and apportionment of pollution sources of Gomti river (India) using multivariate statistical techniques—a case study. Anal Chim Acta 538(1–2):355–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2005.02.006
Steinschneider S, Bernstein A, Palmer R, Polebitski A (2014) Reservoir management optimization for basin-wide ecological restoration in the Connecticut River. J Water Resour Plann Manag 140(9):04014023. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)WR.1943-5452.0000399
Stockholm Environment Institute-SEI (2012) Water evaluation and planning-WEAP: tutorial. Boston USA. https://www.weap21.org/
Sulis A, Sechi GM (2013) Comparison of generic simulation models for water resource systems. Environ Model Softw 40:214–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2012.09.012
Symphorian GR, Madamombe E, van der Zaag P (2003) Dam operation for environmental water releases; the case of Osborne dam, Save catchment, Zimbabwe. Phys Chem Earth A/b/c 28(20–27):985–993. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pce.2003.08.012
Tennant DL (1976) Instream flow regimens for fish, wildlife, recreation and related environmental resources. Fisheries 1(4):6–10
Topping DJ, Rubin DM, Vierra LE Jr (2000) Colorado River sediment transport: 1. Natural sediment supply limitation and the influence of Glen Canyon Dam. Water Resour Res 36(2):515–542. https://doi.org/10.1029/1999WR900285
Zhang Y, Xia J, Liang T, Shao Q (2010) Impact of water projects on river flow regimes and water quality in Huai River Basin. Water Resour Manag 24(5):889–908. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-009-9477-3
Zhang Y, Xia J, Chen J, Zhang M (2011) Water quantity and quality optimization modeling of dams operation based on SWAT in Wenyu River Catchment, China. Environ Monit Assess 173(1–4):409–430. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1396-5
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Babamiri, O., Marofi, S. A multi-objective simulation–optimization approach for water resource planning of reservoir–river systems based on a coupled quantity–quality model. Environ Earth Sci 80, 389 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09681-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09681-9