Abstract
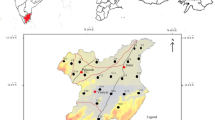
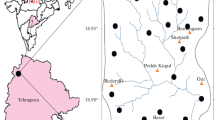
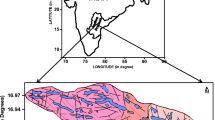
Quality of groundwater is concerned with various processes such as precipitation, weathering and dissolution of mineral, cation exchange and ground water exploitation. Present study aims to interpret the seasonal variation of groundwater quality contaminated with fluoride. Sixty water samples were collected during pre- and post-monsoon seasons from Lalganj Tehsil of Raebareli District, UP (India). Multivariate statistical analyses such as factor analysis (FA), principal component analysis (PCA), cluster analysis and correlation matrix were applied on 14 hydro-chemical constituents, i.e., pH, EC, TDS, TBDT, TH, bicarbonate (BiC), NO3−, SO42−, F−, Cl−, Ca2+, Mg2+, Na+ and K+. Factor analysis explained that TH, Mg2+, SO42−, Cl−, EC, TDS and F− were significantly loaded parameters during both seasons that influence the groundwater quality due to weathering and dissolution of mineral during aquifer recharging. The source of F− appears to be geogenic due to the alluvial sediments deposited in the geological past as no hard rock terrain was present in the nearby areas that were dominantly made up of mud with pocket of sand. The cumulative variance obtained from PCA suggested that the groundwater quality in pre-monsoon was better than that of post-monsoon. Correlation explained that EC of groundwater completely depends on the dissolved solids. Dendrogram of cluster analysis indicated that parameters were grouped into four clusters on the basis of similarity, during both seasons. Values of Mg+, F−, TH, and TDS exceeded more than the drinking water standard during both seasons. It will bring alertness to the people regarding whether the groundwater is suitable or unsuitable for drinking purpose.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayoob S, Gupta AK (2006) Fluoride in drinking water: a review on the status and stress effects. Crit Rev in Environ Sci Technol 36:433–487
Bhardwaj V, Singh DS (2011) Surface and groundwater quality characterization of Deoria District, Ganga Plain, India. Environ Earth Sci 63:383–395
Bhat SA, Gowhar M, Sayar Y, Pandit AK (2014) Statistical assessment of water quality parameters for pollution source identification in Sukhnag stream: an inflow stream of lake Wular (Ramsar Site), Kashmir Himalaya. J Ecosyst. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/898054
CGWB (1999) High fluoride groundwater in India occurrences, genesis and remedies. Ministry of Water Resources, Government of India, 29
CGWB (2010) Groundwater quality in shallow aquifers of India. Central ground water board, Faridabad India 117.
Gaciri SJ, Davies TC (1993) The occurrence and geochemistry of fluoride in some natural waters of Kenya. J Hydrol 143:395–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(93)90201-J
Gajbhiye S, Mishra SK, Pandey A (2014) Simplified sediment yield index model incorporating parameter. Arab J Geosci 8:1993–2004. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1319-9
Gajbhiye S, Sharma SK, Awasthi MK (2015) Application of principal components analysis for interpretation and grouping of water quality parameters. Inter J Hybrid Inf Technol 8(4):89–96
Ghosh A (2007) Current knowledge on the distribution of arsenic in groundwater in five states of India. J Environ Sci Health Part A 42:1–12
Hem JD (1991) Study and interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural water. In: United States Geological Survey professional paper. Scientific Publisher, Jodhpur. https://pubs.usgs.gov/wsp/wsp2254/pdf/wsp2254a.pdf
IS (2012) Guidelines for drinking water. Bureau of Indian standard (BIS: 10500) Second Revision. http://cgwb.gov.in/Documents/WQ-standards.pdf
Jain C, Bandyopadhyay A, Bhadra A (2010) Assessment of groundwater quality for drinking purpose, District Nainital, Uttarakhand,India. Environ Monit Assess 166(1–4):663–676
Kanaujia S, Bharat Singh AB, Singh SK (2013) Mapping of fluoride endemic areas in Raebareli District, Uttar Pradesh, India. Chem Sci Trans 2(4):1411–1417. https://doi.org/10.7598/cst2013.539
Khan MMA, Umar R, Baten MA, Lateh H, Kamil AA (2012) Seasonal variations in groundwater quality: a statistical approach. Int J Phys Sci 7(25):4026–4035
Khanna SP (1992) Hydrogeology of central ganga plain, U. P. Gangetic Plain. Tera Incognita, pp 23–27
Kumar AR, Riyazuddin P (2008) Application of chemometric techniques in the assessment of groundwater pollution in a suburban area of Chennai city, India. Curr Sci 94(8):1012–1022
Kumar S, Saxena A (2011) Chemical weathering of the indo-gangetic alluvium with special reference to release of fluoride in the groundwater, Unnao District, Uttar Pradesh. J Geol Soc India 77:459–477
Liang YZ, Yu RQ (2000) Chemometrics central. South University Press, Changsha
Lui CW, Lin KH, Kuo YM (2003) Application of factor analysis in the assessment of groundwater quality in a blackfoot disease area in Tiwan. Sci Total Environ 313(1–3):77–89
Majumdar D, Gupta N (2000) Nitrate pollution of groundwater and associated human health disorders. Indian J Environ Health 42(1):28–39
Meenakshi, Maheshwari RC (2006) Fluoride in drinking water and its removal. J Hazard Mater 137:456–463
Misra AK, Mishra A (2007) Study of quaternary aquifers in Ganga plain, India: focus on groundwater salinity, fluoride and fluorosis. J Hazard Mater 144:438–448
Mohapatra PK, Vijay R, Pujari PR, Sundaray SK, Mohanty BP (2011) Determination of processes affecting groundwater quality in the coastal aquifer beneath Puri city, India: a multivariate statistical approach. Water Sci Technol 64(4):809–817
Murli K, Swasthik RD, Elangovan R (2011) Assessment of ground water quality in Coimbatore south Taluk, Coimbatore district, India. WQI Approach 10(4):521–524
Ntengwe FW (2006) Pollutant loads and water quality in streams of heavily populated and industrialized towns. Phys Chem Earth 31:832–839
Otto M (1998) Multivariate methods. In: Kellner R, Mermet JM, Widmer HM (eds) Analytical chemistry. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim
Pandey AK (2001) A report on study of fluoride contamination in ground water in parts of Unnao district, U. P. (Annual Action Plan: 1996–97). Central Ground Water Board, Ministry of Water Resources, Govt. of India, 45
Pathak RP, Sharma P, Vyas S, Mahure NV, Kumar R, Murari R (2012) Detection of fluoride contamination in the surface and sub-surface water near thermal power station. Int J Eng Sci 1(1):44–47
Raju JN, Dey S, Das K (2009) Fluoride contamination in groundwaters of Sonbhadra district, Uttar Pradesh, India. Curr Sci 96:979–985
Raju JN, Shukla UK, Ram P (2011) Hydrogeochemistry for the assessment of groundwater quality in Varanasi: a fast urbanizing center in Uttar Pradesh, India. Environ Monit Assess 173:279–300
Rao YRS, Keshari AK, Gosain AK (2010) Evaluation of regional groundwater quality using PCA and geostatistics in the urban coastal aquifer, East Coast of India. Int J Environ Waste Manag 5(1–2):163–180
Sargaonkar AP, Gupta A, Devotta S (2008) Multivariate analysis of groundwater resources in Ganga-Yamuna basin (India). J Environ Sci Eng 50(3):215–222
Shaji E, Bindu VJ, Thambi DS (2007) High fluoride in groundwater of Palghat District. Kerala Curr Sci 92(2):240–245
Sharma SK, Gajbhiye S, Nema RK, Tignath S (2014) Assessing vulnerability to soil erosion of a watershed of tons River basin in Madhya Pradesh using remote sensing and GIS. Int J Environ Res Dev 4(2):153–164
Singh KP, Malik A, Singh VK, Mohan D, Sinha S (2004) Chemometric analysis of groundwater quality data of alluvial aquifer of Gangetic plain, North India. Analytica Chimia Acta 550(1–2):82–91
Singh SK, Singh CK, Kumar KS, Gupta R, Mukherjee S (2005) Spatial-temporal monitoring of groundwater using multivariate statistical techniques in Bareilly District of Uttar Pradesh, India. J Hydrol Hydromech 57(1):45–54
Singh KP, Malik A, Mohan D, Sinha S (2009) Multivariate statistical techniques for the evaluation of spatial and temporal variations in water quality of Gomti River (India)—a case study. Water Res 38:3980–3992
Singh VK, Bikundia DS, Sarswat A, Mohan D (2012) Groundwater quality assessment in the village of Lutfullapur Nawada, Loni, District Ghaziabad, Uttar Pradesh, India. Environ Monit Assess 184:4473–4488
Srikanth R (2009) Challenges of sustainable water quality management in rural India. Curr Sci 3:317–325
Subba Rao N (2002) Geochemistry of groundwater in parts of Guntur district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ Geol 41:552–562
Subba Rao N (2003) Groundwater quality: focus on fluoride concentration in rural parts of Guntur District, Andhra Pradesh, India. Hydrol Sci J 48:835–847
Subba Rao N (2006) Seasonal variation of groundwater quality in a part of Guntur District, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ Geol 49:413–442
Subba Rao N (2008) Factors controlling the salinity in groundwater in parts of Guntur district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ Monit Assess 138(1–3):327–341
Subba Rao N (2011) High-fluoride groundwater. Environ Monit Assess 176:637–645. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1609-y
Subba Rao N, Surya Rao P, Dinakar A, Nageswara Rao PV, Marghade D (2017) Fluoride occurrence in the groundwater in a coastal region of Andhra Pradesh, India. Appl Water Sci 7:1467–1478. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-015-0338-3
Trivedi RK, Goel PK (1986) Chemical and biological methods for water pollution studies. Environmental Publication, Karad
Umar R, Khan MMA, Absar A (2006) Groundwater hydrochemistry of a sugarcane cultivation belt in parts of Muzaffarnagar district, Uttar Pradesh India. Environ Geol 49:999–1008
WEF (2012) Standard methods for examination of water and wastewater, 22nd edn. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC
WHO (2005) Water-related diseases, fluorosis; the disease and how it affects people World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland. http://www.who.int/water sanitation health/diseases/fluorosis/en
WHO (2008) Guidelines for drinking water quality incorporating first addendum to third edition. Recommedation Geneva 1:595
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Professor Alok Dhawan, Director, CSIR-IITR, Lucknow, India for providing all necessary facilities for this work. This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sector.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sahu, P., Kisku, G.C., Singh, P.K. et al. Multivariate statistical interpretation on seasonal variations of fluoride-contaminated groundwater quality of Lalganj Tehsil, Raebareli District (UP), India. Environ Earth Sci 77, 484 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7658-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7658-1