Abstract
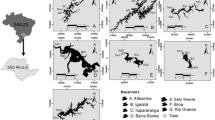
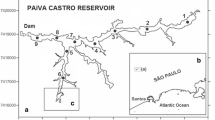
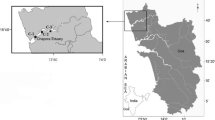
Cascade multisystem reservoirs are extremely complex ecosystems that require studies to improve understanding of their dynamics and functioning, including the effects of contamination with metals. In this work, superficial sediments were collected during two sampling campaigns (in the dry and rainy seasons) at 19 sites along a cascade multisystem reservoir in São Paulo, Brazil, formed by five reservoirs. The sediments were evaluated considering the following parameters: pseudo-total metals (Cu, Cd, Cr, Ni, Pb, Zn, Mn, Fe, and Al); bioavailable metal (Cu); organic matter; total phosphorus; total nitrogen; and grain size. In the last reservoir of this system, the enrichment factors indicated enrichment of Cu, Pb, Zn, and Mn. Despite this increased metals content, the pollution load index indicated an absence of pollution (PLI < 1), and the ecological risk was low (RI < 150). According to sediment quality guideline criteria, toxicity was unlikely to occur. Principal component analysis (PCA) and one-way ANOVA indicated heterogeneity among the reservoirs (P < 0.01) and between the sampling periods. The PCA results confirmed higher levels of nutrients in the upstream reservoirs, suggesting that nutrients were precipitated in the first reservoirs of the system. On the other hand, metal levels were higher in the downstream reservoirs. The main source of metal contamination in the region was the use of copper sulfate as an algicide. This included contamination by Pb and Zn, due to impurities in the copper sulfate employed. High Mn levels were associated with wastewater discharges and erosion. In addition to helping to improve understanding of the dynamics of metals in cascade multisystem reservoirs, this work could serve as a useful tool for the management of reservoirs with contaminated sediments.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alloway BJ, Ayres DC (1997) Chemical principles of environmental pollution, 2nd edn. London, Blue academic professional
Andersen JM (1976) An ignition method for determination of total phosphorus in lake sediments. Water Res 10:329–331
APHA- American Public Health Association (2002) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association, Washington
Barbosa FAR, Padisák J, Espíndola ELG, Borics G, Rocha O (1999) The cascading reservoir continuum concept (CRCC) and its application to the river Tietê basin, São Paulo State, Brazil. In: Tundisi JG, Straškraba M (eds) Theoretical Reservoir Ecology and its Applications. Backhuys Publishers, The Netherlands, pp 425–437
Bastami KD, Bagheri H, Kheirabadi V, Zaferani GG, Teymori MB, Hamzehpoor A, Soltani F, Haghparast S, Harami SRM, Ghorghani NF, Ganji S (2014) Distribution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments along southeast coast of the Caspian Sea. Mar Pollut Bull 81:262–267
Beghelli FGS, Pompêo MLM, Rosa AH, Moschini-Carlos V (2016) Effects of copper in sediments on benthic macroinvertebrate communities in tropical reservoirs. Limnética 35(1):103–116
Cardoso-Silva S, Silva DCVR, Lage F, Rosa AH, Moschini-Carlos V, Pompeo MLM (2016a) Metals in sediments: bioavailability and toxicity in a tropical reservoir used for public water supply. Environ Monit Assess 188:310
Cardoso-Silva S, Ferreira PAL, Moschini-Carlos V, Figueira RCL, Pompêo MLM (2016b) Temporal and spatial accumulation of heavy metals in the sediments at Paiva Castro Reservoir (São Paulo, Brazil). Environmental Earth Sci 75:1–16
CCME- Canadian council of ministers of the environment. (1999) Canadian sediment quality guidelines for the protection of aquatic life–protocol for the derivation of Canadian Sediment quality guidelines for the protection of aquatic life. (CCME EPC-98E)
CETESB - Companhia de Tecnologia de Saneamento Ambiental (2015) Qualidade das águas superficiais no Estado de São Paulo 2014. CETESB: São Paulo. http://www.cetesb.sp.gov.br/agua/aguas-superficiais/35- publicacoes-/- relatorios, Accessed 30 June 2016
Chapman PM, Wang F, Adams WJ, Green A (1999) Appropriate applications of sediment quality values for metals and metalloids. Environ Sci Technol 33(22):3937–3941
Duman F, Kar M (2012) Temporal Variation of Metals in Water, Sediment and Tissues of the European Chup (Squalius cephalus L.) Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 89: 428–433
Enner A, Watanabe F, Rodrigues T, Bernardo N, Rotta L, Carmo A, Curtarelli M, Imai N (2016) Field measurements of the backscattering coefficient in a cascading reservoir system: first results from Nova Avanhandava and Barra Bonita Reservoirs (Sao Paulo, Brazil). Remote Sens Lett 7(5):417–426
Esteves FA (2011) Limnologia. Interciência, Rio de Janeiro, INEP
Fan J, Ho L, Hobson P, Brookes J (2013) Evaluating the effectiveness of copper sulphate, chlorine, potassium permanganate, hydrogen peroxide and ozone on cyanobacterial cell integrity. Water Res 47(14):5153–5164
Håkanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: a sedimentological approach. Water Res 14:975–1001
Hammer Ø, Harper DAT, Ryan PD (2001) PAST: paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol Electron 4(1):9
Hübner R, Astin KB, Herbert JH (2009) Comparison of sediment quality guidelines (SQGs) for the assessment of metal contamination in marine and estuarine environments. Environmt Monit 11:713–722
Kimmel BL, Lind OT, Paulson LJ (1990) Reservoir primary production. In: Thorton KW, Kimmel BL, Payne FE (eds) Reservoir limnology: ecological perspectives. Wiley Interscience, New York, pp 133–194
Kummu M, Varis O (2007) Sediment-related impacts due to upstream reservoir trapping, the Lower Mekong River. Geomorphology 85(3–4):275–293
Landajohttp://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0045653504004187–AFF1 A, Arana G, Diego A, Etxebarria N, Zuloaga O, Amouroux D (2004) Analysis of heavy metal distribution in superficial estuarine sediments (estuary of Bilbao, Basque Country) by open-focused microwave-assisted extraction and ICP-OES. Chemosphere 56(11):1033–1041
Legendre P, Legendre L (1998) Numerical Ecology. Elsevier Science, Amsterdam
Liu Q, Liu S, Zhao H, Deng L, Wang C, Zhao Q, Dong S (2013) Longitudinal variability of phosphorus fractions in sediments of a canyon reservoir due to cascade dam construction: a case study in Lancang River, China. PLoS ONE 8(12):e83329
Liu Q, Liu S, Zhao H, Deng L, Wang C, Zhao Q, Dong S (2015) The phosphorus speciations in the sediments up- and down-stream of cascade dams along the middle Lancang River. Chemosphere 120:653–659
Long ER, MacDonald SL, Smith SL, Calder FD (1995) Incidence of adverse biological effects within ranges of chemical concentrations in marine and estuarine sediments. Environ Manage 19(1):8197
Mariani CF, Pompêo MLM (2008) Potentially bioavailability metals in sediment from a tropical polymictic environment Rio Grande Reservoir, Brazil. J Soils Sediments 8:284–288
Meguro M (2000) Métodos em Ecologia. São Paulo. Apostila de Metodologias para a disciplina BIE–321 Ecologia Vegetal. Instituto de Biociências- USP, São Paulo
Moggridge HL, Hill MJ, Wood PJ (2014) Urban aquatic ecosystems: the good, the bad and the ugly. Fund Appl Limnol 185(1):1–6
Mohiuddin KM, Ogawa U, Zakir HM, Otomo K, Shikazono N (2011) Heavy metals contamination in water and sediments of an urban river in a developing country. Int J Environ Sci Tech 8(4):723–736
Mozeto A A, Yamada T M, Morais C R, Nascimento M R L, Fadini P S, Torres R J, Pompêo M, Moschini-Carlos V, Cardosos-Silva S, López-Doval J C, Rosa A H, Lopez P. Nitrogen and phosphorus dynamics in cascade multi-system tropical reservoirs. Limnol Rev (Submitted to publication)
Nascimento MRL, Mozeto A (2008) Reference values for metals and metalloids concentration in botton sediments of Tietê river basin, southeast of Brasil. Soil Sediment Contam 17(3):269–278
Nogueira MG, Reis-Oliveira PC, Britto YT (2008) Zooplankton assemblages (Copepoda and Cladocera) in a cascade of reservoirs of a large tropical river (SE Brazil). Limnetica 27(1):151–170
Oliveira-Filho EC, Lopes RM, Paumgartten FJR (2004) Comparative study on the susceptibility of freshwater species to copper-based pesticides. Chemosphere 54(4):369–374
Pantelić D, Svirčev Z, Simeunović J, Vidović M, Trajković I (2013) Cyanotoxins: Characteristics, production and degradation routes in drinking water treatment with reference to the situation in Serbia. Chemosphere 91(4):421–441
Pedro CA, Santos MS, Ferreira SMF, Gonçalves SC (2016) The presence of cadmium in the intertidal environments of a moderately impacted coastal lagoon in western Portugal (Óbidos Lagoon)—spatial and seasonal evaluations. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:1960–1969
Perbiche-Neves N, Nogueira MG (2013) Reservoir design and operation: effects on aquatic biota–a case study of planktonic copepods. Hydrobiologia 707(1):187–198
Persaud D, Jaagumagi R, Hayton A (1993) Guidelines for the protection and management of aquatic sediment quality in Ontario. Water Resources Branch, Ontario Ministry of the Environment, Toronto
Petesse ML, Petrere M (2012) Tendency towards homogenization in fish assemblages in the cascade reservoir system of the Tietê river basin, Brazil. Ecol Eng 48:109–116
Petesse ML, Petrere M, Agostinho AA (2014) Defining a fish bio-assessment tool to monitoring the biological condition of a cascade reservoirs system in tropical area. Ecol Eng 69:139–150
Pompêo M, Moschini-Carlos V (2003) Macrófitas aquáticas e perifíton, aspectos ecológicos e metodológicos. São Carlos, RiMa
Pompêo M, Moschini-Carlos V (2012) O abastecimento de água e o esgotamento sanitário: propostas para minimizar os problemas no Brasil. In: Rosa AH, Fraceto LF, Moschini-Carlos V (eds) Meio ambiente e sustentabilidade. Bookman, Porto Alegre
Pompêo MLM, Padial PR, Mariani CF, Cardoso-Silva S, Moschini-Carlos V, Silva DCVR, Paiva TCB, Brandimarte AL (2013) Biodisponibilidade de metais no sedimento de um reservatório tropical urbano (reservatório Guarapiranga–São Paulo (SP), Brasil): há toxicidade potencial e heterogeneidade espacial? Geochim Bras 27(2):104–119
Roberto MC, Santana NF, Thomaz SM (2009) Limnology in the Upper Paraná River floodplain. Braz J Biol 69(2):717–725
Rodgher S, Espíndola ELG, Rocha O, Fracácio R, Pereira RHG, Rodrigues MHS (2005) Limnological and ecotoxicological studies in the cascade of reservoirs in the Tietê River (São Paulo, Brazil). Braz J Biol 65(4):697–710
SABESP Companhia de Saneamento Básico do Estado de São Paulo (2016) Situação dos mananciais. http://www2.sabesp.com.br/mananciais/DivulgacaoSiteSabesp.aspx. Accessed July 2016
Santos IR, Silva-Filho EV, Schaefer CEGR, Albuquerque-Filho MR, Campos LS (2005) Heavy metal contamination in coastal sediments and soils near the Brazilian Antarctic Station, King George Island. Mar Pollut Bull 50:185–194
Santos L, Carneiro N, Santana HS, Dias RM, Borges HLF, Melo VF, Severi W, Gomes LC, Agostinho AA (2016) Distribution of benthic macroinvertebrates in a tropical reservoir cascade. Hydrobiologia 765(1):265–275
Sayadi M, Sayyed M, Kumar S (2010) Short-term accumulative signatures of heavy metals in river bed sediments in the industrial area, Tehran, Iran. Environ Monit Assess 162:465–73
Selborne L (2001) A ética do uso da água doce: um levantamento. UNESCO, Brasília
Silvério PF, Fonseca AL, Botta-Paschoal CMR, Mozeto AA (2005) Release, bioavailability and toxicity of metals in lacustrine sediments: A case study of reservoirs and lakes in SE Brazil. Aquatic Ecoystem Health 8(3):1–10
Smith WS, Espíndola ELG, Rocha O (2014) Environmental gradient in reservoirs of the medium and low Tietê River: limnological diferences through the habitat sequence. Acta Limnol Bras 26(1):73–88
Snape I, Scouller RC, Stark SC, Stark J, Riddle MJ, Gore DB (2004) Characterisation of the dilute HCl extraction method for the identification of metal contamination in Antarctic marine sediments. Chemosphere 57:491–504
Straškraba M, Tundisi JG (2000) Gerenciamento da qualidade da água de represas. São Carlos, ILEC-IIE
Straškraba M, Tundisi JG (2013) Aspectos técnicos da construção de reservatórios, 3a edn. São Carlos, Oficina de Textos
Straškraba M, Tundisi JG, Duncan A (1993) State-of-the-art of reservoir limnology and water quality management. In: Straškraba M, Tundisi JG, Duncan A (eds) Comparative limnology and water management. Kluwer Academic Publishers, The Netherlands, pp 213–288
Sutherland RA (2000) Bed sediment-associated trace metals in an urban stream, Oahu. Hawaii. Env Geol 39(6):611–627
Tomlinson DC, Wilson JG, Harris CR, Jeffrey DW (1980) Problems in the assessment of heavy metals in estuaries and the formation pollution index. Helgoland Mar Res 33:566–575
Tundisi JG, Matsumura-Tundisi T (2008) Limnologia. Oficina de Textos, São Paulo
US EPA United States Environmental Protection Agency (1996) Method 3050B. Acid digestion of sediments, sludges and soil. Revision 2. Washington DC
US EPA—United Sates Environmental Protection Agency (2005) Procedures for the derivation of equilibrium partitioning sediment benchmarks (ESBs) for the protection of benthic organisms: metal mixtures (cadmium, copper, lead, nickel, silver, and zinc). Washington, DC. (EPA/600/R-02/011)
Vieira T N A, Vieira L T A (2016) Análise de Ecologia da paisagem do Sistema Cantareira voltada à questão Hídrica. Greenpeace
Vymazal J, Švehla J (2013) Iron and manganese in sediments of constructed wetlands with horizontal subsurface flow treating municipal sewage. Ecol Eng 50:60–75
Wang C, Liu S, Zhao Q, Deng L, Dong S (2012) Spatial variation and contamination assessment of heavy metals in sediments in the Manwan Reservoir, Lancang River. Ecotoxi Environ Safe 82:32–39
Whately M, Cunha PM (2007) Cantareira 2006: Um olhar sobre o maior manancial de água da Região Metropolitana de São Paulo- Resultados do Diagnóstico Socioambiental Participativo do Sistema Cantareira. Instituto Sócio Ambiental, São Paulo
Zahra A, Hashmi MZ, Malik RN, Ahmed Z (2014) Enrichment and geo-accumulation of heavy metals and risk assessment of sediments of the Kurang Nallah Feeding tributary of the Rawal Lake Reservoir, Pakistan. Sci Total Environ 470–47:925–933
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the Postgraduate Program in Environmental Sciences, at the Sorocaba campus of UNESP, and to the Ecology Department of the Institute of Biosciences, at the University of São Paulo. Financial support for this work was provided by FAPESP (Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo; grant no. 2014/22581-8) and CAPES (Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior; PNPD award). J.C. López-Doval received financial support from the Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP 12/16420-6) and the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness (IJCI-2015-23644).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cardoso-Silva, S., Meirelles, S.T., Frascareli, D. et al. Metals in superficial sediments of a cascade multisystem reservoir: contamination and potential ecological risk. Environ Earth Sci 76, 756 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-7104-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-7104-9