Abstract
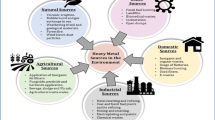
Bio-concentration of elements such as Mo, As, Se, Fe, Cu, Zn, Ni and Pb was analyzed in spring onion (Allium fistulosum L.) in three different locations of central Punjab, Pakistan. At location GW, relatively low level of hazardous elements was found in spring onion, suggesting that groundwater is a safe source of water for irrigating food crops. The pH of soil at wastewater irrigation was found less acidic (pH 7.4) than the other sites. The range of concentration in the different samples of spring onion was as follows: 6.15–8.16 mg kg−1 for Mo, 2.77–4.28 mg kg−1 for As, 0.395–0.705 mg kg−1 for Se, 36.73–48.17 mg kg−1 for Fe, 10.58–16.26 mg kg−1 for Cu, 28.87–39.79 mg kg−1 for Zn, 6.66–8.75 mg kg−1 for Ni and 4.33–6.09 mg kg−1 for Pb, respectively. High bio-concentration of Zn (15.37) from soil to spring onion was found at canal water irrigated location. The estimated daily intake of metal for spring onion was less, but the health risk index was higher than 1 for Mo, As, Cu, Pb and Ni, respectively. This was due to higher proportion of spring onion in diet, which consequently increased the health risk index for metals. Therefore, it is recommended to avoid growing vegetables in untreated urban and rural wastewater containing elevated amounts of metals.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adriano DC, Page AL (1981) Co-recycling of sewage sludge and fly ash: heavy metal uptake by crop. In: International conference on heavy metals in the environment, Amsterdam, pp 185–187
Ahmad K, Khan ZI, Yasmin S, Ashraf M, Ishfaq A (2014) Accumulation of metals and metalloids in turnip (Brassica rapa L.) irrigated with domestic wastewater in the peri-urban areas of Khushab city, Pakistan. Pak J Bot 42:511–514
Ahmad K, Ashfaq A, Khan ZI, Ashraf M, Akram NA, Yasmin S et al (2016) Health risk assessment of heavy metals and metalloids via dietary intake of a potential vegetable (Coriandrum sativum L.) grown in contaminated water irrigated agricultural sites of Sargodha, Pakistan. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 22:597–610
Akan JC, Kolo BG, Yikala BS, Chellube BS (2013) Levels of some agricultural pollutants in soil samples from Biu Local Government Area of Borno State, Nigeria. Merit Res J Environ Sci Toxicol 1:71–81
Ali MHH, Al-Qahtani KM (2012) Assessment of some heavy metals in vegetables, cereals and fruits in Saudi Arabian markets. Egypt J Aquat Res 38:31–37
APHA (American Public Health Association) (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC
Astolfi T, Zuchi S, Passera C (2005) Effect of cadmium on HATPase activity of plasma membrane vesicles isolated from roots of different s-supplied maize (Zea mays) plant. Plant Sci 169:361–368
Buat-Menard P, Chesselet R (1979) Variable influence of the atmospheric flux on the trace metal chemistry of oceanic suspended matter. Earth Planet Sci Lett 42:399–411
Butkus D, Baltrėnaitė E (2007) Modelling of Cu, Ni, Zn and Pb transport from soil to seedlings of coniferous and leafy trees. J Environ Eng Landsc Manag 15:200–207
Chang AC, Granato TC, Page AL (1992) The methodology for establishing phytotoxicity criteria for Cr, Cu, Ni and Zn in agricultural land application of municipal sewage sludge. J Environ Qual 21:521–536
Chao W, Xiao-Chen L, Li-Min Z, Pei-Fang W, Zhi-Yong G (2007) Pb, Cu, Zn and Ni concentrations in vegetables in relation to their extractable fractions in soils in suburban areas of Nanjing, China. Pol J Environ Stud 16:199–207
Chauhan G (2014) Toxicity study of metals contamination on vegetables grown in the vicinity of cement factory. Int J Sci Res Publ 4:1–8
Chiroma TM, Ebewele RO, Hymore FK (2014) Comparative assessment of heavy metal levels in soil, vegetables and urban grey waste water used for irrigation in Yola and Kano. Int J Eng Sci 3:1–9
Chojnacka K, Chojnacki A, GoreckaH GH (2005) Bioavailability of heavy metals from polluted soils to plants. Sci Total Environ 337:175–182
Cui YJ, Zhu YG, Zhai RH, Chen DY, Huang YZ, Qui Y, Liang JZ (2004) Transfer of metals from near a smelter in Nanning, China. Environ Int 30:785–791
Forbes EA, Posner AM, Quirk JP (1976) The specific adsorption of divalent Cd Co, Cu, Pb and Zn in goethite. J Soil Sci 27:154–166
Ge KY (1992) The status of nutrient and metal of Chinese in the 1990s. Beijing People’s Hygiene Press, Beijing, pp 415–434
Hornburg V, Welp G, Brummer GW (1995) Availability of heavy metals in soils and their uptake by vegetable species. Soil Geol 158:137–145
Jassir MS, Shaker A, Khalip MA (2005) Deposition of heavy metals on green leafy vegetables sold on roadsides of Riyadh city, Saudi Arabia. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 75:1020–1027
Kachenko AG, Singh B (2006) Heavy metals contamination in vegetables grown in urban and metal smelter contaminated sites in Australia. Water Air Soil Pollut 169:101–123
Kapungwe EM (2013) Heavy metal contaminated food crops irrigated with wastewater in peri urban areas, Zambia. J Metal 3:77–88
Khan S, Cao Q, Zheng YM, Huang YZ, Zhu YG (2008) Health risks of heavy metals in contaminated soils and food crops irrigated with wastewater in Beijing, China. Environ Pollut 152:686–692
Khan ZI, Ahmad K, Ashraf M, Parveen R, Mustafa I, Khan A, Bibi Z, Akram NA (2015) Bioaccumulation of heavy metals and metalloids in luffa (Luffa cylindrica L.) irrigated with domestic wastewater in Jhang, Pakistan: a prospect for human nutrition. Pak J Bot 47:217–224
Khan ZI, Ahmad K, Ashraf M, Parveen R, Bibi Z, Mustafa I, Noorka IR, Tahir HM, Akram NA, Ullah MF, Yaqoob R, Tufarelli V, Fracchiolla M, Cazzato E (2016a) Risk assessment of heavy metal and metalloid toxicity through a contaminated vegetable (Cucurbita maxima) from wastewater irrigated area: a case study for a site-specific risk assessment in Jhang, Pakistan. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 22:86–98
Khan ZI, Ahmad K, Ashraf M, Shoaib N, Parveen R, Bibi Z et al (2016b) Assessment of toxicological health risk of trace metals in vegetables mostly consumed in Punjab, Pakistan. Environ Earth Sci 75:433
Kirkhan MB (1983) Study on accumulation of heavy metals in soil receiving sewage and effluent water. Agric Ecosyst Environ 9:251
Liu WH, Zhao JZ, Ouyang ZY, Soderlund L, Liu GH (2005) Impacts of sewage irrigation on heavy metals distribution and contamination in Beijing, China. Environ Int 31:805–812
Lone MI, Saleem S, Mahmood T, Saifullah K, Hussain G (2003) Heavy metal contents of vegetables irrigated by sewage/tubewell water. Int J Agric Biol 5:533–535
Madrid L, Diaz-Barrientos E, Madrid F (2002) Distribution of heavy metals contents of urban soils in parks of Seville. Chemosphere 49:1301–1308
McLean EO (1982) Soil pH and lime requirement. In: Page AL et al. (eds) Methods of soil analysis, part 2. Chemical and microbiological properties, 2nd edition, No. 9. American Society of Agronomy, Madison, Wisconsin, pp 199–223
Nazir R, Khan M, Masab M, Rehman HU, Rrauf NU, Shahab S, Ameer N, Sajed M, Ullah M, Rafeeq M, Shaheen Z (2015) Accumulation of heavy metals (Ni, Cu, Cd, Cr, Pb, Zn, Fe) in the soil, water and plants and analysis of physico-chemical parameters of soil and water collected from Tanda Dam Kohat. J Pharm Sci Res 7:89–97
Radwan MA, Salama AK (2006) Market basket survey for some heavy metals in Egyptian fruits and vegetables. Food Chem Toxicol 44:1273–1278
Rapheal O, Adebayo KS (2011) Assessment of trace heavy metal contaminations of some selected vegetables irrigated with water from River Benue within Makurdi Metropolis, Benue State Nigeria. Adv Appl Sci Res 2:590–601
Rayment GE, Higginson FR (1992) Australian Laboratory handbook of soil and water chemical methods. Inkata Press, Melbourne
Sajjad K, Farooq R, Shahbaz S, Khan MA, Sadique M (2009) Health risk assessment of heavy metals for population via consumption of vegetables. World Appl Sci J 6:1602–1606
Sharma RK, Agrawal M, Marshall FM (2006) Heavy metals contamination in vegetables grown in wastewater irrigated areas of Varanasi, India. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 77:312–318
Singh KP, Mohon D, Sinha S, Dalwani R (2004) Impact assessment of treated/untreated wastewater toxicants discharge by sewage treatment plants on health, agricultural, and environmental quality in wastewater disposal area. Chemosphere 55:227–255
Singh A, Sharma RK, Agarwal M, Marshall FM (2010) Health risk assessment of heavy metals via dietary intake of foodstuffs, from waste water irrigated site of dry tropical area of India. Food Chem Toxicol 48:611–619
Smith SR (2009) A critical review of the bioavailability and impacts of heavy metals in municipal solid waste composts compared to sewage sludge. Environ Int 35:142–156
Steel RGD, Torrie JH (1980) Principles and procedures of statistics. A biometrical approach, vol 2. McGraw-Hill, New York
Stephens SR, Alloway BJ, Carter JE, Parker JEA (2001) Towards the characterization of heavy metals in dredged canal sediments and an appreciation of availability: two examples from the UK. Environ Pollut 113:395–401
Tinker PB (1981) Levels, distribution and chemical forms of trace elements in food plants. Philos Trans B 294:41–55
Uboh FE, Akpanabiatu MI, Edet EE, Okon IE (2011) Distribution of heavy metals in fluted pumpkin (Telfeiria occidentalis) leaves planted at different distances away from the traffic congested highways. Int J Adv Biotechnol Res 2:250–256
USEPA (US Environmental Protection Agency) (1997) Exposure factors handbook. Volume II-food ingestion factors. EPA/600//P-95/002Fa. Office of Research and Development, Washington, DC
Uwah EI, Ndahi NP, Ogugbuaja VO (2009) Study of the levels of some agricultural pollutants in soils, and water leaf (Talinum triangulare) obtained in Maiduguri, Nigeria. J Appl Sci Environ Sanit 4:71–78
Vukadinović V, Bertić B (1988) Agrochemistry and plant nutrition. University J.J. Strossmayer in Osijek, Faculty of Agriculture (in Croatian), Osijek, p 56
Wang X, Sato T, Xing B, Tao S (2005) Health risks of heavy metals to the general public in Tianjin, China via consumption of vegetables and fish. Sci Total Environ 350:28–37
Wang Y, Qiao M, Liu Y, Zhu Y (2012) Health risk assessment of heavy metals in soils and vegetables from wastewater irrigated area, Beijing-Tianjin city cluster, China. J Environ Sci 24:690–698
WHO (1996) Trace elements in human nutrition and health. World Health Organization, Geneva. Prepared in Collaboration with the FAO of the UN and the IAEA
WWF (2007) Report on National surface water classification criteria, irrigation water quality. Guidelines for Pakistan, February-2007. Waste Water Forum, Pakistan
Xue ZJ, Liu SQ, Liu YL, Yan YL (2012) Health risk assessment of heavy metals for edible parts of vegetables grown in sewage-irrigated soils in suburbs of Baoding City, China. Environ Monit Assess 184:3503–3513
Yang HX (2002) Effects of irrigation with wastewater on crops in Datong, Shanxi China. Agro Environ Dev 4:18–19
Zango MS, Anim-Gyampo M, Ampadu B (2013) Health risks of heavy metals in selected food crops cultivated in small-scale gold-mining areas in Wassa-Amenfi-West District of Ghana. J Nat Sci Res 3:96–105
Zhang J, Liu CL (2002) Riverine composition and estuarine geochemistry of particulate metals in China—weathering features, anthropogenic impact and chemical fluxes. Estar Coast Shelf 54:1070–1951
Acknowledgements
The financial support by the Higher Education Commission through a research Project # 2484/13 to the first and second authors is gratefully acknowledged. The authors also appreciate all the supporters of this project and the reviewers for their critical evaluation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmad, K., Khan, Z.I., Ashfaq, A. et al. Uptake of hazardous elements by spring onion (Allium fistulosum L.) from soil irrigated with different types of water and possible health risk. Environ Earth Sci 76, 322 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6645-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6645-2