Abstract
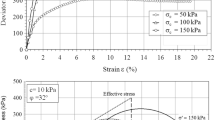
As the number of large reservoirs has grown rapidly, drawdown of water level has become a major factor in inducing landslides. A new simulator was developed to simulate the in-flight drawdown in a centrifuge model test. A series of centrifuge model tests was conducted on slopes with different gradients under drawdown conditions. The failure mechanism was obtained via an integrated analysis of deformation and failure processes according to the displacement histories of the slopes measured by the image capture and displacement measurement system. The slip surface, with slippage failure, was developed from the top downwards due to the drawdown. The displacement histories of the sliding body could be divided into three stages with the increase rate changing from small to large and finally becoming negligible. The deformation of the slope only appeared within a limited zone with a nearly invariable boundary surface during the drawdown. The boundary surface moved closer to the slope surface with the deceasing slope gradient. The drawdown caused a significant coupling process of local failure and deformation localization, which developed from the upper part to the lower part. The upper part of the sliding body behaved as a rigid body, and the lower parts exhibited significant deformation after the slip surface formed, which should be reasonably captured in a stability analysis of a slope under drawdown conditions.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gao YF, Zhu DS, Zhang F, Lei GH, Qin HY (2014) Stability analysis of three-dimensional slopes under water drawdown conditions. Can Geotech J 51(11):1355–1364
Huang MS, Jia CQ (2009) Strength reduction FEM in stability analysis of soil slopes subjected to transient unsaturated seepage. Comput Geotech 36(1–2):93–101
Hudacsek P, Bransby MF, Hallett PD, Bengough AG (2009) Centrifuge modelling of climatic effects on clay embankments. Proc ICE Eng Sustain 162(2):91–100
Indrasenan N, Thusyanthan SP, Madabhushi G, Singh S (2006) Centrifuge modeling of solid waste landfill systems—Part 2: centrifuge testing of model waste. Geotech Test J 29(3):223–229
Jia GW, Zhan TLT, Chen YM, Fredlund DG (2009) Performance of a large-scale slope model subjected to rising and lowering water levels. Eng Geol 106(1–2):92–103
Jian WX, Xu Q, Yang HF, Wang FW (2014) Mechanism and failure process of Qianjiangping landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Environ Earth Sci 72(8):2999–3013
Kaunda RB (2010) A linear regression framework for predicting subsurface geometries and displacement rates in deep-seated, slow-moving landslides. Eng Geol 114(1–2):1–9
Li M, Zhang G, Zhang JM, Lee CF (2011) Centrifuge model tests on a cohesive soil slope under excavation conditions. Soils Found 51(5):801–812
Liang C, Jaksa MB, Ostendorf B, Kuo YL (2015) Influence of river level fluctuations and climate on riverbank stability. Comput Geotech 63:83–98
Ozer AT, Bromwell LG (2012) Stability assessment of an earth dam on silt/clay tailings foundation: a case study. Eng Geol 151:89–99
Piccinini L, Berti M, Simoni A, Bernardi AR, Ghirotti M, Gargini A (2014) Slope stability and groundwater flow system in the area of Lizzano in Belvedere (Northern Apennines, Italy). Eng Geol 183:276–289
Sommers AN, Viswanadham BVS (2009) Centrifuge model tests on the behavior of strip footing on geotextile-reinforced slopes. Geotext Geomembr 27(6):497–505
Stark TD, Jafari NH, Leopold AL, Brandon TL (2014) Soil compressibility in transient unsaturated seepage analyses. Can Geotech J 51(8):858–868
Thusyanthan NI, Madabhushi SPG, Singh S (2005) Seismic performance of geomembrane placed on a slope in a MSW landfill cell—a centrifuge study. ASCE Geotech Spec Publ 130–142:2841–2852
Vandamme J, Zou QP (2013) Investigation of slope instability induced by seepage and erosion by a particle method. Comput Geotech 48:9–20
Viratjandr C, Michalowski RL (2006) Limit analysis of submerged slopes subjected to water drawdown. Can Geotech J 43(8):802–814
Viswanadham BVS, Mahajan RR (2007) Centrifuge model tests on geotextile reinforced slopes. Geosynth Int 14(6):365–379
Wang LP, Zhang G (2014) Centrifuge model test study on pile reinforcement behavior of cohesive soil slopes under earthquake conditions. Landslides 11(2):213–223
Wang JJ, Zhang HP, Zhang L, Liang Y (2012) Experimental study on heterogeneous slope responses to drawdown. Eng Geol 147:52–56
Zhang G, Hu Y, Zhang JM (2009) New image-analysis-based displacement-measurement system for geotechnical centrifuge modeling tests. Measurement 42(1):87–96
Zhang TT, Yan EC, Cheng JT, Zheng Y (2010) Mechanism of reservoir water in the deformation of Hefeng landslide. J Earth Sci 21(6):870–875
Zhang G, Li M, Wang LP (2014) Analysis of the effect of the loading path on the failure behaviour of slopes. KSCE J Civil Eng 18(7):2080–2084
Zhang G, Hu Y, Wang LP (2015) Behaviour and mechanism of failure process of soil slopes. Environ Earth Sci 73(4):1701–1713
Acknowledgments
The study is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51479096), the State Key Laboratory of Hydroscience and Engineering (No. 2014-KY-1), Tsinghua University Initiative Scientific Research Program, and National Program for Support of Top-notch Young Professionals.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, F., Zhang, G. Progressive failure behavior of cohesive soil slopes under water drawdown conditions. Environ Earth Sci 75, 973 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5802-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5802-3