Abstract
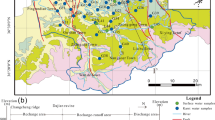
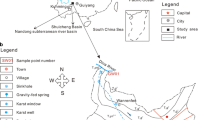
Karst groundwater is one of the most important water resources for agriculture and industry in Fenyang City of Shanxi province, northern China. In the last few decades, excessive exploitation of groundwater and other human activities have caused serious environmental problems in this area. Hence, it is essential to identify the resources of pollutants that deteriorate the water quality in the area. A total of 16 water samples were collected to assess the hydrochemical characteristics from wells and springs in bare karst area, northern Fenyang and covered karst region, south of the city. The chemical composition of groundwater was characterized by a dominance of Ca2+, Mg2+, HCO3 −, and SO4 2−, which accounted for more than 85 % of the total ion concentrations, indicating that limestone dissolution by weathering controls water chemical composition. SO4 2− in the groundwater showed high positive significant correlation with HCO3 − and δ13CDIC, showing that carbonate dissolution by sulfuric acid has important contribution to groundwater chemical composition and δ13CDIC value. The relationship between δ34S and 1/SO4 2− revealed that the sources of SO4 2− are different in various types of groundwater. In the bare karst area, SO4 2− in springs mainly came from atmospheric precipitation, while in the shallow wells it mainly came from human activities; in the covered karst region, SO4 2− in quaternary pores water was mainly from anthropogenic inputs, while in the deep wells it was mainly from gypsum dissolution; in gypsum mine water, SO4 2+ was mainly from gypsum dissolution. Comparing with the bare karst area, human activities have significantly changed the chemical composition of groundwater in the covered karst region. Therefore, more control policies and measures should be formulated and applied to protect the covered karst region in the future.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atekwana EA, Krishnamurthy RV (1998) Seasonal variations of dissolved inorganic carbon and δ13C of surface water: application of a modified gas evolution technique. J Hydrol 205:265–278
Beynen P, Feliciano N, North L, Townsend K (2007) Application of a karst disturbance index in Hillsborough County, Florida. Environ Manag 39(2):261–277
Bottrell S, Tellam J, Bartlett R, Hughes A (2008) Isotopic composition of sulfate as a tracer of natural and anthropogenic influences on groundwater geochemistry in an urban sandstone aquifer, Birmingham, UK. Appl Geochem 23(8):2382–2394
Calmels D, Gaillardet J, Brenot A, France-Lanord C (2007) Sustained sulfide oxidation by physical erosion processes in the Mackenzie River basin: climatic perspectives. Geology 35:1003–1006
Cane G, Clark ID (1999) Tracing ground water recharge in an agricultural watershed with isotopes. Ground Water 37:133–139
Chen JT, Chough SK, Han ZZ, Lee JH (2011) An extensive erosion surface of a strongly deformed limestone bed in the Gushan and Chaomidian formations (late Middle Cambrian to Furongian), Shandong Province, China: sequence–stratigraphic implications. Sed Geol 233(1–4):129–149
Clark ID, Fritz P (1997) Environmental Isotopes in Hydrogeology. Lewis Publishers, New York
Duan GW, Liang YP (2006) The use of δ34S in the analysis of sulfate contamination on karst groundwater in Yangquan. West-China Exp Eng 18(1):100–103 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Fan YH, Huo XL, Hao YH, Liu Y, Wang TK, Liu YC, Yeh TJ (2013) An assembled extreme value statistical model of karst spring discharge. J Hydrol 504:57–68
Galy A, France-Lanord C (1999) Weathering processes in the Ganges–Brahmaputra basin and the riverine alkalinity budget. Chem Geol 159:31–60
Gams I, Nicod J, Julian M, Anthory E, Sauro U (1993) Environmental change and human impacts on the Mediterranean karsts of France, Italy and the Dinaric Region. In: Williams PW (ed) Karst terrians: environmental changes, human impact: catena supplement 25. Catena Verlag, Cremlingen-Destedt, Germany
Guo Q, Wang Y, Ma T, Li L (2005) Variation of karst springs discharge in recent five decades as an indicator of global climate change: a case study at Shanxi, northern China. Sci China Series D Earth Sci 48(11):2001–2010
Han GL, Liu CQ (2004) Water geochemistry controlled by carbonate dissolution: a study of the river waters draining karst-dominated terrain, Guizhou Province, China. Chem Geol 204:1–21
Han DM, Xu HL, Liang X (2006) GIS-based regionalization of a karst water system in Xishan Mountain area of Taiyuan Basin, north China. J Hydrol 331:459–470
Heinz B, Birk S, Liedl R, Geyer T, Straub KL, Andresen J, Bester K, Kappler A (2008) Water quality deterioration at a karst spring (Gallusquelle, Germany) dueto combined sewer overflow: evidence of bacterial and micro-pollutant contamination. Environ Geol 57(4):797–801
Hong YT, Zhang HH, Zhu YX, Pu HC, Jiang HB, Liu DP (1994) Characteristics of sulfur isotopic composition of meteoric water in China. Prog Nat Sci 4(6):741–745 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Hosono T, Wang C, UmezawaY Nakano T, Onodera S, Nagata T, Yoshimizu C, Tayasu I, Taniguchi M (2010) Multiple isotope (H, O, N, S and Sr) approach elucidates complex pollution causes in the shallow groundwaters of the Taipei urban area. J Hydrol 397(1–2):23–36
Huai HY, Gaines A, Tye RE (2011) Relation between the deposition and petrology of Shanxi coals and the composition of their extracts. Appl Geochem 26(8):1377–1385
Huang QB, Qin XQ, Liu PY (2012) The δ13C characteristics of groundwater in different karst environmental conditions. Earth and Environment 40(4):505–511 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Jemcov I (2007) Water supply potential and optimal exploitation capacity of karst aquifer systems. Environ Geol 51(5):767–773
Krouse HR, Mayer B (2000) Sulphur and oxygen isotopes in sulphate. In: Cook PG, Herczeg AL (eds) Environmental Tracers in Subsurface Hydrology. Kluwer Academic Press, Boston
Lang YC, Liu CQ, Li SL, Zhao ZQ, Zhou ZH (2011) Tracing natural and anthropogenic sources of dissolved sulfate in a karst region by using major ion chemistry and stable sulfur isotopes. Applied Geochemistry 26:S202–S205
Li YP (2012) The analysis on characteristics and trend of precipitation in Yuncheng City. Sci Technol Enterp 3(9):154–155 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li YL, Wang YX, Liu J, Lou ZH (1998) Pollution analysis of SO4 2−, Ca2+, Mg2+ in karst water in Niang Ziguan Spring area. Geol Sci Technol Inform 17(2):111–114 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li SL, Liu CQ, Tao FX, Lang YC, Han GL (2005) Carbon biogeochemistry of ground water, Guiyang, Southwest China. Ground Water 43:494–499
Li XD, Masuda H, Kusakabe M, Yanagisawa F, Zeng HA (2006) Degradation of groundwater quality due to anthropogenic sulfur and nitrogen contamination in the Sichuan Basin, China. Geochem J 40(4):309–332
Li SL, Calmels D, Han GL, Gaillardet J, Liu CQ (2008) Sulfuric acid as an agent of carbonate weathering constrained by δ13CDIC: examples from Southwest China. Earth Planet Sci Lett 270:180–199
Li SL, Liu CQ, Li J, Lang YC, Ding H, Li LB (2010a) Geochemistry of dissolved inorganic carbon and carbonate weathering in a small typical karstic catchment of Southwest China: isotopic and chemical constraints. Chem Geol 277:301–309
Li XD, Liu CQ, Harue M, Li SL, Liu XL (2010b) The use of environmental isotopic (C, Sr, S) and hydrochemical tracers tocharacterize anthropogenic effects on karst groundwater quality: a case study of the Shuicheng Basin, SW China. Appl Geochem 25:1924–1936
Li XD, Liu CQ, Liu XL, LiR Bao (2011) Identification of dissolved sulfate sources and the role of sulfuric acid in carbonate weathering using dual-isotopic data from the Jialing River, Southwest China. J Asian Earth Sci 42:370–380
Liang YP, Wang WT, Zhao CH, Wang W, Tang CL (2013) Variations of karst water and environmental problems in North China. Carsologica Sinica 32(1):34–42 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu ZH, Yuan DX, He SY (1997) Stable Carbon Isotope Geochemical and Hydrochemical Features in the System of Carbonate–H2O–CO2 and Their Implications-Evidence from Several Typical Karst Area of China. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition) 71(4):446–454
Liu CQ, Lang YC, Satake H, Wu JH, Li SL (2008) Identification of anthropogenic and natural inputs of sulfate and chloride into the karstic ground water of Guiyang, SW China: combined δ37Cl and δ34S approach. Environ Sci Technol 429(15):5421–5427
Lu HY, ZhouYL Liu WG, Mason J (2012) Organic stable carbon isotopic composition reveals late Quaternary vegetation changes in the dune fields of northern China. Quatern Res 77(3):433–444
Otero N, Canals À, Soler A (2007) Using dual-isotope data to trace the origin and processes of dissolved sulphate: a case study in Calders stream (Llobregat basin, Spain). Aquat Geochem 13:109–126
Parkhurst DL, Appelo CAJ (1999) User’s Guide to PHREEQC (Version 2)-A Computer Program for Speciation, Batch-reaction, One-dimensional Transport, and Inverse Geochemical Calculations. US Geol Surv Water-Resour Invest Rep 99–4259
Raab M, Spiro B (1991) Sulfur isotopic variations during seawater evaporation with fractional crystallization. Chem Geol 86(4):323–333
Sauro U (1993) Human impact on the karst of the Venetian Fore-Alps. Italy. Environmental Geology 21(3):115–121
Spence J, Telmer K (2005) The role of sulfur in chemical weathering and atmospheric CO2 fluxes: evidence from major ions, δ13CDIC, andδ34SSO4 in rivers of the Canadian Cordillera. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 69:5441–5458
Valdes D, Dupont JP, Laignel B, Oiger S, Leboulanger T, Mahler BJ (2007) A spatial analysis of structural controls on karsts groundwater geochemistry at a regional scale. J Hydrol 340:244–255
Wang TJ, Jin LS, Lia ZK, Lam KS (2000) A modeling study on acid rain and recommended emission control strategies in China. Atmos Environ 34(26):4467–4477
Wang YX, Guo QH, Su CL, Ma T (2006) Strontium isotope characterization and major ion geochemistry of karst water flow, Shentou, northern China. J Hydrol 328:592–603
Xu ZF, Liu CQ (2007) Chemical weathering in the upper reaches of Xijiang River draining the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau. Southwest China. Chem. Geol 239:83–95
Yanagisawa F, Sakai H (1983) Thermal decomposition of barium sulfate-vanadium pentoxide-silica glass mixtures for preparation of sulfur dioxide in sulfur isotope ratio measurements. Anal Chem 55(6):985–987
Yang YC, Shen ZL,Wen DG, Hou GC, She HQ, Zhao ZH, Wang D, Li JW (2010) Distribution of δ34S and δ18O in SO4 2− in groundwater from the ordos cretaceous groundwater baisn and geological implications. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition) 84(2):432–440
Yoon J, Huh Y, Lee I, Moon S, Noh H, Qin JH (2008) Weathering processes in the Min Jiang: major elements, 87Sr/86Sr, δ34SSO4, andδ18OSO4. Aquat Geochem 14:147–170
Yuan DX (1997) Sensitivity of karst process to environmental change along the PEP II transect. Quatern Int 35:105–113
Zhang SR, Lu XX, Higgitt DL, Chen CTA, Sun HG, Han JT (2007) Water chemistry of the Zhujiang (Pearl River): natural processes and anthropogenic influences. J Geophys Res 112:F01011. doi:10.1029/2006JF000493
Zhang JH, Liang YP, Wang WT, Han XR, Hou GC (2009) A practical use of δ34S in the investigation of karst groundwater resource in North China. Carsologica Sinica 28(3):235–241 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang HB, Yu S, He SY, Liu Q, Li YL (2012) Analysis on the chemical characteristics of the atmospheric precipitation in Guilin. Carsologica Sinica 31(3):289–295 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No: 41302211), the Special Fund for Public Benefit Scientific Research of Ministry of Land and Resources of China (No: 12120113005200). Special thanks are given to the prof. Liang Yongping for his valuable comments and suggestions. Thanks are also given to Mr. Zhao Shiyong and Wang Weitang for their help in the field.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qibo, H., Xiaoqun, Q., Qiyong, Y. et al. Identification of dissolved sulfate sources and the role of sulfuric acid in carbonate weathering using δ13CDIC and δ34S in karst area, northern China. Environ Earth Sci 75, 51 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4869-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4869-6