Abstract
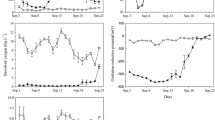
The objective of this study was to link hydrodynamic disturbance with sediment resuspension, phosphorus release, and algal growth in Lake Tai, a typical shallow lake located in the south of the Yangtze River Delta in China. With this regard, a sediment–water-algae laboratory experiment was conducted and extrapolated to the real situation in terms of field observations. The results show that the algal growth rate synchronically increased with dissolved total phosphorus (DTP) release rate. The DTP decreased with increase of bottom flow velocity, indicating that the phosphorus release rate was lower than its transfer rate into algal biomass. While all levels of hydrodynamic disturbances could increase sediment resuspension and phosphorus release, a low to moderate disturbance was beneficial, but a strong disturbance was harmful for algal growth. Also, a low to moderate disturbance caused the dissolved alkaline phosphatase activity (DAPA) to increase with time, which provided the enzyme for hydrolyzing a variety of organic phosphorus compounds from bed sediment into algae-needed nutritional DTP. The experiment proved to be an efficient means to understanding eutrophication mechanisms of large shallow lakes such as Lake Tai.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen Y, Fan C, Teubner K, Dokulil M (2003a) Changes of nutrients and phytoplankton chlorophyll-a in a large shallow Lake Taihu, China: an 8-year investigation. Hydrobiologia 506–509:273–279
Chen Y, Qin B, Teubner K, Dokulil MT (2003b) Long-term dynamics of phytoplankton assemblages: Microcystis-domination in Lake Taihu, a large shallow lake in China. Plankton Res 25(1):445–453
Chen J, Lu S, Zhao Y, Wang W, Huang M (2011) Effects of overlying water aeration on phosphorus fractions and alkaline phosphatase activity in surface sediment. J Environ Sci 23(2):206–211
Chuai X, Ding W, Chen X, Wang X, Miao A, Xi B, He L, Yang L (2011) Phosphorus release from cyanobacterial blooms in Meiliang Bay of Lake Taihu, China. Ecol Eng 37:842–849
Ding L, Wu J, Pang Y, Li L, Gao G, Hu D (2007) Simulation study on algal dynamics based on ecological flume experiment in Taihu Lake, China. Ecol Eng 31:200–206
Duong TT, Jähnichen S, Le TPQ, Ho CT, Hoang TK, Nguyen TK, Vu TN, Dang DK (2014) The occurrence of cyanobacteria and microcystins in the Hoan Kiem Lake and the Nui Coc reservoir (North Vietnam). Environ Earth Sci 71:2419–2427
Fan J, Wang D, Zhang K (2010) Experimental study on a dynamic contaminant release into overlying water-body across sediment-water interface. J Hydrodyn 22(5):354–357
Finnemore EJ, Franzini JB (2002) Fluid mechanics with engineering application, 10th edn. McGraw Hall, New York
Gao G, Zhu G, Qin B, Chen J, Wang K (2006) Alkaline phosphatase activity and the phosphorus mineralization rate of Lake Taihu. Sci China Ser D Earth Sci 49:176–185
Hawley N (2000) Sediment resuspension near the Keweenaw Peninsula, Lake Superior during the fall and winter 1990-1991. Great Lake Resour 26(4):495–505
Horppila J, Nurminen L (2005) Effects of different macrophyte growth forms on sediment and P resuspendionin a shallow lake. Hydrobiologia 545:167–175
Hu K, Pang Y, Wang H, Wang X, Wu X, Bao K, Liu Q (2011) Simulation study on water quality based on sediment release flume experiment in Lake Taihu, China. Ecol Eng 37:607–615
Huang C, Li Y, Yang H, Sun D, Yu Z, Zhang Z, Chen X, Xu L (2014a) Detection of algal bloom and factors influencing its formation in Taihu Lake from 2000 to 2011 by MODIS. Environ Earth Sci 71:3705–3714
Huang J, Gao J, Hörmann G, Fohrer N (2014b) Modeling the effects of environmental variables on short-term spatial changes in phytoplankton biomass in a large shallow lake, Lake Taihu. Environ Earth Sci 72:3609–3621
Jiang X, Jin X, Yao Y, Li L, Wu F (2008) Effects of biological activity, light, temperature and oxygen on phosphorus release processes at the sediment and water interface of Taihu Lake, China. Water Res 42:2251–2259
Jin K, Ji Z (2004) Modeling of sediment transport and wind-wave impact in Lake Okeechobee. J Hydraul Eng 130(11):1055–1067
Jin X, Chu Z, Yan F, Zeng Q (2009) Effects of lanthanum (III) and EDTA on the growth and competition of Microcystis aeruginosa and Scendesmus quadricauda. Limnologica 39:86–93
Kelderman P, Ang’weya RO, De Rozari P, Vijverberg T (2012) Sediment characteristics and wind-induced sediment dynamics in shallow lake Markermeer, the Netherlands. Aquat Sci 74:301–313
Labry C, Delmas D, Herbland A (2005) Phytoplankton and bacterial alkaline phosphatase activities in relation to phosphate and DOP availability within the Gironde plume waters (Bay of Biscay). J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 318:213–225
Laenen A, LeTourneau AP (1996) Upper Klamath Basin nutrient-loading study: Estimate of wind-induced resuspension of bed sediment during periods of low lake elevation. Open-File Report 95-414. US Geological Survey, Washington DC
Laima MJC, Matthiesen H, Lund-Hansen LC (1998) Resuspension studies in cylindrical microcosms: effects of stirring velocity on the dynamics of redox sensitive elements in a coastal sediment. Biogeochemistry 43:293–309
Luettich RA, Harleman DRF, Somlyödz L (1990) Dynamic behavior of suspended sediment concentrations in a shallow lake perturbed by episodic wind events. Limnol Oceanogr 35(5):1050–1067
Luo L, Qin B (2003) Comparison between wave effects and current effects on sediment resuspension in Lake Taihu. Hydrology 23(3):1–4 (Chinese)
Meis S, Spears BM, Maberly SC, Perkins RG (2013) Assessing the mode of action of phoslock in the control of phosphorus release from the bed sediments in a shallow lake (Loch Flemington, UK). Water Res 47:4460–4473
Ndong M, Bird D, Nguyen-Quang T, de Boutray M, Zamyadi A, Vincon-Leite B, Lemaire BJ, Prévost M, Dorner S (2014) Estimating the risk of cyanobacterial occurrence using an index integrating meteorological factors: application to drinking water production. Water Res 56:98–108
Neter J, Kutner MH, Nachtsheim CJ, Wasserman W (1996) Applied Linear Statistical Models, 4th edn. McGraw-Hill Companies Inc, New York
Ogilvie BG, Mitchell SF (1998) Does sediment resuspension have persistent effects on phytoplankton? Experimental studies in three shallow lakes. Freshw Biol 40:51–63
Ono E, Cuello JL (2007) Carbon dioxide mitigation using thermophilic cyanobacteria. Biosyst Eng 96:129–134
Padisák J, Reynolds CS (2003) Shallow lakes: the absolute, the relative, the functional and the pragmatic. Hydrobiologia 506–509(1–3):1–11
Paerl HW, Xu H, Macarthy MJ, Zhu G, Qin B, Li Y, Gardner W (2011) Controlling harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a hyper-eutrophic lake (Lake Taihu, China): the need for a dual nutrient (N&P) management strategy. Water Res 45:1973–1983
Qin B, Hu W, Gao G, Luo L, Zhang J (2004) Dynamics of sediment resuspension and the conceptual schema of nutrient release in the large shallow Lake Taihu, China. Chin Sci Bull 49:54–64
Qin B, Zhu G, Gao G, Zhang Y, Li W, Paerl HW, Carmichael WW (2010) A drinking water crisis in Lake Taihu, China: linkage to climatic variability and lake management. Environ Manage 45:105–112
Read JS, Hamilton DP, Jones ID, Muraoka K, Winslow LA, Kroiss R, Wu CH, Gaiser E (2011) Derivation of lake mixing and stratification indices from high-resolution lake buoy data. Environ Model Softw 26:1325–1336
Reddy KR, Fisher MM, Ivanoff D (1996) Resuspension and diffusive flux of nitrogen and phosphorus in a hypereutrophic lake. J Environ Qual 25:363–371
Reichardt W (1971) Catalytic mobilization of phosphate in lake water and by Cyanophyta. Hydrobiologia 38:377–394
Sheng YP, Lick W (1979) The transport and resuspension of sediments in a shallow lake. J Geophys Res 84:1809–1826
Søndergaard M, Bjerring R, Jeppesen E (2013) Persistent internal phosphorus loading during summer in shallow eutrophic lakes. Hydrobiologia 710(1):95–107
Sun X, Qin B, Zhu G, Zhang Z, Gao Y (2007) Release of colloidal N and P from sediment of lake caused by continuing hydrodynamic disturbance. Environ Sci 28(6):1223–1229 (in Chinese)
United States EPA (1997) In vitro determination of chlorophylls a, b, c1 + c2 and pheopigments in marine and freshwater algae by visible spectrophotometry. EPA Method 446.0. US Environmental Protection Agency, Washington DC
Vicente ID, Lopez R, Pozo I, Green AJ (2012) Nutrient and sediment dynamics in a Mediterranean shallow lake in southwest Spain. Limnetica 31(2):231–250
Wang X, Hao C, Zhang F, Feng C, Yang Y (2011) Inhibition of the growth of two blue-green algae species (Microsystis aruginosa and Anabaena spiroides) by acidification treatments using carbon dioxide. Bioresour Technol 102:5742–5748
Wilhelm SW, Farnsley SE, LeCleir GR, Layton AC, Satchwell MF, DeBruyn JM, Boyer GL, Zhu G, Paerl HW (2011) The relationships between nutrients, cyanobacterial toxins and the microbial community in Taihu (Lake Tai), China. Harmful Algae 10:207–215
Wu XD, Kong FX, Chen YW, Qian X, Zhang LJ, Yu Y, Zhang M, Xing P (2010) Horizontal distribution and transport processes of bloom-forming Microcystis in a large shallow lake (Taihu, China). Limnologica 40:8–15
Wu X, Eadaoin MJ, Timothy JM (2012) Evaluation of the mechanisms of the effect of ultrasound on Microcystis aeruginosa at different ultrasonic frequencies. Water Res 46:2851–2858
Wu T, Qin B, Zhu G, Li W, Luan C (2013) Modeling of turbidity dynamics caused by wind-induced waves and current in the Taihu Lake. Int J Sedim Res 28:139–148
Wüest A, Lorke A (2003) Small-scale hydrodynamics in lakes. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 35:373–412
Xie L, Xie P, Tang H (2003) Enhancement of dissolved phosphorus release from sediment to lake water by Microcystis blooms-an enclosure experiment in a hyper-eutrophic, subtropical Chinese lake. Environ Pollut 122:391–399
Xu JP (1998) Wave-current bottom shear stresses and sediment resuspension in Cleveland Bay, Australia, by Lou and Ridd: comments. Coast Eng 33(1):61–64
Yan R, Pang Y, Wang K (2007) Disturbance effect on growth of two species of algae under different culture conditions. Environ Sci Technol 30(3):10–13 (in Chinese)
You B, Zhong J, Fan C, Wang T, Zhang L, Ding S (2007) Effects of hydrodynamics process on phosphorus fluxes from sediment in large, shallow Taihu Lake. J Environ Sci 19:1055–1060
Yuan H, An S, Shen J, Liu E (2014) The characteristic and environmental pollution records of phosphorus species in different trophic regions of Taihu Lake, China. Environ Earth Sci 71:783–792
Zhai SJ, Hu W, Zhu Z (2010) Ecological impacts of water transfers on Lake Taihu from the Yangtze River, China. Ecol Eng 36:406–420
Zhang T, Wang X, Jin X (2007) Variations of alkaline phosphatase activity and P fractions in sediments of a shallow Chinese eutrophic lake (Lake Taihu). Environ Pollut 150:288–294
Zhang Y, Tang CY, Li G (2012) The role of hydrodynamic conditions and pH on algal-rich water fouling of ultrafiltration. Water Res 46:4783–4789
Zhou Y, Song C, Cao X, Li J, Chen G, Xia Z, Jiang P (2008) Phosphorus fractions and alkaline phosphatase activity in sediments of a large eutrophic Chinese lake (Lake Taihu). Hydrobiologia 599:119–125
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC)’s project on the Effect of Hydrology and Hydrodynamic on Eutrophication in Chinese Shallow Lakes (41473110), the Water Pollution Control and Management of Major Projects (WPCMMP) Committee of China (2012ZX07101-002), and the Integrated Technology for Water Pollution Control and Remediation at Watershed Scale and its Benefit Assessment (2014ZX07510-001). Also, the China Scholarship Council (CSC) provided the primary author (Huang) with a scholarship to support a joint Ph.D. studentship at Old Dominion University in the USA. We would like to thank our colleagues at the Groundwater and Environmental Systems Engineering Innovation Base of the Chinese Research Academy of Environment Sciences (CRAES).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, J., Xu, Q., Xi, B. et al. Impacts of hydrodynamic disturbance on sediment resuspension, phosphorus and phosphatase release, and cyanobacterial growth in Lake Tai. Environ Earth Sci 74, 3945–3954 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4083-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4083-6