Abstract
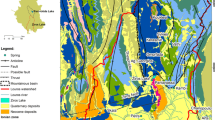
Mar Chiquita is a coastal lagoon located in the Argentine Buenos Aires province in South America. The aim of this study was to perform a hydrochemical and stable isotopes characterization in order to better the understanding of the hydrology of the Mar Chiquita lagoon’s catchment and its water budget. Groundwater samples were taken from 144 wells and 21 samples from main streams, and seven lagoon water samples were also collected. Chemical analyses were carried out using standard laboratory methods, and isotopic determinations were made through laser spectroscopy using a DLT-100 liquid–water isotope analyzer. Hydrochemical analysis permits a general classification of groundwater and streamwater as sodium bicarbonate waters, while the lagoon chemical composition shows an evolution toward seawater composition, from the north to its mouth, which is located southerly. Isotopic data show a source of aquifer recharge from rainfall and a groundwater domain into the streams’ flow. Three main components can be recognized as end members in a plot of electrical conductivity (EC) versus δ18O: seawater, streamwater and groundwater. Obtained EC values for groundwater in the discharge zone (EC average value = 3,516 μS/cm) allow minimizing its direct contribution and to take into consideration two dominating end members: streamwater and seawater. Mar Chiquita lagoon’s water falls close to the line between streamwater and seawater end members according to its EC and δ18O. The obtained seawater proportion for these samples ranges from 84 % in the lagoon’s mouth to around 0 % in the more distal area.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA (1992) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 18th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington, p 1100
Back W (1961) Techniques for mapping hydrochemical facies. Prof Pap US Geol Surv 424-D:380–382
Bonorino G, Albouny R, Rossi S (2001) La influencia del sistema carbonatado sobre el quimismo del agua subterránea (cuenca superior del arroyo Chasicó). Geoacta 26:1–11
Calmbach and Waterloo Hydrogeologic (2003) Water quality data analysis, plotting, and modeling; Aquachem user’s manual v.4.0., co-developed by Lukas Calmbach and Waterloo Hydro-geologic, Inc., USA, p 276
Chebotarev II (1955) Metamorphism of natural waters in the crust of weathering. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 8:22–48
Christophersen N, Neal C, Hooper R, Vogt R, Andersen S (1990) Modeling streamwater chemistry as a mixture of soilwater end-members—a step towards 2nd-generation acidification models. J Hydrol 116(1–4):307–320
Clark ID, Fritz P (1997) Environmental isotopes in hydrogeology. CRC, Boca Raton, p 328
Cook PG, Herczeg AL (1999) Environmental tracers in subsurface hydrology. Kluwer, Boston, p 529
Dalla Salda L, Iñiguez RA (1979) La Tinta, Precámbrico y Paleozoico de Buenos Aires. VII Congreso Geológico Argentino, Neuquén 1:539–550
ESRI (2007) Environment System Research Institute. http://www.esri.com
Fasano JL (1980) Geohidrología de la laguna Mar Chiquita y alrededores, provincia de Buenos Aires. Simp sobre Probl Geol del Lit Atl Bonaer Abstracts. Mar del Plata
Gat JR, Tzur Y (1967) Modification of the isotopic composition of rainwater by processes which occur before groundwater recharge. In: Proceedings symposium isotopes in hydrology, IAEA, Vienna, pp 49–60
Geyh M (2000) Groundwater, vol 4. Environmental isotopes in the hydrologic cycle. In: Mook WG (ed) IHP-V technical documents in hydrology, no. 39, UNESCO, Paris, p 196
Glok Galli M, Martínez DE, Kruse EE, Lima ML (2012) Descarga de aguas subterráneas en arroyos de la llanura y cambios químicos. II RAGSU. Book of extended abstracts. Bahía Blanca, Bs. As. ISBN 978-987-1620-86-9, pp 108–111
Gonfiantini R (1978) Standards for stable isotope measurements in natural compounds. Nature 271:534–536
Hem JD (1992) Study and interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural waters. USGS water-supply paper, 2254, fourth printing, p 263
Hooper RP (2003) Diagnostic tools for mixing models of stream water chemistry. Water Resour Res 39(3):1055. doi:10.1029/2002WR001528
Iribarne O (2001) Reserva de Biósfera Mar Chiquita: Características físicas, biológicas y ecológicas. Martín Editorial, Argentina, p 320
Kruse EE (1986) Aspectos geohidrológicos de la región sudoriental de Tandilla. Cuencas de los Aos. Vivoratá, las Brusquitas y el Durazno. Revista de la Asociación Geológica Argentina, Buenos Aires XLI(3–4):367–374
Lanfredi NW, Balestrini CF, Mazio CA, Schmidt SA (1981) Tidal sandbanks in Mar Chiquita Coastal Lagoon, Argentina. J Coast Res 3(4):515–520
Levin M, Fasano J, Ospital C, Panarello HO, Albero MC, Bocanegra EM (1988) Aplicaciones isotópicas e hidroquímicas en estudios hidrogeológicos del área de Mar Chiquita, provincia de Buenos Aires. II Jornadas Geológicas Bonaerenses, Bahía Blanca. Proceedings, pp 631–640
Lima ML, Romanelli A, Massone H (2013) Decision support model for assessing aquifer pollution hazard and prioritizing groundwater resources management in the wet Pampa plain, Argentina. Environ Monit Assess 185:5125–5139. doi:10.1007/s10661-012-2930-4
Lis G, Wassenaar LI, Hendry MJ (2008) High precision laser spectroscopy D/H and 18O/16O measurements of microliter natural water samples. Anal Chem 80:287–293
Mangiarotti J, Cañete R (2002) Informe del Servicio de Guardaparques de la Reserva Natural Mar Chiquita. Mar Chiquita Party web page (marchiquitadigital.com.ar.; June 2002)
Marcovecchio JE, Freije RH, De Marco S, Gavio MA, Beltrame MO, Asteasuain R (2006) Seasonality of hydrographic variables in a coastal lagoon: Mar Chiquita, Argentina. Aquat Conserv: Mar Freshw Ecosyst 16(4):335–347
Martínez DE, Bocanegra EM (2002) Hydrochemistry and cationic exchange processes in the coastal aquifer of Mar del Plata, Argentina. Hydrogeol J 10(3):393–408
Martínez DE, Bocanegra EM, Manzano M (2000) La modelación Hidrogeoquímica como herramienta en estudios Hidrogeológicos. Boletín Geológico y Minero 111(4):83–98
Martínez DE, Dapeña C, Betancur Vargas T, Panarello HO, Quiroz Londoño OM, Massone HE (2007) Environmental isotopes in the water cycle in the catchment of the Quequen Grande River, Argentina. International symposium on advances in isotope hydrology and its role in sustainable water resources management, (IHS–2007), Proceedings, Viena, 1:381–388
Martínez DE, Quiroz Londoño OM, Glok Galli M, Grondona SI, Massone HE (2013) Datación de agua subterránea en el Acuífero Pampeano del sudeste bonaerense y su significado ambiental. VIII Congreso Argentino de Hidrogeología y VI Seminario Hispano Latinoamericano sobre temas actuales de la hidrología subterránea. La Plata, Bs. As., Proceedings 3:279–286
Martos P, Reta R (1997) Aspectos Hidrográficos de la Región Estuarial de la Laguna de Mar Chiquita, Pcia. de Buenos Aires. II Congreso Argentino de Limnología. I Reunión Argentina sobre Sistemas Costeros Mixohalinos. Museo Argentino de Ciencias Naturales Bernardino Rivadavia. Buenos Aires province, Abstract
Massone HE (2000) Geología y Planificación Territorial en la Cuenca Superior del Arroyo Grande (provincia de Buenos Aires). PhD thesis, Facultad de Ciencias Naturales y Museo. Universidad Nacional de La Plata, p 238
Massone HE, Martínez DE, Tomás M (2005) Caracterización hidroquímica superficial y subterránea en la Cuenca Superior del Arroyo Grande (Prov. de Buenos Aires). II Seminario Hispano Latinoamericano sobre temas de Hidrología Subterránea: relación aguas superficiales-aguas subterráneas. Río Cuarto. Córdoba, Proceedings, pp 47–55
MA, Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (2005) Ecosystems and human well-being: wetlands and water synthesis. Millennium ecosystem assessment report to the ramsar convention. World Resources Institute, Washington
Parkhurst DL, Appelo CA (1999) User’s guide to PHREEQC, a computer program for speciation, reaction path, advective–transport, and inverse geochemical calculations. US Geological Survey. Water resources investigation report 99–4259
Quiroz Londoño OM, Martínez DE, Dapeña C, Massone HE (2008) Hydrogeochemistry and isotope analyses used to determine groundwater recharge and flow in low-gradient catchments of the province of Buenos Aires, Argentina. Hydrogeol J 16(6):1113–1127
Romanelli A, Quiroz Londoño OM, Massone HE, Martínez DE, Bocanegra EM (2010) El agua subterránea en el funcionamiento hidrológico de los humedales del Sudeste Bonaerense, Provincia de Buenos Aires, Argentina. Boletín Geológico y Minero 121(4):373–386
Sala JM (1975) Recursos Hídricos. Relatorio VI, Congreso Geológico Argentino. Bs. As, pp 169–194
Sala JM (1977) Caracterización hidrológica preliminar del ambiente periserrano de Balcarce. Technical report Min. As. Agr.-Fac. Cienc. Nat. y Museo, La Plata, p 32
Teruggi M (1954) El mineral volcánico-piroclástico en la sedimentación cuaternaria argentina. Buenos Aires, Revista de la Asociación Geológica Argentina IX(3):184–191
Thornthwaite CW (1948) An approach towards a rational classification of climate. Geogr Rev 38:55–94
Tricart JL (1973) Geomorfología de la Pampa Deprimida. INTA. Scientific collection N XII, p 197
Vázquez-Suñé E, Carrera J, Tubau I, Sánchez-Vila X, Soler A (2010) An approach to identify urban groundwater recharge. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 14(10):2085–2097
Wang Y, Guo Q, Su C, Ma T (2006) Strontium isotope characterization and major ion geochemistry of karst water flow, Shentou, northern China. J Hydrol 328:592–603
Winter TC (1999) Relation of streams, lakes, and wetlands to groundwater flow systems. Hydrogeol J 7:28–45
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the financial support of CONICET (National Council of Scientific and Technical Research—Argentina) for the period 2009–2011, through PIP 112 200801 01318 KE1 “EVOLUCIÓN Y DINÁMICA DE LA PLANICIE COSTERA DE MAR CHIQUITA,” and to the ANPCyT that also contributes through the project PICT 2001 0768. We are also thankful to Tec. A. Ferrante, who collaborated in the sampling and Tec. G.V. Bernava, who performed the chemical analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Glok Galli, M., Martínez, D.E., Kruse, E.E. et al. Hydrochemical and isotopic characterization of the hydrological budget of a MAB Reserve: Mar Chiquita lagoon, province of Buenos Aires, Argentina. Environ Earth Sci 72, 2821–2835 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3187-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3187-8