Abstract
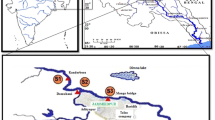
The present study was carried out to investigate the impact of anthropogenic influences on Cuddalore coast, Southeast coast of India, with regard to physicochemical parameters and heavy metal concentration in the surface water and sediment samples of the study area. The samples were collected in different seasons of the year (January–December 2010) and analysed for physicochemical parameters (Temperature, pH, salinity, nitrate, nitrite, ammonia, phosphate and silicate) and heavy metals (Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn) using standard methods. Results showed that physicochemical characteristics and heavy metals concentration in the samples of the study area were varied seasonally and spatially. The concentrations of heavy metals in water and sediment samples of the study area were higher in the monsoon season compared with those of other seasons. The heavy metal concentration in collected samples was found to be above WHO standards. The order of heavy metals in water and sediment samples was Pb > Cu > Cd > Zn. The heavy metal data were analysed through widely using multivariate statistical methods including principle component analysis (PCA) and cluster analysis (CA). CA classified the sampling sites into three clusters based on contamination sources and season. The PCA revealed that the season has a huge impact on the levels, types and distribution of metals found in water and sediment samples. The study also shows the main basis of heavy metals pollution at Cuddalore coast is land based anthropogenic inputs as a result of discharging of waste from industries, municipal, agricultural activities and sewage into estuarine regions, which carries the wastes into coastal area during tidal action. Statistical analyses and experimental data revealed that the Cuddalore coast may cause health risk to the recreational users and fisher folk, ultimately warrants environmental quality management to control heavy metal contamination.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ananthan G, Sampathkumar P, Soundarapandian P, Kannan L (2005) Heavy metal concentrations in Ariyankuppam estuary and Verampattinam coast of Pondicherry. Indian J Fish 52:501–506
APHA, Clescerl LS, Greenberg AE, Eaton AD (1998) Standard methods for examination of water & wastewater, 20th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC
Asha PS, Diwakar K (2007) Recent trends in the hydrobiology of coastal and inshore waters off Tuticorin in the Gulf of Mannar, India. J Mar Biol Assoc India 49:7–11
Ashok Prabu V, Rajkumar M, Perumal P (2008) Seasonal variations in physico-chemical characteristics of Pichavaram mangroves, southeast coast of India. J Environ Biol 29:945–950
Aston SR (1980) Nutrients dissolved gasses and general biochemistry in estuaries. In: Olausson E, Cato I (eds) Chemistry and biogeochemistry of estuaries. Wiley, New York, pp 233–262
Balasubramanian R, Kannan L (2005) Physico-chemical characteristics of the coral reef environs of the Gulf of Mannar Biosphere Reserve, India. Int J Ecol Environ Sci 31:265–271
Bragadeeswaran S, Rajasegar M, Srinivasan M, Kanagarajan U (2007) Sediment texture and nutrients of Arasalar estuary, Karaikkal, Southeast coast of India. J Environ Biol 28:237–240
Diagomanolin V, Farhang M, Ghazi-Khansari M, Jafarzadeh N (2004) Heavy metals (Ni, Cr, Cu) in the Karoon waterway river, Iran. Toxicol Lett 151(1):63–67
Emerton L (2006) Ounting coastal ecosystems as an economic part of development infrastructure, ecosystems and livelihoods Group Asia. World Conservation Union (IUCN), Colombo
Gbaruko BC, Fridya OU (2007) Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in some fauna and flora. Int J Environ Sci Technol 4(2):197–202
Gouda R, Panigrahy RC (1992) Seasonal distribution and behaviour of silicates in the Rushikulya estuary, east coast of India. Indian J Mar Sci 24:111–115
Govindasamy C, Kannan L, Azariah Jayapaul (2000) Seasonal variation in physico-chemical properties and primary production in the coastal water biotopes of Coromandel coast, India. J Environ Biol 21:1–7
Jadoon WA, Arshad M, Ullah I (2012) Spatio-temporal microbial water quality assessment of selected natural streams of Islamabad, Pakistan. Rec Zool Surv Pak 21:14–18
Jonathan MP, Srinivasalu S, Thangadurai N, Ayyamperumal T, Armstrong-Altrin JS, Ram-Mohan V (2008) Contamination of Uppanar River and coastal waters off Cuddalore, Southeast coast of India. Environ Geol 53:1391–1404
Karbassi A, Saeedi M, Amirnejad R (2008) Historical changes of heavy metals content and sequential extraction in a sediment core from the Gorgan Bay, Southeastern Caspian Sea. Indian J Mar Sci 37(3): 267–272
Karthikeyan R, Vijayalakshmi S, Balasubramanian T (2007) Monthly variations of heavy metals and metal resistant bacteria from the Uppanar estuary (Southeast coast of India). Res J Microbiol 2:50–57
Kumar RN, Solanki R, Kumar JIN (2013) Seasonal variation in heavy metal contamination in water and sediments of river Sabarmati and Kharicut canal at Ahmedabad, Gujarat. Environ Monit Assess 185:359–368
Lohani MB, Singh A, Rupainwar DC, Dhar DN (2008) Seasonal variations of heavy metal contamination in river Gomti of Lukhnow city region. Environ Monit Assess 147:253–263
Murugan K, Prabhakaran P, Al-Sohaibani S, Sekar K (2012) Identification of source of faecal pollution of Tirumanimuttar River, Tamilnadu, India using microbial source tracking. Environ Monit Assess 184:6001–6012
Osman AGM, Kloas W (2010) Water quality and heavy metal monitoring in water, sediments, and tissues of the African catfish Clarias gariepinus (Burchell, 1822) from the river Nile, Egypt. J Environ Prot 1:389–400
Qishlaqi A, Moore F, Forghani G (2008) Impact of untreated wastewater irrigation on soils and crops in Shiraz sub urban area, SW Iran. Environ Monit Assess 141:257–273
Prasanna MV, Chidambaram S, Shahul Hameed A, Srinivasamoorthy K (2010) Study of evaluation of groundwater in Gadilam basin using hydrogeochemical and isotope data. Environ Monit Assess 168:63–90
Prasanna MV, Praveena SM, Chidambaram S, Nagarajan R, Elayaraja A (2012) Evaluation of water quality pollution indices for heavy metal contamination monitoring: a case study from Curtin Lake, Miri City, East Malaysia. Environ Earth Sci 67:1987–2001
Rajaram R, Srinivasan M, Rajasegar M (2005) Seasonal distribution of physico-chemical parameters in effluent discharge area of Uppanar estuary, Cuddalore, South-east coast of India. J Environ Biol 26:291–297
Rajaram R, Sumitha Banu J, Mathivanan K (2013) Biosorption of Cu (II) ions by indigenous copper-resistant bacteria isolated from polluted coastal environment. Toxicol Environ Chem 95(4):590–604
Rajasegar M (2003) Physico-chemical characteristics of the Vellar estuary in relation to shrimp farming. J Environ Biol 24:95–101
Ramelow GJ, Biven SL, Zhang Y, Beck J, Young JC, Callahan JD, Marcon MF (1992) The identification of point sources of heavy metals in industrially impacted water way by periphyton and surface sediment monitoring. Water Air Soil Pollut 65:157–190
Sankar R, Ramkumar L, Rajkumar M, Sun J, Ananthan G (2010) Seasonal variations in physico-chemical parameters and heavy metals in water and sediments of Uppanar estuary, Nagapattinam, India. J Environ Biol 31(5):681–686
Saravanakumar A, Rajkumar M, Sesh Serebiah J, Thivakaran GA (2008) Seasonal variations in physico-chemical characteristics of water, sediment and soil texture in arid zone mangroves of Kachchh-Gujarat. J Environ Biol 29:725–732
Satpathy KK, Mohanty AK, Natesan U, Prasad MVR, Sarkar SK (2010) Seasonal variation in physicochemical properties of coastal waters of Kalpakkam, east coast of India with special emphasis on nutrients. Environ Monit Assess 164:153–171
Satyanarayanan D, Prabhakara Murthy PVS, Sarma VV (1990) Distribution of particulate trace metals in the Western Bay of Bengal. Mahasagar Bull Natl Inst Oceanogr 23:103–115
Singare PU, Mishra RM, Trivedi MP (2012) Sediment contamination due to toxic heavy metals in Mithi River of Mumbai. Adv Anal Chem 2(3):14–24
Soundarapandian P, Premkumar T, Dinakaran GK (2009) Studies on the physico-chemical characteristics and nutrients in the Uppanar estuary of Cuddalore, South East coast of India. Curr Res J Biol Sci 1(3):102–105
Sridhar R, Thangaradjou T, Senthil Kumar S, Kannan L (2006) Water quality and phytoplankton characteristics in the Palk Bay, southeast coast of India. J Environ Biol 27:561–566
Tabari S, Saravi SSS, Bandany GA, Dehghan A, Shokrzadeh M (2010) Heavy metals (Zn, Pb, Cd and Cr) in fish, water and sediments sampled form Southern Caspian Sea, Iran. Toxicol Ind Health 26(10):649–656
Unnikrishnan P, Nair SM (2004) Partitioning of trace metals between dissolved and particulate phases in a typical backwater system of Kerala, India. Int J Environ Stud 61(6):659–676
Wang XL, Lu YL, Han JY, He GZ, Wang TY (2007) Identification of anthropogenic influences on water quality of rivers in Taihu watershed. J Environ Sci 19:475–481
WHO (2004) Guidelines for drinking water quality, 3rd edn. World Health Organization, Geneva, p 515
Zhou Q, Zhang J, Fu J, Shi J, Jiang G (2008) Biomonitoring: an appealing tool for assessment of metal pollution in the aquatic ecosystem. Anal Chim Acta 606:135–150
Acknowledgments
Authors are thankful to the authorities of Bharathidasan University for the infrastructure facilities and acknowledge the University Grant Commission (UGC), Government of India for providing the financial support in carrying out this work (Ref. No. F. No. 36-55/2008 (SR) Dated 24-03-2009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mathivanan, K., Rajaram, R. Anthropogenic influences on toxic metals in water and sediment samples collected from industrially polluted Cuddalore coast, Southeast coast of India. Environ Earth Sci 72, 997–1010 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-3017-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-3017-4