Abstract
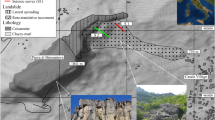
Electrical resistivity tomography (ERT), single-point-resistance logging with time-lapse, and geological and groundwater level data, are utilized to determine the mechanism of, and a hydrogeological model of, the Gangxianlane landslide in the west-central part of Taiwan. The rock surface and geometry of the colluviums were found by integrating ERT and borehole data. The iso-resistivity line in the bedrock broadly followed the bedding plane, indicating that the contribution of lithology to resistivity exceeds that of groundwater. The results of single-point-resistance logging with time-lapse and borehole data reveal that the bedrock has low permeability, which is associated with poorly developed joints and fractures. The fine grain content part (including the clayey layer), almost parallel to the bedding plane of the bedrock and between the colluvium and the bedrock in the upper part of the landslide, served as the slip surface and is believed to have been recently produced. It can block and retain water in the colluviums. Accordingly, this slip surface has the potential to re-slip in the future. Another slope failure involved rock collapse by a well-developed open release joint close to the Huoshaoping Terrace. It is also related to groundwater flow over a large gradient from the Huoshaoping Terrace. It is a key to determining whether this landslide will expand in the future.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bauer P, Supper R, Zimmermann S, Kinzelbach W (2006) Geoelectrical imaging of groundwater salinization in the Okavango Delta. Botswana Journal of Applied Geophysics 60:126–141
Buselli G, Lu K (2001) Groundwater contamination monitoring with multichannel electrical and electromagnetic methods. Journal of Applied Geophysics 48:11–23
Cassiani G, Bruno V, Villa A, Fusi N, Binley AM (2006) A saline trace test monitored via time-lapse surface electrical resistivity tomography. Journal of Applied Geophysics 59:244–259
Drahor MG, Göktürkler G, Berge MA, Özgür Kurtulmuş T (2006) Application of electrical resistivity tomography technique for investigation of landslides: a case from Turkey. Env Geol 50:147–155
Franco R, Biella G, Tosi L, Teatini P, Lozej A, Chiozzotto B, Giada M, Rizzetto F, Claude C, Mayer A, Bassan V, Gasparetto-Stori G (2009) Monitoring the saltwater intrusion by time lapse electrical resistivity tomography: The Chioggia test site (Venice Lagoon, Italy). Journal of Applied Geophysics 69:117–130
Frohlich RK, Barosh PJ, Boving T (2008) Investigating changes of electrical characteristics of the saturated zone affected by hazardous organic waste. Journal of Applied Geophysics 64:25–36
Griffiths DH, Barker RD (1993) Two-dimensional resistivity imaging and modelling in areas of complex geology. Journal of Applied Geophysics 29:211–226
Helmclark CM, Rodgers DW, Smith RP (2004) Borehole geophysical techniques to define stratigraphy, alteration and aquifers in basalt. Journal of Applied Geophysics 55:3–38
Jongmans D, Bièvre G, Renalier F, Schwartz S, Beaurez N, Orengo Y (2009) Geophysical investigation of a large landslide in glaciolacustrine clays in the Trièves area (French Alps). Eng Geol 109:45–56
Josef VD, Miroslav K, Martin P (2009) Well logging methods in groundwater surveys of complicated aquifer systems: Bohemian Cretaceous Basin. Env Geol 57:1021–1034
Lapenna V, Lorenzo P, Perrone A, Piscitelli S, Rizzo E, Sdao F (2004) 2D electrical resistivity imaging of some complex landslides in the Lucanian Apennine chain, sourthern Italy. Geophysics 70:B11–B18
Lee JF (2000) Explanatory text of the geological map of Taiwan, sheet 18: Tungshih. Centr Geol Surv, Taipei, Taiwan
Lee CC, Yang CH, Liu HC, Wen KL, Wang ZB, Chen YJ (2008) A Study of the hydrogeological environment of the lishan landslide area using resistivity image profiling and borehole data. Eng Geol 98:115–125
Lile OB, Morris M, Rønning JS (1997) Estimating groundwater flow velocity from changes in contact resistance during a saltwater tracer experiment. Journal of Applied Geophysics 38:105–114
Loke MH (2001) Tutorial: 2-D and 3-D electrical imaging surveys. http://www.geoelectrical.com
Loke MH, Barker RD (1996) Rapid least-squares inversion of apparent resistivity pseudosections by a quasi-Newton method. Geophys Prospect 44:499–524
Marescot L, Monnet R, Chapellier D (2008) Resistivity and induced polarization surveys for slope instability studies in the Swiss Alps. Eng Geol 98:18–28
McCann DM, Forster A (1990) Reconnaissance geophysical methods in landslide investigations. Eng Geol 29:59–78
Mota R, Monteiro Santos FA, Mateus A, Marques FO, Goncalves MA, Figueiras J, Amaral H (2004) Granite fracturing and incipient pollution beneath a recent landfill facility as detected by geoelectrical surveys. Journal of Applied Geophysics 57:11–22
Paillet FL (1993) Using borehole geophysics and cross-borehole flow testing to define hydraulic connections between fracture zones in bedrock. Journal of Applied Geophysics 30:261–279
Perrone A, Iannuzzi A, Lapenna V, Lorenzo P, Piscitelli S, Rizzo E, Sdao F (2004) High-resolution electrical imaging of the Varco d’, Izzo earthflow (sourthern Italy). Journal of Applied Geophysics 56:17–29
Perrone A, Vassallo R, Lapenna V, Di Maio C (2008) Pore water pressures and slope stability: a joint geophysical and geotechnical analysis. Journal of Geophysics Engineering 5:323–337
Sjödahl P, Dahlin T, Johansson S, Loke MH (2008) Resistivity monitoring for leakage and internal erosion detection at Hällby embankment dam. Journal of Applied Geophysics 65:155–164
Šumanovac F (2006) Mapping of thin sandy aquifers by using high resolution reflection seismics and 2-D electrical tomography. Journal of Applied Geophysics 58:144–157
Šumanovac F, Weisser M (2001) Evaluation of resistivity and seismic methods for hydrogeological mapping in karst terrains. Journal of Applied Geophysics 47:13–28
Suzuki K, Higashi S (2001) Groundwater flow after heavy rain in landslide-slope area from 2-D inversion of resistivity monitoring data. Geophysics 66:733–743
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Soil and Water Conservation Bureau of the Republic of China, Taiwan, for financially supporting this research under Contract No. SWCB-98-105.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, CC., Zeng, LS., Hsieh, CH. et al. Determination of mechanisms and hydrogeological environments of Gangxianlane landslides using geoelectrical and geological data in central Taiwan. Environ Earth Sci 66, 1641–1651 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-1522-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-1522-5