Abstract
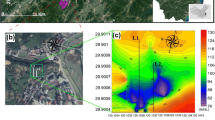
The dynamic monitoring of landslides in engineering geology has focused on the correlation among landslide stability, rainwater infiltration, and subsurface hydrogeology. However, the understanding of this complicated correlation is still poor and inadequate. Thus, in this study, we investigated a typical landslide in southwestern China via time-lapse electrical resistivity tomography (TLERT) in November 2013 and August 2014. We studied landslide mechanisms based on the spatiotemporal characteristics of surface water infiltration and flow within the landslide body. Combined with borehole data, inverted resistivity models accurately defined the interface between Quaternary sediments and bedrock. Preferential flow pathways attributed to fracture zones and fissures were also delineated. In addition, we found that surface water permeates through these pathways into the slipping mass and drains away as fissure water in the fractured bedrock, probably causing the weakly weathered layer to gradually soften and erode, eventually leading to a landslide. Clearly, TLERT dynamic monitoring can provide precursory information of critical sliding and can be used in landslide stability analysis and prediction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benoit, L., Briole, P., Martin, O., Thom, C., Malet, J. P., and Ulrich, P., 2015, Monitoring landslide displacements with the Geocube wireless network of low-cost GPS: Engineering Geology, 195, 111–121.
Bièvre, G., Jongmans, D., Winiarski, T., and Zumbo, V., 2012, Application of geophysical measurements for assessing the role of fissures in water infiltration within a clay landslide (Trièves area, French Alps): Hydrological Processes, 26(14), 2128–2142.
Binley, A., Cassiani, G., and Deiana, R., 2010, Hydrogeophysics: opportunities and challenges: Bollettino Di Geofisica Teorica Ed Applicata, 51(4), 267–284.
Binley, A., Hubbard, S., Huisman, J., Revil, A., Robinson, D., Singha, K., and Slater, L. D., 2015, The emergence of hydrogeophysics for improved understanding of subsurface processes over multiple scales: Water Resources Research, 51(6), 3837–3866.
Bruno, F., and Martillier, F., 2000, Test Of High-Resolution Seismic Reflection And Other Geophysical Techniques On The Boup Landslide In The Swiss Alps: Surveys in Geophysics, 21(4), 335–350.
Cassiani, G., Godio, A., Stocco, S., Villa, A., Deiana, R., Frattini, P., and Rossi, M., 2009, Monitoring the hydrologic behaviour of a mountain slope via timelapse electrical resistivity tomography: Near Surface Geophysics, 7(5–6), 475–486.
Chambers, J. E., Gunn, D. A., Wilkinson, P. B., Meldrum, P. I., Haslam, E., Holyoake, S., Kirkham, M., Kuras, O., Merritt, A., and Wragg, J., 2014, 4D electrical resistivity tomography monitoring of soil moisture dynamics in an operational railway embankment: Near Surface Geophysics, 12(1), 61–72.
Chambers, J. E., Wilkinson, P. B., Kuras, O., Ford, J. R., Gunn, D. A., Meldrum, P. I., Pennington, C. V. L., Weller, A. L., Hobbs, P. R. N., and Ogilvy, R. D., 2011, Three-dimensional geophysical anatomy of an active landslide in Lias Group mudrocks, Cleveland Basin, UK: Geomorphology, 125(4), 472–484.
Chu, R., Ni, S., Hu, X., Bao, F., Lu, P., and Li, Z., 2014, Joint Study of the Xishancun Landslide, Sichuan, Using Seismological and Electromagnetic Methods: AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts, 1, 08.
Dahlin, T., and Zhou, B., 2004, A numerical comparison of 2D resistivity imaging with 10 electrode arrays: Geophysical Prospecting, 52(5), 379–398.
de Franco, R., et al., 2009, Monitoring the saltwater intrusion by time lapse electrical resistivity tomography: The Chioggia test site (Venice Lagoon, Italy): Journal of Applied Geophysics, 69(3–4), 117–130.
Gasperikova, E., Hubbard, S. S., Watson, D. B., Baker, G. S., Peterson, J. E., Kowalsky, M. B., Smith, M., and Brooks, S., 2012, Long-term electrical resistivity monitoring of recharge-induced contaminant plume behavior: Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 142–143C(6), 33–49.
Gunther, T., Rucker, C., and Spitzer, K., 2006, Threedimensional modelling and inversion of dc resistivity data incorporating topography — II. Inversion: Geophysical Journal International, 166(2), 506–517.
Guo, X. J., Huang, X. Y., and Jia, Y. G., 2005, Forward modeling of different types of landslides with multielectrode electric method: Applied Geophysics, 2(1), 14–20.
Hayley, K., Bentley, L. R., and Gharibi, M., 2009, Timelapse electrical resistivity monitoring of salt-affected soil and groundwater: Water Resources Research, 45(7), 171–183.
Huang, R. Q., and Li, W. L., 2009, Analysis of the geohazards triggered by the 12 May 2008 Wenchuan Earthquake, China: Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 68(3), 363–371.
Huang, R. Q., Zhao, J., Ju, N., Li, G., Lee, M. L., and Li, Y., 2013, Analysis of an anti-dip landslide triggered by the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake in China: Natural Hazards, 68(2), 1021–1039.
Hubner, R., Heller, K., Gunther, T., and Kleber, A., 2015, Monitoring hillslope moisture dynamics with surface ERT for enhancing spatial significance of hydrometric point measurements: Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 19(1), 225–240.
Johnson, T. C., Slater, L. D., Ntarlagiannis, D., Day-Lewis, F. D., and Elwaseif, M., 2012, Monitoring groundwatersurface water interaction using time-series and timefrequency analysis of transient three-dimensional electrical resistivity changes: Water Resources Research, 48(7), W07506.
Karaoulis, M., Tsourlos, P., Kim, J. H., and Revil, A., 2014, 4D time-lapse ERT inversion: introducing combined time and space constraints: Near Surface Geophysics, 12(1), 25–34.
Kim, J. H., Supper, R., Tsourlos, P., and Yi, M. J., 2013, Four-dimensional inversion of resistivity monitoring data through Lp norm minimizations: Geophysical Journal International, 195(3), 1640–1656.
Kim, J. H., Yi, M. J., Park, S. G., and Kim, J. G., 2009, 4-D inversion of DC resistivity monitoring data acquired over a dynamically changing earth model: Journal of Applied Geophysics, 68(4), 522–532.
Kuras, O., Pritchard, J. D., Meldrum, P. I., Chambers, J. E., Wilkinson, P. B., Ogilvy, R. D., and Wealthall, G. P., 2009, Monitoring hydraulic processes with automated time-lapse electrical resistivity tomography (ALERT): Comptes Rendus Geoscience, 341(10–11), 868–885.
LaBrecque, D. J., and Yang, X. J., 2001, Difference Inversion of ERT Data: a Fast Inversion Method for 3-D in Situ Monitoring: Journal of Environment and Engineering Geophysics, 6(2), 83–89.
Lapenna, V., Lorenzo, P., Perrone, A., Piscitelli, S., Rizzo, E., and Sdao, F., 2005, 2D electrical resistivity imaging of some complex landslides in the Lucanian Apennine chain, southern Italy: Geophysics, 70(3), B11–B18.
Lebourg, T., Binet, S., Tric, E., Jomard, H., and El Bedoui, S., 2005, Geophysical survey to estimate the 3D sliding surface and the 4D evolution of the water pressure on part of a deep seated landslide: Terra Nova, 17(5), 399–406.
Lebourg, T., Hernandez, M., Zerathe, S., El Bedoui, S., Jomard, H., and Fresia, B., 2010, Landslides triggered factors analysed by time lapse electrical survey and multidimensional statistical approach: Engineering Geology, 114(3–4), 238–250.
Lee, C. C., Zeng, L. S., Hsieh, C. H., Yu, C. Y., and Hsieh, S. H., 2012, Determination of mechanisms and hydrogeological environments of Gangxianlane landslides using geoelectrical and geological data in central Taiwan: Environmental Earth Sciences, 66(6), 1641–1651.
Li, S. C., Nie, L. C., Liu, B., Song, J., Liu, Z. Y., Su, M. X., and Xu, L., 2014, 3D electrical resistivity inversion using prior spatial shape constraints: Applied Geophysics, 10(4), 361–372.
Liu, C., Li, W., Wu, H., Lu, P., Sang, K., Sun, W., Chen, W., Hong, Y., and Li, R., 2013, Susceptibility evaluation and mapping of China’s landslides based on multi-source data: Natural Hazards, 69(3), 1477–1495.
Loke, M. H., 2014, RES2DINVx64 ver 4.03 Rapid 2-D Resistivity & IP inversion using the least-squares method: Software Manual.
Loke, M. H., Chambers, J. E., Rucker, D. F., Kuras, O., and Wilkinson, P. B., 2013, Recent developments in the direct-current geoelectrical imaging method: Journal of Applied Geophysics, 95(8), 135–156.
Loke, M. H., Dahlin, T., and Rucker, D. F., 2014, Smoothness-constrained time-lapse inversion of data from 3D resistivity surveys: Near Surface Geophysics, 12(2007), 5–24.
Martorana, R., Lombardo, L., Messina, N., and Luzio, D., 2014, Integrated geophysical survey for 3D modelling of a coastal aquifer polluted by seawater: Near Surface Geophysics, 12(1), 45–59.
Miller, C. R., Routh, P. S., Brosten, T. R., and McNamara, J. P., 2008, Application of time-lapse ERT imaging to watershed characterization: Geophysics, 73(3), G7–G17.
Niesner, E., 2010, Subsurface resistivity changes and triggering influences detected by continuous geoelectric monitoring: The Leading Edge, 29(8), 952–955.
Oldenborger, G. A., Knoll, M. D., Routh, P. S., and LaBrecque, D. J., 2007, Time-lapse ERT monitoring of an injection/withdrawal experiment in a shallow unconfined aquifer: Geophysics, 72(4), F177–F187.
Oldenburg, D. W., and Li, Y. G., 1999, Estimating depth of investigation in dc resistivity and IP surveys: Geophysics, 64(2), 403–416.
Perrone, A., Iannuzzi, A., Lapenna, V., Lorenzo, P., Piscitelli, S., Rizzo, E., and Sdao, F., 2004, Highresolution electrical imaging of the Varco d’Izzo earthflow (southern Italy): Journal of Applied Geophysics, 56(1), 17–29.
Perrone, A., Lapenna, V., and Piscitelli, S., 2014, Electrical resistivity tomography technique for landslide investigation: A review: Earth-Science Reviews, 135(4), 65–82.
Qi, S., Xu, Q., Lan, H., Zhang, B., and Liu, J., 2010, Spatial distribution analysis of landslides triggered by 2008.5. 12 Wenchuan Earthquake, China: Engineering Geology, 116(1), 95–108.
Revil, A., Skold, M., Karaoulis, M., Schmutz, M., Hubbard, S. S., Mehlhorn, T. L., and Watson, D. B., 2013, Hydrogeophysical investigations of the former S-3 ponds contaminant plumes, Oak Ridge Integrated Field Research Challenge site, Tennessee: Geophysics, 78(4), En29–En41.
Rucker, C., Gunther, T., and Spitzer, K., 2006, Threedimensional modelling and inversion of dc resistivity data incorporating topography — I. Modelling: Geophysical Journal International, 166(2), 495–505.
Shan, C., Bastani, M., Malehmir, A., Persson, L., and Engdahl, M., 2014, Integrated 2d modeling and interpretation of geophysical and geotechnical data to delineate quick clays at a landslide site in southwest Sweden: Geophysics, 79(4), EN61–EN75.
Su, L. J., Xu, X. Q., Liao, H. J., and Geng, X. Y., 2015, Shear wave velocity analysis of a deep seated gravel landslide structure using the microtremor survey method: Proceedings of the International Symposium on Geohazards and Geomechanics (ISGG), Warwick, ENGLAND, 012026.
Supper, R., Römer, A., Jochum, B., Bieber, G., and Jaritz, W., 2008, A complex geo-scientific strategy for landslide hazard mitigation – from airborne mapping to ground monitoring: Adv. Geosci., 14(14), 195–200.
Thomsen, R., Sondergaard, V. H., and Sorensen, K. I., 2004, Hydrogeological mapping as a basis for establishing site-specific groundwater protection zones in Denmark: Hydrogeology Journal, 12(5), 550–562.
Travelletti, J., Sailhac, P., Malet, J. P., Grandjean, G., and Ponton, J., 2012, Hydrological response of weathered clay-shale slopes: water infiltration monitoring with timelapse electrical resistivity tomography: Hydrological Processes, 26(14), 2106–2119.
Wilkinson, P. B., Chambers, J. E., Meldrum, P. I., Gunn, D. A., Ogilvy, R. D., and Kuras, O., 2010, Predicting the movements of permanently installed electrodes on an active landslide using time-lapse geoelectrical resistivity data only: Geophysical Journal International, 183(2), 543–556.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This study was funded by the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program) (No. 2013CB733203) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41474055).
Xu Dong is a Ph.D. student at the Institute of Geophysics and Geomatics, China University of Geosciences (Wuhan). He received his B.S. from East China University of Technology in 2013. His research interests are electrical resistivity tomography and hydrogeophysics.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, D., Hu, XY., Shan, CL. et al. Landslide monitoring in southwestern China via time-lapse electrical resistivity tomography. Appl. Geophys. 13, 1–12 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11770-016-0543-3
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11770-016-0543-3