Abstract
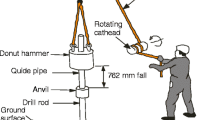
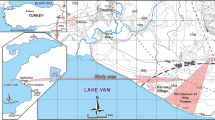
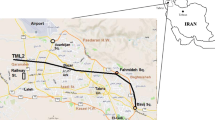
The Standard Penetration Test (SPT) is one of the most frequently applied tests during the geotechnical investigation of soils. Due to its usefulness, the development of empirical equations to predict mechanical and compressibility of soil parameters from the SPT blow count has been an attractive subject for geotechnical engineers and engineering geologists. The purpose of this study is to perform regression analyses between the SPT blow counts and the pressuremeter test parameters obtained from a geotechnical investigation performed in a Mersin (Turkey) city sewerage project. In accordance with this purpose, new empirical equations between pressuremeter modulus (E M) and corrected SPT blow counts (N 60) and between limit pressure (P L) and corrected SPT blow counts (N 60) are developed in the study. When developing the empirical equations, in addition to the SPT blow counts, the role of moisture content and the plasticity index of soils on the pressuremeter parameters are also assessed. A series of simple and nonlinear multiple regression analyses are performed. As a result of the analyses, several empirical equations are developed. It is shown that the empirical equations between N 60 and E M, and N 60 and P L developed in this study are statistically acceptable. An assessment of the prediction performances of some existing empirical equations, depending on the new data, is also performed in the study. However, the prediction equations proposed in this study and the previous studies are developed using a limited number of data. For this reason, a cross-check should be applied before using these empirical equations for design purposes.





















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akça N (2003) Correlation of SPT-CPT data from United Arab Emirates. Eng Geol 67:219–231
Alvarez Grima M, Babuska R (1999) Fuzzy model for the prediction of unconfined compressive strength of rock samples. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 36:339–349
APAGEO (2006) Menard Pressuremeter (G Type) operating instructions. 2006 edition
Apte MG, Price PN, Nero AV, Revzan K (1999) Predicting New Hampshire indoor radon concentrations from geologic information and other covariates. Env Geol 37:181–194
ASTM (American society for testing and materials) (1994) Annual book of ASTM Standards, Section 4, Construction, V. 0408 Soil and Rock; Building Stones. ASTM Publication, Pennsylvania, p 978
Baquelin F, Jezequel JF, Shields DH (1978) The pressuremeter and foundation engineering. Trans Tech Publications, Clausthal-Zellerfeld
Benavente D, Cueto N, Martinez–Martinez J, García Del Cura MA, Cañaveras JC (2007) The influence of petrophysical properties on the salt weathering of porous building rocks. Environ Geol 52:197–206
Bowles JE (1988) Foundation analysis and design, 4th edn. McGraw-Hill International Editions, Tokyo
Bozbey İ, Togrol E (2010) Correlation of standard penetration test and pressuremeter data: a case study from Istanbul, Turkey. Bull Eng Geol Environ 69:505–515
British Standard 1377 (1975) Method of test for soils for civil engineering purposes. British Standard Institution, London
Cassan M (1968–1969) “Les essays in situ en mècanique des sols”- Construction, No.10, Octobre ’68, pp 337–347; No. 5, Mai ’69, pp 178–187; No. 7–8, Julliet-Aoǔt ’69, pp 244–256
Chen-Chang L, Cheng-Haw L, Hsin-Fu Y, Hung-I L (2011) Modeling spatial fracture intensity as a control on flow in fractured rock. Environ Earth Sci 63:1199–1211
Chiang YC, Ho YM, (1980) Pressuremeter method for foundation design in Hong Hong. In: International proceedings of sixth Southeast Asian conference on soil engineering, vol 1, pp 31–42
Clarke BG (1995) Pressuremeters in geotechnical design (1. Edition). Chapman and Hall, London
Craig RF (1987) Soil mechanics. Department of Civil Engineering, 4th edn. University of Dundee, Longman, England
Dagdelenler G, Sezer EA, Gokceoglu C (2011) Some non-linear models to predict the weathering degrees of a granitic rock from physical and mechanical parameters. Expert Syst Appl 38:7476–7485
ENV (Eurocode 7) (1997) Geotechnical design-Part 3: design assisted by field testing
Finol J, Guo YK, Jing XD (2001) A rule based fuzzy model for the prediction of prediction of petrophysical rock parameters. J Petr Sci Eng 29:97–113
Gokceoglu C (2002) A fuzzy triangular chart to predict the uniaxial compressive strength of the Ankara agglomerates from their petrographic composition. Eng Geol 66(1–2):39–51
Gokceoglu C, Zorlu K (2004) A fuzzy model to predict the uniaxial compressive strength and the modulus of elasticity of a problematic rock. Eng Appl Artif Intell 17(1):61–72
Gokceoglu C, Sonmez H, Kayabasi A (2003) Predicting deformation moduli of rock masses. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 41(2):337–341
Gokceoglu C, Sonmez H, Zorlu K (2009) Estimating the uniaxial compressive strength of some clay bearing rocks selected from Turkey by nonlinear multivariable regression and rule-based fuzzy models. Expert Syst 26(2):176–190
Gunaydin O (2009) Estimation of soil compaction parameters by using statistical analyses and artificial neural networks. Environ Geol 57:203–215
Hobbs N-B, Dixon J-C (1969) In situ testing for Bridge Foundations in the Devonian Marl. In: Proceedings of the Conference on in situ investigations in soils and rocks, British Geotechnical Society, London, May 13–15, pp 31–38
Iphar M, Yavuz M, Ak H (2008) Prediction of ground vibrations resulting from the blasting operations in an open-pit mine by adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system. Env Geol 56:97–107
Kayabasi A, Gokceoglu C, Ercanoglu M (2003) Estimating the deformation modulus of rock masses:a comparative study. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 40(1):55–63
Lee KM, Rowe RK (1989) Deformation caused by surface loading and tunneling: the role of elastic anisotropy. Geotechnique 39(1):125–140
Lee MJ, Hong SJ, Choi YM, Lee W (2010) Evaluation of deformation modulus of cemented sand using CPT and DMT. Eng Geol 115:28–35
Leischner W (1966) Die bautechnische Baugrundbeurteilung mittels horizontaler Belastungsversuche im Bohrloch nach dem Koglerverfahren, Der Bauingenier, 12
Leonards GA (1962) Foundation Engineering. McGraw Hill, Tokyo, p 113
Means RE, Parcher JW (1963) Physical Properties of Soils. In: Charls E (ed) Merril Publ Comp, Columbia, p 467
Mitchell JK (1975) Fundamentals of soil behaviour. Wiley, Newyork, p 422
Seed HB, Woodward RJ, Lundgren R (1964) Fundamental Aspects of the Atterberg Limits. J Soil Mech Found Div, ASCE, 90(SM6):75–105
Sharma PK, Singh TN (2008) A correlation between P-wave velocity, impact strength index, slake durability index and uniaxial strength index. Bull Eng Geol Environ 67:17–22
Shields DH, Bauer GH (1975) Determination of the modulus of deformation of sensitive clay using laboratory and in situ tests. In: Proceedings of the ASCE Special Conference on in situ measurement of soil properties, Raleigh, vol 1, pp 395–421
Sivrikaya O (2008) Models of compacted fine-grained soils used as mineral liner for solid waste. Environ Geol 53:1585–1595
Skempton AW (1953) The colloidal activity of clays. In: 3rd International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering, Switzerland, vol 1, p 57
Sonmez H, Gokceoglu C, Nefeslioglu HA, Kayabasi A (2006) Estimation of rock modulus. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 43(2):224–235
SPSS (2002) Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (v.11.5). SPSS Inc, Chicago
Terzaghi K, Peck RB (1968) Foundation design and construction. Pitman, London
Türk Standartları Enstitüsü (TSE) (1988) In situ measurement methods of the properties of foundation soils in civil engineering (in Türkish)
Türk Standartları Enstitüsü (TSE) (1997) Jeoteknik Tasarım Bölüm 3, Arazi Deneyleri Yardımıyla Tasarım (TS ENV 1997-3, Eurocode 7), (in Turkish)
Uddameri V (2007) Using statistical and artificial neural network models to forecast potentiometric levels at a deep well in South Texas. Environ Geol 51:885–895
USBR (United States Dep. Int. Bur. Reclamation) (1974) Earth manual. A Water Resources Technical Publication, Denver, p 810
Waschkowski E (1974) “Pénétrométrétres dynamiques”- Comtes rendus des Journées des Laboratoires des Ponts et Chausssées. Saint-Brieue. 19-21 Novembre, pp 1–37. Not Published
Waschkowski E (1976) “Comparaisons entre les résultats des essais pressiométriques et le SPT”- Rapport de Recherche du Laboratorie Régional des Ponts et Chaussées de Blois, F.A.E.R. 1.05.23.5, Juin. Not Published
Yagiz S, Gokceoglu C (2010) Application of fuzzy inference system and nonlinear regression models for predicting rock brittleness. Expert Syst Appl 37:2265–2272
Yagiz S, Akyol E, Sen G (2008) Relationship between the standart penetration test and the pressuremeter test on sandy silty clays: a case study from Denizli. Bull Eng Geol Environ 67:405–410
Yagiz S, Gokceoglu C, Sezer E, Iplikci S (2009) Application of two non-linear prediction tools to the estimation of tunnel boring machine performance. Eng Appl Artif Intell 22:818–824
Zorlu K, Gokceoglu C, Ocakoglu F, Nefeslioglu HA, Acikalin S (2008) Prediction of uniaxial compressive strength of sandstones using petrography-based models. Eng Geol 96(3/4):141–158
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kayabasi, A. Prediction of pressuremeter modulus and limit pressure of clayey soils by simple and non-linear multiple regression techniques: a case study from Mersin, Turkey. Environ Earth Sci 66, 2171–2183 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-1439-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-1439-4