Abstract
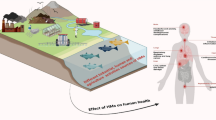
The article presents the geochemical and biogeochemical characteristics of heavy metal elements within the soil–plant system in the Hetai mine-abandoned areas and wasteland, China. The cytogenetic toxic effects of gold mine wastelands environment on the chromosome and micronucleus were analyzed by genetic methods. The results showed that abundances of Au and Au-associated heavy metal elements such as Cu, As, Cd, Pb and Hg in soils, plants and the pigments in those abandoned mine areas were much higher than those in the background region. The cell structures of the plants in the abandoned mine areas were anomalous and aberrant, and there were many nano-metal particles diffused in the cells. Moreover, the heavy metal elements in those abandoned mine areas had entered the ultrastructure and caused toxicities to the organism.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ansari MI, Mali A (2009) Genotoxicity of agricultural soils in the vicinity of industrial area. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 673(2):124–132
Boswell C, Sharma NC, Sahi SV (2002) Copper tolerance and accumulation potential of Chalamydomonas reinhardtii. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 69:546–553
Brooks RR, Dunn CE, Hall GEM (1995) Biological system in mineral exploration and processing. Eills Horwood Limited, Hemel Hempstead, p 538
Burgeot T, His E, Galgani F (1995) The micronucleus assay in Crassostrea gigas for the detection of seawater genotoxicity. Mutat Res 342:125–140
Cabral JP (2003) Copper toxicity to five Parmelia lichens in vitro. Environ Exp Bot 49(3):237–250
Carbonell-Barrachina AA, Porthouse JD, Mulbah CK et al (1999) Metal solubility in phosphogypsum-amended sediment under controlled pH and redox conditions. J Environ Qual 28:232–324
Carbonell-Barrachina AA, Rocamora A, García-Gomis C et al (2004) Arsenic and zinc biogeochemistry in pyrite mine waste from the Aznalcóllar environmental disaster. Geoderma 122:195–203
Carreras HA, Pignata ML (2007) Effects of the heavy metals Cu2+, Ni2+, Pb2+, and Zn2+ on some physiological parameters of the lichen Usnea amblyoclada. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 67(1):59–66
Caspi V, Droppa M, Horváth G et al (1999) The effect of copper on chlorophyll organization during greening of barley leaves. Photosynth Res 62(2):165–174
Chen Y, Wang C, Wang Z et al (2004) Assessment of the contamination and genotoxicity of soil irrigated with wastewater. Plant Soil 261:189–196
Chettri MK, Cook CM, Vardaka E et al (1998) The effect of Cu, Zn and Pb on the chlorophyll content of the lichens Cladonia convoluta and Cladonia rangiformis. Environ Exp Bot 39(1):1–10
Ciftci E, Kolayli H, Tokel S (2005) Lead–arsenic soil geochemical study as an exploration guide over the Killik volcanogenic massive sulfide deposit, Northeastern Turkey. J Geochem Explor 86(1):49–59
Dovgaliuk AL, Kaliniiak TB, Blium LAB (2001) Assessment of phyto- and cytotoxic effects of heavy metals and aluminum compounds using onion apical meristem. Tsitol Genet 35:3–9
Duan J, He S, Zhou C et al (1992) On the structural characteristics of Hetai gold deposit Guangdong and the gold-deposit model of shear zone type. J Cent South Inst Mineral Metall 23:245–253 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Dudka S, Adriano DC (1997) Environmental impacts of metal ore mining and processing, a review. J Environ Qual 26:590–602
Eom IC, Rast C, Veber AM et al (2007) Ecotoxicity of a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH)-contaminated soil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 67:190–205
Fernandez MD, Cagigal E, Vega MM et al (2005) Ecological risk assessment of contaminated soils through direct toxicity assessment. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 62:174–184
Hajjouji HE, Pinelli E, Guiresse M et al (2007) Assessment of the genotoxicity of olive mill waste water (OMWW) with the Vicia faba micronucleus test. Mutat Res 634:25–31
Kirsch-Volders M, Sofuni T, Aaderma M et al (2003) Report from the vitro micronucleus assay working group. Mutat Res 540(2):153–163
Li MS (2006) Ecological restoration of mineland with particular reference to the metalliferous mine wasteland in China, a review of research and practice. Sci Total Environ 357:38–53
Liu Y, Liu HC, Li XH (1996) Simultaneous and precise determination of 40 trace elements in rock samples using ICP-MS. Geochimica 25(6):552–558 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Manier N, Deram A, Curieux FL et al (2009) Comparison between new wild plant Trifolium repens and Vicia faba on their sensitivity in detecting the genotoxic potential of heavy metal solutions and heavy metal-contaminated soils. Water Air Soil Pollut 201:342–352
Marcato-Romain CE, Guiresse M, Cecchi M et al (2009) New direct contact approach to evaluate soil genotoxicity using the Vicia faba micronucleus test. Chemosphere 77(3):345–350
Marco AD, Boccardi P, Simone CD et al (1990) Induction of micronuclei in Vicia faba root tips treated in different soils with the herbicide alachlor. Mutat Res 241:1–6
Marinella F, Damià B (2003) Toxicity testing of wastewater and sewage sludge by biosensors, bioassays and chemical analysis. Trends Anal Chem 22:299–310
Navarro MC, Perez-Sirvent C, Martinez-Sanchez MJ et al (2008) Abandoned mine sites as a source of contamination by heavy metals, a case study in a semi-arid zone. J Geochem Explor 96:183–193
Patra M, Bhowmik N, Bandopadhyay B et al (2004) Comparison of mercury, lead and arsenic with respect to genotoxic effects on plant systems and the development of genetic tolerance. Environ Exp Bot 52:199–223
Pijut PM, Lineberger RD, Domir SC et al (1990) Ultra structure of cells of Ulmus americana cultured in vitro and exposed to the culture filtrate of Ceratocystis ulmi. Phytopathology 80(8):764–767
Rahman A, Hasegawa H, Rahfuzur MM et al (2007) Effect of arsenic on photosynthesis, growth and yield of five widely cultivated rice (Oryza sativa L.) varieties in Bangladesh. Chemosphere 67(6):1072–1079
Rizzoni M, Gustavino B, Ferrari C et al (1995) An integrated approach to the assessment of the environmental quality of the Tiber River in the urban area of Rome: a mutagenesis assay (micronucleus test) and an analysis of macrobenthic community structure. Sci Total Environ 162:127–137
Sheoran AS, Sheoran V (2006) Heavy metal removal mechanism of acid mine drainage in wetlands: a critical review. Miner Eng 19:105–116
Simkiss K, Taylor M, Mason AZ (1982) Metal detoxification and bioaccumulation in molluscs. Mar Biol Lett 3:187–201
Song C, Lei L, Cheng S (2004) Gold biogeochemical anomaly and aberrance effect of botanic cell tissue. Geochemica 33(2):191–196 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Song Y, Wilke BM, Song XY et al (2006) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and heavy metals (HMs) as well as their genotoxicity in soil after long-term wastewater irrigation. Chemosphere 65:1859–1868
Stobart AK, Griffiths WT, Ameen BI (1985) The effect of Cd2+ on the biosynthesis of chlorophyll in leaves of barley. Plant Physiol 63(3):293–298
Zhang G, Boulter CliveA et al (2001) Brittle origins for disseminated gold mineralization in mylonite: Gaocun Gold Deposit, Hetai Goldfield, Guangdong Province, South China. Econ Geol Bull Soc Econ Geol 96:49–59
Zhuang P, McBride MB, Xia H et al (2009) Health risk from heavy metals via consumption of food crops in the vicinity of Dabaoshan mine, South China. Sci Total Environ 407(5):1551–1561
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the Scientific Frontier Program for Young Talents of the South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. SQ200807) and the Open Fund of Key Laboratory of Marginal Sea Geology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. MSG200902). The authors would like to thank the two anonymous reviewers whose critical review and comments greatly helped to improve the quality of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miao, L., Ma, Y., Xu, R. et al. Geochemistry and genotoxicity of the heavy metals in mine-abandoned areas and wasteland in the Hetai goldfields, Guangdong Province, China. Environ Earth Sci 65, 1955–1964 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-1176-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-1176-8