Abstract
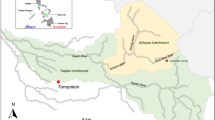
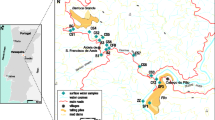
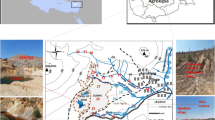
Public awareness of environmental health issues has increased significantly in recent years, creating the need for detailed scientific studies that can identify potential environmental problems. This paper reports the results of hydrogeochemical surveys carried out in Sardinia, an Italian region with a long mining history. When mining operations in Sardinia ceased, actions for limiting the potential adverse effects of mine closure on the water system were not undertaken. Drainages from flooded mines and seeps from mining residues left on the ground are the main mining-related sources of contamination in Sardinia. Due to the proximity of mining sites to water resources and land that is within reach of animals and humans, the major risks to human health are associated with the direct discharge of contaminated waters into the streams and soils located down-gradient of the abandoned mines. Results of hydrogeochemical surveys carried out under different seasonal conditions showed that the dispersion of toxic and harmful elements (As, Cd, Ni, Pb, Sb and Zn) increases during the rainy season, especially under high runoff conditions. These results should help regional and national authorities to address present environmental regulations, particularly those regarding the quality of water resources. Furthermore, the results might be useful elsewhere for planning remediation actions at abandoned mining sites. Lessons learned by past mining in Sardinia indicate that correct disposal and management of mining residues should be mandatory from the beginning of exploitation and processing at each active mine. This would allow reduction of the environmental risks as well as the cost of remediation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Biddau M (1978) Indagine chimica-idrologica sulle possibilità di utilizzazione delle acque edotte nel Sulcis-Iglesiente. La Programmazione in Sardegna 67/68:99–115. (in Italian)
Boni M (1994) Ores in southwestern Sardinia. In: Bechstädt T, Boni M (eds), Sedimentological, stratigraphical and ore deposits field guide of the autochthonous Cambro–Ordovician of southwestern Sardinia. Mem Descr Carta Geol It, Serv Geol Naz 48:155–184
Caboi R, Cidu R, Cristini A, Fanfani L, Massoli-Novelli R, Zuddas P (1993) The abandoned Pb-Zn mine of Ingurtosu, Sardinia (Italy). Engineering Geol 34:211–218
Caboi R, Cidu R, Cristini A, Fanfani L, Zuddas P (1995) Contaminazione di corpi idrici superficiali nell’area mineraria di Montevecchio (Sardegna). Quaderni Geol Appl, Pitagora Bologna 2:509–519 (in Italian)
Caboi R, Cidu R, Fanfani L, Zuddas P (1996) Abandoned mine sites: implications for water quality. In: Ciccu R (ed) Proceedings SWEMP-96, pp 797–805. DIGITA University of Cagliari, Italy
Caboi R, Cidu R, Fanfani L, Lattanzi P, Zuddas P (1999) Environmental mineralogy and geochemistry of the abandoned Pb–Zn Montevecchio-Ingurtosu mining district, Sardinia, Italy. Chron Rech Minière 534:21–28
Cidu R (2007) Influence of past mining on the quality of surface waters at Funtana Raminosa (Sardinia). Mine Water Environ 26:199–208
Cidu R, Biagini C, Fanfani L, La Ruffa G, Marras I (2001) Mine closure at Monteponi (Italy): effect of the cessation of dewatering on the quality of shallow groundwater. Appl Geochem 16:489–502
Cidu R, Biddau R, Spano T (2005) Temporal variations in water chemistry at abandoned underground mines hosted in a carbonate environment. Mine Water Environ 24:77–87
Cidu R, Caboi R, Biddau R, Petrini R, Slejko F, Flora O, Aiuppa A, Parello F, Valenza M (2008a) Caratterizzazione idrogeochimica ed isotopica e valutazione della qualità delle acque superficiali e sotterranee campionate nel Foglio 549 Muravera. In: Ottonello G (ed) GEOBASI. Pacini Editore, Pisa, pp 149–183 (in Italian)
Cidu R, Fanfani L, Frau F, Biddau R, Cabras R, Da Pelo S (2008b) The abandoned antimony-mines of SE Sardinia: impact on surface waters. Proceedings IMWA 2008, pp 127–130, Karlovy Vary, Czech Republic, 1–5 June 2008
Da Pelo S (1998) Mineralogia e geochimica ambientale di aree minerarie attive e dismesse. PhD Thesis, University of Cagliari, Italy, p 95 (in Italian)
Funedda A, Naitza S, Tocco S (2005) Caratteri giacimentologici e controlli strutturali nelle mineralizzazioni idrotermali tardo-erciniche ad As-Sb-W-Au del basamento metamorfico paleozoico della Sardegna sud-orientale. Resoconti Associazione Mineraria Sarda CX 25–46 (in Italian)
Gaillardet J, Viers J, Dupré B (2003) Trace elements in river waters. In: Drever JI (ed), Surface and ground water, weathering and soils. Treatise on Geochemistry (Holland HD, Turekian KK Eds), vol. 5. Elsevier–Pergamon, Oxford, pp 225–272
Gandy CJ, Younger PL (2007) Predicting groundwater rebound in the South Yorkshire Coalfield, UK. Mine Water Environ 26:70–78
Garavan C, Breen J, Moles R, O’Regan B (2008) A case study of the health impacts in an abandoned lead mining area, using children’s blood lead levels. Int J Mining Reclam Environ 22:265–284
Gilchrist S, Gates A, Szabo Z, Lamothe PJ (2009) Impact of AMD on water quality in critical watershed in the Hudson River drainage basin: Phillips Mine, Hudson Highlands, New York. Environ Geol 57:397–409
Gómez-Alvarez A, Meza-Figueroa D, Villalba-Atondo AI, Valenzuela-Garcia JL, Ramirez-Hernandez J, Almendariz-Tapia J (2009) Estimation of potential pollution from mine tailings in the San Pedro River (1993–2005), Mexico–US border. Environ Geol 57:1469–1479
Harrison J, Heijnis H, Caprarelli G (2003) Historical pollution variability from abandoned mine sites, Greater Blue Mountains World Heritage Area, New South Wales, Australia. Environ Geol 43:680–687
Kimball BA, Bianchi F, Walton-Day K, Runkel RL, Nannucci M, Salvadori A (2007) Quantification of changes in metal loading from storm runoff, Merse River (Tuscany, Italy). Mine Water Environ 26:209–216
Kruse NAS, Younger PL (2009) Sinks of iron and manganese in underground coal mine workings. Environ Geol 57:1893–1899
Loredo J, Álvarez R, Ordóñez A, Bros T (2008) Mineralogy and geochemistry of the Texeo Cu–Co mine site (NW Spain): screening tools for environmental assessment. Environ Geol 55:1299–1310
Marini L (2007) Geological sequestration of carbon dioxide: thermodynamics, kinetics, and reaction path modelling. Elsevier Science, Amsterdam
Monjezi M, Shahriar K, Dehghani H, Samimi Namin F (2009) Environmental impact assessment of open pit mining in Iran. Environ Geol 58:205–216
Nachtegaal M, Marcus MA, Sonke JE, Vangronsveld J, Livi KJT, Van Der Lelie D, Sparks DL (2005) Effects of in situ remediation on the speciation and bioavailability of zinc in a smelter contaminated soil. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 69:4649–4664
Neal C, Whitehead PG, Jeffery H, Neal M (2005) The water quality of the River Carnon, west Cornwall, November 1992 to March 1994: the impacts of Wheal Jane discharges. Sci Total Environ 338:23–39
Nordstrom DK (2009) Acid rock drainage and climate change. J Geochem Explor 100:97–104
Parkhurst DL, Appelo CAJ (1999) User’s Guide to PHREEQC (Version 2): a computer program for speciation, batch-reaction, one-dimensional transport, and inverse geochemical calculations. Water-Resources Investigations Report 99–4259. US Geological Survey, Denver
Peplow D, Edmonds R (2006) Cell pathology and development effects of mine waste contamination on invertebrates and fish in the Methow river, Okanogan County, Washington (USA). Mine Water Environ 25:190–203
Podda F, Zuddas P, Minacci A, Pepi M, Baldi F (2000) Heavy metals coprecipitation with hydrozincite [(Zn5(CO3)2(OH)6] from mine waters caused by photosynthetic microorganisms. Appl Environ Microbiology 66:5092–5098
RAS (1998) Nuovo studio dell’idrologia superficiale della Sardegna. Regione Autonoma della Sardegna, Assessorato della Programmazione, Bilancio ed Assetto del Territorio, Ente Autonomo del Flumendosa, Cagliari (in Italian)
RAS (2003) Piano regionale di gestione dei rifiuti. Regione Autonoma della Sardegna. p 255 (in Italian)
Stumm W, Morgan JJ (1996) Aquatic chemistry, 3rd edn. Wiley, New York
WHO (2006) Guidelines for Drinking-water Quality, 3rd edn. World Health Organization, Geneva
Wolkersdorfer C, Bowell R (eds) (2005) Contemporary reviews of mine water studies in Europe. Mine Water Environ 24, Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Ministero Università Ricerca Scientifica Tecnologica (PRIN 2005 R. Cidu), the University of Cagliari (60% R. Cidu) and the Fondazione Banco di Sardegna. Thanks to anonymous reviewers and R.B. Wanty for their useful suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cidu, R. Mobility of aqueous contaminants at abandoned mining sites: insights from case studies in Sardinia with implications for remediation. Environ Earth Sci 64, 503–512 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0874-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0874-y